Abstract
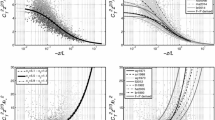
Fluxes calculated from three flux-variance methods, which depend upon three different forms of the normalized standard deviation functions (referred to as universal functions) of the surface atmospheric stability have been tested and compared with measurements for temperature and water vapour. The flux measurements were made over a fully leafed deciduous forest, a leafless deciduous forest and over a wetland region during the summer. The first method (referred to as the variance method) allows for certain constants, which are associated with the universal functions, to vary with land-use type and the scalar for which the flux is computed; the second method uses the form of the universal function developed by Tillman, which depends upon two constants; and the third method, known as the Wyngaard method, is the simplest and depends upon one constant only. Flux estimates from the variance method yield the best agreement with observations over the three hand-use types and the Wyngaard method appears to yield estimates that are quite comparable. The measurements for the univeral functions agree better with the Wyngaard function for temperature and better with the Tillman function for water vapour, although both show some scatter. The simplest formula developed by Wyngaard may be considered adequate for computing fluxes of temperature and water vapour from their variances. The main advantage of the formulae is to help define an upper limit for actual fluxes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Bruin, H. A. R., Bink, N. I. and Kroon, L. J. M.: 1991, ‘Fluxes in the Surface Layer under Advective Conditions’, in Schmugge, T. J. and André, J. C. (Eds.),Workshop on Land Surface Evaporation, Measurement and Parameterization, Springer-Verlag, New York, pp. 157–169.
Chipanshi, A. C. 1991. ‘Exchange of CO2 between a Northern Wetland and the Atmosphere near Kinosheo Lake’, M. Sc. Thesis, Department of Land Resource Science, University of Guelph, Ontario, Canada.
Hicks, B. B., Wesely, M. L. and Durham, J. L.: 1980, ‘Critique of Methods to Measure Dry Deposition; Workshop Summary’, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency report EPA-600/9-80-050 (available from NTIS, Springfield, Virginia, as publication No. PB81-126443), 70 pp.
Kanemasu, E. T., Wesely, M. L., Hicks, B. B. and Heilman, J. L.: 1979, ‘Techniques for Calculating Energy and Mass Fluxes’, in Barfield, B. J. and Gerber, J. F. (Eds.),Modification of the Aerial Environment of Crops, ASAE Monograph No. 2, American Society of Agricultural Engineers, St. Joseph, Michigan, pp. 156–182.
Lloyd, C. R., Culf, A. D., Dolman, J. J. and Gash, J. H. C.: 1991, ‘Estimates of Sensible Heat Flux from Observations of Temperature Fluctuations’Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 57, 311–322.
Neumann, H. H. and den Hartog, G.: 1985, ‘Eddy Correlation Measurements of Atmospheric Fluxes of Ozone, Sulphur and Particulates during the Champaign Intercomparison Study’,J. G. R. 90, 2097–2110.
Neumann, H. H., den Hartog, G. and Shaw, H. H.: 1989, ‘Leaf Area Measurements Based on Hemispheric Photographs and Leaf-Litter Collection in a Deciduous Forest during Autumn Leaf-Fall’,Agric. For. Meteorol. 45, 325–345.
Padro, J., den Hartog, G. and Neumann, H. H.: 1991, ‘An Investigation of the ADOM Dry Deposition Module using Summertime O3 Measurements above a Deciduous Forest’,Atmos. Environ. 25A, 1689–1704.
Padro, J., Neumann, H. H. and den Hartog, G.: 1992a, “Modelled and Observed Dry Deposition Velocity of O3 above a Deciduous Forest in the Winter’,Atmos. Environ. 26A, 775–784.
Padro, J., den Hartog, G., Neumann, H. H. and Woolridge, D.: 1992b, ‘Using Measured Variances to Compute Surface Fluxes and Dry Deposition Velocities: A Comparison with Measurements from Three Surface Types’,Atmos.-Ocean 30, 363–382.
Tillman, J. E.: 1972, ‘The Indirect Determination of Stability, Heat and Momentum Fluxes in the Atmospheric Boundary Layer from Simple Scalar Variables during Dry Unstable Conditions’,J. Appl. Meteorol. 11, 783–792.
Weaver, H. L.: 1990, ‘Temperature and Humidity Flux-Variance Relations Determined by One-Dimensional Eddy Correlation’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 53, 77–91.
Wesely, M. L., Thurtell, G. W. and Tanner, C. B.: 1970, ‘Eddy Correlation Measurements of Sensible Heat Flux near the Earth's Surface’,J. Appl. Meteorol. 9, 45–50.
Wesely, M. L., Cook, D. R. and Hart, R. L.: 1983, ‘Fluxes of Gases and Particles above a Deciduous Forest in Wintertime’,Boundary Layer Meteorol. 27, 237–255.
Wesely, M. L.: 1988, ‘Use of Variance Techniques to Measure Dry Air-Surface Exchange Rates’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 44, 13–31.
Wyngaard, J. C., Cote, O. R. and Izumi, Y.: 1971, ‘Local Free Convection, Similarity and the Budgets of Shear Stress and Heat Flux’,J. Atmos. Sci. 28, 1171–1182.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Padro, J. An investigation of flux-variance methods and universal functions applied to three land-use types in unstable conditions. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 66, 413–425 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00712731
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00712731