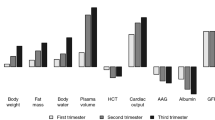
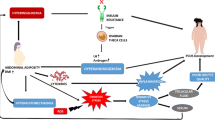
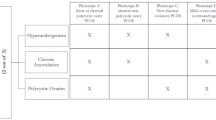
Summary
We report two female patients, one with a known inborn error of ureagenesis and the other of unknown cause, in whom recurrent, transient episodes of severe hyperammonaemia increased in frequency and severity with sexual maturity and parturition. Both responded to ovarian steroids administered continuously to suppress ovulation and menstruation, and ultimately to simple hysterectomy. These studies suggest a new therapeutic approach to defective ureagenesis in female patients and a relationship between ammonia production or disposal and the menstrual cycle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arn PH, Hauser ER, Thomas GH, Herman G, Hess D, Brusilow SW (1990) Hyperammonemia in women with a mutation at the ornithine carbamoyltransferase locus: A cause of postpartum coma.N Engl J Med 322: 1652–1655.
Batshaw ML, Brusilow SW (1980) Treatment of hyperammonemic coma caused by inborn errors of urea cycle synthesis.J Pediatr 97: 893–900.
Batshaw ML, Brusilow S, Waber L et al (1982) Treatment of inborn errors of urea cycle synthesis: Activation of alternative pathways of waste nitrogen synthesis and excretion.N Engl J Med 306: 1387–1392.
Brusilow SW, Batshaw ML (1979) Arginine therapy of argininosuccinase deficiency.Lancet 1: 244–247.
Brusilow SW, Horwich AL (1989) Urea cycle enzymes. In Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D, eds.The Metabolic Basis of Inherited Disease, 6th edn. New York: McGraw-Hill, 629–663.
Carson NA, Redmond OA (1977) Lysinuric protein intolerance.Ann Clin Biochem 14: 135.
Catherlineau L (1979) L'hyperammoniemie dans la pathologie pediatrique.Arch Fr Pediatr 36: 724–735.
Cederbaum SD, Shaw KNF, Spector EB, Verity MA, Snodgrass PJ, Sugerman GI (1979) Hyperargininemia with arginase deficiency.Pediatr Res 13: 827–833.
Chapoy PR, Angelini C, Brown WJ, Stiff JE, Shug AL, Cederbaum SD (1980) Systemic carnitine deficiency: A treatable inherited lipid-storage disease presenting as Reye's syndrome.N Engl J Med 303: 1389–1394.
Flannery DB, Hsia YE, Wolf B (1982) Current status of hyperammonemic syndromes.Hepatology 2: 495–506.
Grody WW, Argyle C, Kern RM et al (1989) Differential expression of the two human arginase genes in hyperargininemia: Enzymatic, pathologic, and molecular analysis.J Clin Invest 83: 602–609.
Grody WW, Kern RM, Klein D et al (1993) Arginase deficiency manifesting delayed clinical sequelae and induction of a kidney arginase isozyme.Hum Genet 91: 1–5.
Guillaume C, Magnin C, Butin E, Bui-Xuan B, Godard J, Motin J (1988) Coma hyperammoniemique secondaire a une uretero-sigmoidostomie.Press Méd 17: 822.
Haggerty DF, Spector EB, Lynch M, Kern R, Frank LB, Cederbaum SD (1982) Regulation by glucorticoids of arginase and argininosuccinate synthetase in cultured rat hepatoma cells.J Biol Chem 257: 2246–2253.
Hammond JE, Savory J (1976) Advances in the detection of amino acids in biological fluids.Ann Clin Lab Sci 6: 158–166.
Hauser ER, Finkelstein JE, Valle D, Brusilow SW (1990) Allopurinol-induced orotidinuria: A new test for mutations at the ornithine carbamoyltransferase locus in women.N Engl J Med 322: 1641–1645.
Hjelm M, Oberholzer V, Seakins J, Thomas S, Kay JDS (1986) Valproate-induced inhibition of urea synthesis and hyperammonemia in healthy subjects (Letter).Lancet 2: 859.
Hoyumpta AM, Desmond PV, Avant GR, Roberts RK, Schenker S (1979) Hepatic encephalopathy.Gastroenterology 76: 184–195.
Hudak ML, Jones D, Brusilow SW (1985) Differentiation of transient hyperammonemia of the newborn and urea cycle enzyme defects by clinical presentation.J Pediatr 107: 712–719.
Kang ES, Snodgrass PJ, Gerald PS (1973) Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency in the newborn infant.J Pediatr 82:642–649.
Matsuda Y, Tsuji A, Katunuma N (1982) Qualitative abnormality of liver argininosuccinate synthetase in a patient with citrullinemia.Adv Exp Med Biol 153: 77–82.
Morris SM, Moneman CL, Rand KD, Dizikes GJ, Cederbaum SD, O'Brien WE (1987) Regulation of mRNA levels for five urea cycle enzymes in rat liver by diet, cyclic AMP, and glucocorticoids.Arch Biochem Biophys 256: 343–353.
Moure JM, Whitecar JP, Bodey GP (1970) Electroencephalogram changes secondary to asparaginase.Arch Neurol 23: 365–368.
Nyhan WL, Sakati NO (1987)Diagnostic Recognition of Genetic Disease. Philadelphia: Lea and Febiger, 152–153.
Rajantie J, Simell O, Rapola J, Perheentupa J (1980) Lysinuric protein intolerance: A two-year trial of dietary supplementation therapy with citrulline and lysine.J Pediatr 97: 927–932.
Santoy B, De Benkelaer MM (1980) Ammonia encephalopathy secondary to urinary tract infection withProteus mirabilis.Pediatrics 65: 294–297.
Schimke RT (1964) Enzymes of arginine metabolism in mammalian cell culture. I. Repression of argininosuccinate synthetase and argininosuccinase.J Biol Chem 239: 136–144.
Shannon DC, DeLong GR, Bercu B et al (1975) Studies on the pathophysiology of encephalopathy in Reye's syndrome: Hyperammonemia in Reye's syndrome.Pediatrics 56: 999–1004.
Shih VE, Efron M, Moser HW (1969) Hyperornithinemia, hyperammonemia and homocitrullinemia: A new disorder of amino acid metabolism associated with myoclonic seizures and mental retardation.Am J Dis Child 116: 83–92.
Spector EB, Kiernan M, Bernard B, Cederbaum SD (1980) Properties of fetal and adult red blood cell arginase: A possible prenatal diagnostic test for arginase deficiency.Am J Hum Genet 32: 79–87.
Vockley JG, Tabor DE, Kern RM et al (1994) Identification of mutations in the liver arginase gene of patients with hyperargininemia.Hum Mutat (in press).
Watson AJ, Chambers T, Karp JE, Risch VR, Walker WG, Brusilow SW (1985) Transient idiopathic hyperammonemia in adults.Lancet 2: 1271–1274.
Yajima Y, Hirasawa T, Saheki T (1981) Treatment of adult-type citrullinemia with administration of citrate.Tohoku J Exp Med 134: 321–330.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grody, W.W., Chang, R.J., Panagiotis, N.M. et al. Menstrual cycle and gonadal steroid effects on symptomatic hyperammonaemia of urea-cycle-based and idiopathic aetiologies. J Inherit Metab Dis 17, 566–574 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00711592
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00711592