Abstract
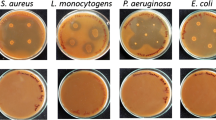
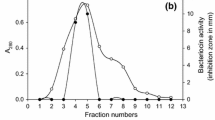
The production of a dialysable peptidic antibacterial named microcin E492 by the strain of faecal originKlebsiella pneumoniae RYC492 has previously been reported. In this paper, a procedure to extract this antibiotic from liquid cultures of the producer strain is described. This method was based in the quantitative retention of the microcin on the hydrophobic matrix Bondapak C18 and led to highly active pigment- and salf-free concentrates appropriate for further purification by high pressure liquid chromatography. The characterization of purified preparations indicated that microcin E492 was a basic and hydrophobic peptide with an apparent molecular mass of about 5,000, acid- and heat-resistant and much more active in minimal than in rich medium. These properties are discussed with regard to the likely ecological role of the microcin in the microbial ecosystem of the intestine.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AU:
-
Antibiotic Unit
- CFU:
-
Colony-forming units
- HPLC:
-
High Pressure Liquid Chromatography
- Mr:
-
Relative molecular mass
- RP:
-
Reversed phase
- TEAP:
-
Triethylamine-phosphoric acid
References
Aguilar A, Perez Diaz JC, Baquero F, Asensio C (1982) Microcin 15 m fromEscherichia coli: Mechanism of antibiotic action. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 21:381–386
Asensio C, Perez Diaz JC, Martínez MC, Baquero F (1976) A new family of low molecular weight antibiotics from Enterobacteria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 69:7–14
Baquero F, Asensio C (1979) Microcins as ecological effectors in human intestinal flora: preliminary findings. In: Waaij D van der, Verhoef J (eds) New criteria for antimicrobial therapy. Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam, pp 90–94
Bij KE, Horvath C, Melander WR, Nahum A (1981) Surface silanols in silica-bonded hydrocarbonaceous stationary phases: Irregular retention behavior and effect of silanol masking. J Chromatogr 203:65–84
Gerhardt P (1981) Manual of methods for general bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington
Hancock WS, Sparrow JT (1981) Use of mixed-mode high pressure liquid chromatography for the separation of peptide and protein mixtures. J Chromatogr 206:71–82
Hashimoto F, Horigone T, Kanbayashi M, Yoshida K, Sugano H (1983) An improved method for separation of low molecular weight polypeptides by eletrophoresis in sodium-dodecylsulphate-polyacrylamide gel. Anal Biochem 129:192–199
Hernández-Chico C, Herrero M, Rejas M, San Millán JL, Moreno F (1982) Geneomp R and the regulation of microcin 17 and colicin E2 syntheses. J Bacteriol 152:897–900
Konisky J (1978) The Bacteriocins. In: Ornston LN, Sokatch JR (eds) The bacteria, vol 6, Academic Press, New York, pp 71–136
Lorenzo V de, Aguilar A (1984) Antibiotics from Gram-negative bacteria: Do they play a role in microbial ecology? Trends Biochem Sci 9:266–269
Lorenzo V de, Martínez JL, Asensio C (1984) Microcin-mediated interactions betweenKlebsiella pneumoniae andEscherichia coli strains. J Gen Microbiol 130:391–400
Mayr-Harting A, Hedges AJ, Berkeley RCW (1972) Methods for studying bacteriocins. In: Norris JR, Ribbons DW (eds) Methods in microbiology, vol 7A. Academic Press, London, pp 315–422
Steck G, Leuthard P, Buck R (1980) Detection of basic proteins and low molecular weight peptides in polyacrylamide gels by formaldehyde fixation. Anal Biochem 107:21–24
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Lorenzo, V. Isolation and characterization of microcin E 492 fromKlebsiella pneumoniae . Arch. Microbiol. 139, 72–75 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00692715
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00692715