Summary
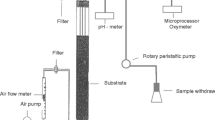
The growth parameters ofPenicillium cyclopium have been evaluated in a continuous culture system for the production of fungal protein from whey. Dilution rates varied from 0.05 to 0.20 h−1 under constant conditions of temperature (28°C) and pH (3.5). The saturation coefficients in the Monod equation were 0.74 g l−1 for lactose and 0.14 mg l−1 for oxygen, respectively. For a wide range of dilution rates, the yield was 0.68 g g−1 biomass per lactose and the maintenance coefficient 0.005 g g−1 h−1 lactose per biomass, respectively. The maximum biomass productivity achieved was 2 g l−1 h−1 biomass at dilution rates of 0.16–0.17 h−1 with a lactose concentration of 20 g l−1 in the feed. The crude protein and total nucleic acid contents increased with a dilution rate, crude protein content varied from 43% to 54% and total nucleic acids from 6 to 9% in the range of dilution rates from 0.05 to 0.2 h−1, while the Lowry protein content was almost constant at approximately 37.5% of dry matter.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- (mg l−1):
-
Co initial concentration of dissolved oxygen
- (h−1):
-
D dilution rate
- (mg l−1):
-
K02 saturation coefficient for oxygen
- (g l−1):
-
Ks saturation coefficient for substrate
- (g g−1 h−1) lactose per biomass):
-
m maintenance energy coefficient
- (mM g−1 h−1O2 per biomass):
-
Q02 specific oxygen uptake rate
- (g l−1):
-
S residual substrate concentration at steady state
- (g l−1):
-
So initial substrate concentration in feed
- (min):
-
t1/2 time when Co is equal to Co/2
- (g l−1):
-
X biomass concentration
- (g l−1):
-
X biomass concentration at steady state
- (g g−1 biomass per lactose):
-
YG yield coefficient for cell growth
- (g g−1 biomass per lactose):
-
Yx/s overall yield coefficient
- (h−1):
-
μ specific growth rate
References
Anderson C, Longton J, Maddix C, Scammel GW, Solomons GL (1975) In: Tannenbaum SR, Wang DIC (eds) Signel-Cell Protein II. MIT Press, Cambridge, p 314
Hartree EF (1972) Anal Biochem 48:422
Herbert D, Elsworth R, Telling RC (1956) J Gen Microbiol 14:601
Kim JH, Iibuchi S, Lebeault JM (1981) Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol submitted
Macris BJ, Kokke R (1978) Biotechnol Bioeng 20:1027
Monod J (1949) Ann Review of Microbiol 3:371
Paredes-Lopez O, Camargo-Rubio E, Ornelas-Vale A (1976) Appl Environ Microbiol 31:487
Pirt SJ (1965) Proc Roy Soc B 163:224
Righelato RC, Imrie FKE, Vlitos AJ (1976) Resour Recovery Conserv 1:257
Romantschuk H, Lektomäki M (1978) Process Biochem 13:16
Taguchi H, Humphrey AE (1966) J Ferment Technol 44:881
Terui G, Konno N, Sase M (1960) J Ferment Technol 38:278
Wang HY, Cooney CL, Wang DIC (1977) Biotechnol Bioeng 18:69
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J.H., Lebeault, J.M. Protein production from whey usingPenicillium cyclopium; growth parameters and cellular composition. European J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 13, 151–154 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00703044
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00703044