Summary
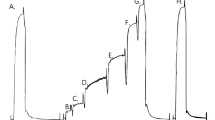
The relationship between maximum shortening velocity (V max) and free calcium concentration has been studied in skinned single fibres from rabbit psoas and soleus muscles. At both 10 and 15° C,V max measured in the psoas fibres was found to decrease by 40% when the pCa (-log[Ca2+]) was increased from 5.49 (maximally activating) to 6.21. Further decreases inV max were observed when the pCa was increased to 6.32.V max measured in soleus fibres at 15° C also decreased when the Ca2+ concentration was lowered, though the magnitude of this effect was slightly less than in the psoas fibres. Thus, a distinct effect of Ca2+ uponV max has been shown to occur in mammalian skeletal muscle. The occurrence of this effect in both fast and slow muscle types may indicate that the underlying mechanism in the two cases is similar.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BAGSHAW, C. R. & REED, G. H. (1977) The significance of the slow dissociation of divalent metal ions from myosin ‘regulatory’ light chains.FEBS Lett. 81, 386–90.
BÁRÁNY, K., BÁRÁNY, M., GILLIS, J. M. & KUSHMERICK, M. J. (1979) Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of the 18 000-dalton chain of myosin during the contraction-relaxation cycle of frog muscle.J. biol. Chem. 254, 3617–23.
BRENNER, B. (1980) Effect of free sarcoplasmic Ca2+ concentration on maximum unloaded shortening velocity. Measurements on single glycerinated rabbit psoas muscle fibres.J. Musc. Res. Cell Motility 1, 409–28.
CIVAN, M. M. & PODOLSKY, R. J. (1966) Contraction kinetics of striated muscle fibres following quick changes in load.J. Physiol. 184, 511–34.
CLOSE, R. (1965) The relation between intrinsic speed of shortening and duration of the active state of muscle.J. Physiol. 180, 542–59.
EBASHI, S. & ENDO, M. (1968) Calcium ion and muscle contraction.Prog. Biophys. molec. Biol. 18, 123–83.
EDMAN, K. A. P. (1979) The velocity of unloaded shortening and its relation to sarcomere length and isometric force in vertebrate muscle fibres.J. Physiol. 291, 143–50.
GODT, R. E. (1974) Calcium-activated tension of skinned muscle fibers of the frog.J. gen. Physiol. 63, 722–39.
GULATI, J. (1976) Force-velocity characteristics for calcium-activated mammalian slow-twitch and fast-twitch skeletal fibers from the guinea pig.Proc. natn. Acad. Sci., U.S.A. 73, 4693–7.
HILL, A. V. (1970)First and Last Experiments in Muscle Mechanics. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
JULIAN, F. J. (1971) The effect of calcium on the force-velocity relation of briefly glycerinated frog muscle fibres.J. Physiol. 218, 117–45.
JULIAN, F. J. & MORGAN, D. L. (1979) The effect on tension of non-uniform distribution of length changes applied to frog muscle fibres.J. Physiol. 293, 379–92.
JULIAN, F. J. & MOSS, R. L. (1981) Effects of calcium and ionic strength on shortening velocity and tension development in frog skinned muscle fibres.J. Physiol. 311, 179–99.
JULIAN, F. J., MOSS, R. L. & WALLER, G. S. (1981) Mechanical properties and myosin light chain composition of skinned muscle fibres from adult and new-born rabbits.J. Physiol. 311, 201–18.
KATZ, B. (1939) The relation between force and speed in muscular contraction.J. Physiol. 96, 45–64.
LEHMAN, W. H. (1978) Thick-filament-linked calcium regulation in vertebrate striated muscle.Nature 274, 80–1.
MANNING, D. R. & STULL, J. T. (1979) Myosin light chain phosphorylation and phosphorylasea activity in rat extensor digitorum longus muscle.Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 90, 164–70.
MORGAN, M., PERRY, S. V. & OTTAWAY, J. (1976) Myosin light-chain phosphatase.Biochem. J. 157, 687–97.
MORIMOTO, K. & HARRINGTON, W. F. (1974) Evidence for structural changes in vertebrate thick filaments induced by calcium.J. molec. Biol. 88, 693–709.
MOSS, R. L. (1979) Sarcomere length-tension relations of frog skinned muscle fibres during calcium activation at short lengths.J. Physiol. 292, 177–92.
MOSS, R. L. (1981) The effect of calcium on the maximum velocity of shortening in mammalian fast and slow skeletal muscle fibres.Biophys. J. 33, 28a.
PEMRICK, S. M. (1980) The phosphorylated LC2 light chain of skeletal myosin is a modifier of the actomyosin ATPase.J. biol. Chem. 255, 8836–41.
PIRES, E. M. V. & PERRY, S. V. (1977) Purification and properties of myosin light-chain kinase from fast skeletal muscle.Biochem. J. 167, 137–46.
STULL, J. T. & HIGH, C. W. (1977) Phosphorylation of skeletal muscle contractile proteinsin vivo.Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 77, 1078–83.
THAMES, M. D., TEICHHOLZ, L. E. & PODOLSKY, R. J. (1974) Ionic strength and the contraction kinetics of skinned muscle fibers.J. gen. Physiol. 63, 509–30.
WEEDS, A. G. (1976) Light chains from slow-twitch muscle myosin.Eur. J. Biochem. 66, 157–73.
WEEDS, A. G., HALL, R. & SPURWAY, N. C. S. (1975) Characterization of myosin light chains from histochemically identified fibres of rabbit psoas muscle.FEBS Lett. 49, 320–4.
WISE, R. M., RONDINONE, J. F. & BRIGGS, F. N. (1971) Effect of calcium on force-velocity characteristics of glycerinated skeletal muscle.Am. J. Physiol. 221, 973–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moss, R.L. The effect of calcium on the maximum velocity of shortening in skinned skeletal muscle fibres of the rabbit. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 3, 295–311 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00713039
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00713039