Summary
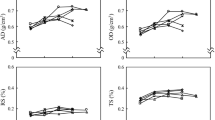
This paper reports experimental results concerning the transverse shrinkage variability within and between trees of two samples composed of 17 eleven-year-old and 20 twenty-year-old maritime pine trees harvested in two stands at the Forest Research Centre of INRA Pierroton in Aquitaine. The within tree variations are divided into a height effect and a radial effect, both related to the occurrence of juvenile wood. It is shown that the tangential shrinkage and the anisotropic ratio between radial and tangential dimensional variations are increasing from the top to the base of the stems (+14.9% and +16.9%, respectively), and that this effect is independent of the tree. The variations from the pith outward are also significant for these parameters (+25.0% for at and −9.5% for the ratio) and for the radial shrinkage (+37.2% ), but in this case, the amplitude of the effect is depending on a tree effect. The relationship between shrinkage and density is also studied, showing poorly significant correlation when considering each sampling positions independently.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Gadir, A. Y.;Krahmer, R. L. 1993: Estimating the Age of Demarcation of Juvenile and Mature Wood in Douglas-Fir. Wood and Fiber Science, Vol. 25, No 3, p 242–249
Barber, N. F.;Meylan, B. A. 1964: The Anisotropic Shrinkage of Wood: A Theoretical Model. Holzforschung, Bd 18, p 146–156
Bendtsen, B. A.;Senft, J. 1986: Mechanical and Anatomical Properties in Individual Growth Rings of Plantation-Grown Eastern Cottonwood and Loblolly Pine. Wood and Fiber Science, Vol. 18, No 1, p 23–38
Boyd, J. D. 1974: Anisotropic Shrinkage of Wood: Identification of the Dominant Determinants. Mokuzai Gakkaishi, Vol. 20, No 10, p. 473–482
Burdon, R. D. Harris, J. M. 1973: Wood Density in Radiata Pine Clones on Four Different Sites. New-Zealand Journal of Forestry Science, Vol. 3, p 286–303
Cave, I. D. 1972: A Theory of the Shrinkage of Wood. Wood Science and Technology, Vol. 6, p 284–292
Cave, I. D. 1978: Modelling Moisture-Related Mechanical Properties of Wood. Part II: Computation of properties of a Model of Wood and Comparison with Experimental Data. Wood Science and Technology, Vol. 12, p 127–139
Cown, D. J.; McConchie, D. L. 1983: Radiata Pine Wood Properties Survey (1977–1982). New-Zealand Forest Service, FRI Bulletin No 50
Donaldson, L. A. 1992: Within and Between-tree Variation in Microfibril Angle in Pinus Radiata. New-Zealand Journal of Forestry Science, Vol. 22, No 1, p 77–86
Dumail, J. F. 1995: Caractéristiques Physiques et Mécaniques du Bois Juvénile de Pin maritime (Pinus Pinaster). Thèse de I'Université Bordeaux I, 228 p, in French
Harris, J. M.;Meylan B. A. 1965: The Influence of Microfibril Angle on Longitudinal and Tangential Shrinkage in Pinus Radiata. Holzforschung, Bd 19, p 144–153
Kennedy, R. W. 1995: Coniferous Wood Quality in the Future: Concerns and Strategies. Wood Science and Technology, Vol. 29, p 321–338
Kollmann, F. P., Coté, W. 1968: Principles of Wood Science and Technology. Vol. 1: Solid Wood. Berlin Heidelberg New York: Springer
Koponen, S.;Toratti, T.;Kanerva, P. 1991: Modelling Elastic and Shrinkage Properties of Wood Based on Cell Structure. Wood Science and Technology, Vol. 25, p 25–32
Megraw, R. A. 1985: Wood Quality Factors in Loblolly Pine. Tappi Press Atlanta, Georgia, 89p
Nepveu, G. 1984: L'amelioration de la Qualite de la Production Forestière: Le Cas du Pin Maritime. 3ème Rencontre Recherche- Formation- Professionels du Bois et de la Forêt, ENITA, Bordeaux
Panshin, A. J.; De Zeeuw C. E. 1980: Textbook of Wood Technology: 4th Edition. McGrawHill Series in Forest Resources, 722 p
Sekhar, A. C.;Rajput, S. S. 1967: Some Studies on the Shrinkage Behaviour of Wood. Wood Science and Technology, Vol. 1, p 99–108
Talbert, J. T.;Jett, J. B.;Bryant, R. L. 1983: Inheritance of Wood Specific Gravity in an Unimproved Loblolly Pine Population: 20 years results. Silvae Genetica, Vol. 32, No 1-2, p 33–37
Wilkes, J. 1989: Variation in Wood Density of Pinus Radiata in New South Wales, Australia. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, Vol 19, p 289–294
Ylinen, A.;Jumppanen, P. 1967: Theory of the Shrinkage of Wood. Wood Science and Technology, Vol. 1, p 241–252
Zobel, B. J.; Van Buijtenen, J. P. 1989: Wood Variation: its Causes and Control. Springer-Verlag
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dumail, J.F., Castera, P. Transverse shrinkage in maritime pine juvenile wood. Wood Sci.Technol. 31, 251–264 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00702613
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00702613