Abstract
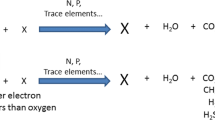
Batch experiments on the simultaneous utilization of phenol (primary substrate) and 4-chlorophenol (cometabolic secondary substrate) demonstrated two critical substrate interactions. First, the cometabolic degradation of 4-chlorophenol was proportional to the rate of phenol oxidation, which provided the electrons for the initial monooxygenase reaction. Second, 4-chlorophenol inhibited the oxidation of the primary substrate, phenol. Modeling analyses of the degradation of phenol alone and of phenol and 4-chlorophenol together showed that the proportionality between phenol and 4-chlorophenol degradation rates averaged 0.1 mg 4-CP/mg phenol, which corresponds to 0.5% of the electrons generated by phenol oxidation being used as a cosubstrate for the monooxygenase reaction of 4-chlorophenol. In addition, modeling analyses suggest that 4-chlorophenol was a noncompetitive inhibitor of phenol oxidation for high phenol concentrations, but a competitive inhibitor for low phenol concentrations.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GC:
-
gas chromatography
- FID:
-
flame-ionization detector
- DO:
-
dissolved oxygen
- 4-CP:
-
4-chlorophenol
- Ph:
-
phenol
- RLS:
-
relative least squares criterion
- NAD:
-
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
- NADP:
-
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
References
Andrews JF (1968) A mathematical model for the continuous culture of microorganisms utilizing inhibitory substrates. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 10: 707–723
Gottschalk G (1986) Bacterial Metabolism. 2nd ed. Springer-Verlag, Inc., New York
Roels JA (1983) Energetics and Kinetics in Biotechnology. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Saéz PB & Rittmann BE (1991) Biodegradation kinetics of 4-chlorophenol, an inhibitory co-metabolite. Res. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 63: 838–847
Saéz PB & Rittmann BE (1992) Model-parameter estimation using least squares. Water Research 39: 790–793
Spain JC & Gibson DT (1988) Oxidation of substituted phenols byPseudomonas putida Fl andPseudomonas sp. strain JS6. Appl. Environ. Microb. 54: 1399–1404
Stratton R, Namkung E & Rittmann BE (1983) Secondary utilization of trace organics by biofilms on porous media. J. Amer. Water Works Assn. 75: 463–469
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saéz, P.B., Rittmann, B.E. Biodegradation kinetics of a mixture containing a primary substrate (phenol) and an inhibitory co-metabolite (4-chlorophenol). Biodegradation 4, 3–21 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00701451
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00701451