Abstract
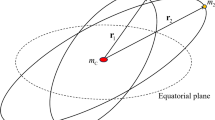
The luni-solar effects of a geosynchronous artificial satellite orbiting near the critical inclination is investigated. To tackle this four-degrees-of-freedom problem, a preliminary exploration separately analyzing each harmonic formed by a combination of the satellite longitude of the node and the Moon longitude of the node is opportune. This study demonstrates that the dynamics induced by these harmonics does not show resonance phenomena. In a second approach, the number of degrees of freedom is halved by averaging the total Hamiltonian over the two non-resonant angular variables. A semi-numerical method can now be applied as was done when considering solely the inhomogeneity of the geopotential (see Delhaise et Henrard, 1992). Approximate surfaces of section are constructed in the plane of the inclination and argument of perigee. The main effects of the Sun and Moon attractions compared to the terrestrial attraction alone are a strong increase in the amplitude of libration in inclination (from 0.6° to 3.2°) and a decrease of the corresponding libration period (from the order of 200 years to the order of 20 years).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brouwer, D.: 1959, “Solution of the Problem of Artificial Satellite Theory without Drag”,Astron. J 64, 378–397
Delhaise, F.: 1989, “The Effects of Luni-Solar Gravitation and Solar Radiation Pressure on the Molniya and Tundra Orbits”,ESA, MAS Working Paper,295
Delhaise, F. and Henrard, J.: 1992, “The Problem of Critical Inclination Combined with a Resonance in Mean Motion in Artificial Satellite Theory”, in press inCelest. Mech.
Delhaise, F.: 1992, “Analytical and Semi-Numerical Treatments of two Typical Problems in Artificial Satellite Theory: Air-Drag and Critical Inclination”,Ph. D. Thesis, FUNDP, Namur, Internal report.
Exertier, P., 1989, “Extensions de la Théorie de Kaula aux Fonctions Perturbatrices Luni-Solaires et de Marées”,CNES, Internal Report.
Giacaglia, G. E.: 1974, “Lunar Perturbations of Artificial Satellites of the Earth”,Celest. Mech. 9, 239–267
Giacaglia, G. E.: 1976, “A Note on Hansen's Coefficients in Satellite Theory”,Celest. Mech. 14, 515–523
Garfinkel, B.: 1959, “The orbit of a Satellite of an Oblate Planet”,Astron. J 64, 353
Henrard, J.: 1990, “A Semi-Numerical Perturbation Method for Separable Hamiltonian systems”,Celest. Mech. 49, 43–67
Hough, M.E.: 1981, “Orbits near Critical Inclination, Including Lunisolar Perturbations”,Celest. Mech. 25, 111–136
Jupp, A. H.: 1988, “The Critical Inclination Problem - 30 Years of Progress”,Celest. Mech. 43, 127–138
Kaula, W. M.: 1962, “Development of the Lunar and Solar Disturbing Functions for a Close Satellite”,Astron. J. 67, 300–303
Kaula, W. M.: 1966, “Theory of satellite geodesy”,Blaisdell Publishing Co.,
Kozai, Y.: 1959, “The Motion of a Close Earth Satellite”,Astron. J. 64, 367–377
Lane, M. T.: 1989, “On Analytic Modeling of Lunar Perturbations of Artificial Satellites of the Earth”,Celest. Mech. 46, 287–305
Lecohier, G., Guermonprez, V. and Delhaise, F.: 1989, “European Molniya and Tundra Orbit Control”,CNES, Mécanique Spatiale, Symposium International en Mécanique Spatiale, Toulouse (France), 165–191
Morbidelli, A.: 1991, “On the Successive Eliminations of Perturbation Harmonics”, in press inCelest. Mech.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Research Assistant for the Belgian National Fund for Scientific Research
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Delhaise, F., Morbidelli, A. Luni-solar effects of geosynchronous orbits at the critical inclination. Celestial Mech Dyn Astr 57, 155–173 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00692471
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00692471