Summary
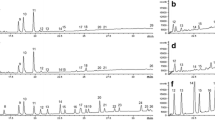
Two methods are described, both currently used in our laboratory, for the quantitative analysis of very long-chain fatty acids, phytanic acid and pristanic acid in plasma and cultured fibroblasts by gas-liquid chromatography. The first method is based on the procedure developed by Moser and Moser (1991) and the second is based on the method of Onkenhout and colleagues (1989), which is an application of the original method of Lepage and Roy for plasma and fibroblasts. A survey is given of the concentrations of very long-chain fatty acids, pristanic and phytanic acid in plasma and fibroblasts from control subjects and all patients investigated so far in our laboratory.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lepage G, Roy CC (1986) Direct transesterification of all classes of lipids in a one-step reaction.J Lipid Res 27: 114–120.
Moser HW, Moser AB (1991) Measurement of saturated very long chain fatty acid in plasma. In Hommes FA, ed.Techniques in Diagnostic Human Biochemical Genetics. New York: Wiley-Liss, 177–191.
Onkenhout W, Pael PFH vd, Heuvel MPH vd (1989) Improved determination of very long-chain fatty acids in plasma and cultured skin fibroblasts: application to the diagnosis of peroxisomal disorders.J Chromatography 494: 31–41.
Schutgens RBH, Bouman IW, Nijenhuis AA, Wanders RJA, Frumau MEJ (1993) Profiles of very long chain fatty acids in plasma, fibroblasts and blood cells in Zellweger syndrome, X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy and rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata.Clin Chem 39: 1632–1637.
Singh I, Moser AB, Goldfisher S, Moser HW (1984) Lignoceric acid is oxidized in the peroxisome: implications for the Zellweger cerebro-hepato-renal syndrome and adrenoleukodystrophy.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81, 4203–4207.
ten Brink HJ, Stellaard F, Heuvel CMM vd et al (1992) Pristanic and phytanic acid in plasma from patients with peroxisomal disorders: stable isotope dilution analysis with electron capture negative ion mass fragmentography.J Lipid Res 33: 31–37.
Vanhove GF, Veldhoven PP v, Fransen M et al (1993) The CoA esters of 2-methyl branched chain fatty acids and of the bile acid intermediates di- and trihydroxycoprostanic acids are oxidized by one single peroxisomal branched chain acyl CoA oxidase in human liver and kidney.J Biol Chem 286: 10335–10344.
Wanders RJA, Schutgens RBH, Barth PG, Tager JM, Bosch H vd (1993) Postnatal diagnosis of peroxisomal disorders: a biochemical approach.Biochemie 75: 269–279.
Willems P, Vits L, Wanders RJA et al (1990) Linkage of DNA markers at Xq 28 to adrenoleukodystrophy and adrenomyeloneuropathy present within the same family.Arch Neurol 47: 665–669.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dacremont, G., Cocquyt, G. & Vincent, G. Measurement of very long-chain fatty acids, phytanic and pristanic acid in plasma and cultured fibroblasts by gas chromatography. J Inherit Metab Dis 18 (Suppl 1), 76–83 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00711430
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00711430