Abstract
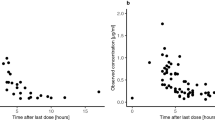
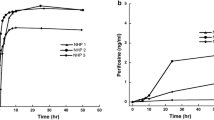
The purpose of this study was to describe the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) penetration of topotecan in humans, to generate a pharmacokinetic model to simultaneously describe topotecan lactone and total concentrations in the plasma and CSF, and to characterize the CSF and plasma pharmacokinetics of topotecan administered as a continuous infusion (CI). Plasma and CSF samples were collected from 17 patients receiving 5.5 or 7.5 mg/m2 per day as a 24-h CI (5 patients, 7 courses), or 0.5 to 1.25 mg/m2 per day as a 72-h CI (12 patients, 12 courses). CSF samples were obtained from either a ventricular reservoir (VR) or a lumbar puncture (LP). Topotecan lactone and total (lactone plus hydroxy acid) concentrations were determined by HPLC and fluorescence detection. Using MAP-Bayesian modelling, a three-compartment model was fitted simultaneously to topotecan lactone and total concentrations in the plasma and CSF. The penetration of topotecan into the CSF was determined from the ratio of the CSF to the plasma area under the concentration-time curve. The median CSF ventricular lactone concentrations, obtained prior to the end of infusion (EOI), were 0.86, 1.4, 0.73, 5.3 and 4.6 ng/ml for patients receiving 0.5, 1.0, 1.25, 5.5, and 7.5 mg/m2 per day, respectively. EOI CSF lumbar lactone concentrations measured in three patients were 0.44, 1.1, and 1.7 ng/ml for topotecan doses of 1.0, 5.5, and 7.5 mg/m2 per day, respectively. In two patients receiving 1.25 mg/m2 per day, EOI CSF concentrations were obtained simultaneously from a VR and LP; the lumbar lactone concentrations were 30% and 49% lower than the ventricular concentrations. During a 24-h and a 72-h CI, the median CSF penetration of topotecan lactone was 0.29 (range 0.10 to 0.59) and 0.42 (range 0.11 to 0.86), respectively. A three-compartment model adequately described topotecan lactone and total concentrations in the plasma and CSF. Topotecan was therefore found to significantly penetrate into the CSF in humans. The pharmacokinetic model presented may be useful in the design of clinical studies of topotecan to treat CNS tumors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arndt CAS, Balis FM, McCully CL, Colvin OM, Poplack DG (1988) Cerebrospinal fluid penetration of active metabolites of cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide in rhesus monkeys. Cancer Res 48: 2113–2115
Blaney SM, Balis FM, Cole DE, Craig C, Reid JM, Ames MM, Krailo M, Reaman G, Hammond D, Poplack D (1993) Pediatric phase I trial and pharmacokinetic study of topotecan administered as a 24-hour continuous infusion. Cancer Res 53: 1032–1036
Blaney SM, Cole DE, Balis FM, Godwin K, Poplack DG (1993) Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid pharmacokinetic study of topotecan in nonhuman primates. Cancer Res 53: 725–727
Blasberg RG, Patlak CS, Shapiro WR (1977) Distribution in the cerebrospinal fluid and brain after intraventricular administration. Cancer Treat Rep 61: 633–641
Bleyer WA, Dedrick RL (1977) Clinical pharmacology of intrathecal methotrexate. I. Pharmacokinetics in nontoxic patients after lumbar injection. Cancer Treat Rep 61: 703–708
Burke TG, Zihou M (1994) The structural basis of camptothecin interactions with human serum albumin: impact on drug stability. J Med Chem 37: 40–46
Burke TG, Mishra AK, Wani MC, Wall ME (1993) Lipid bilayer partitioning and stability of camptothecin drugs. Biochemistry 32: 5352–5364
Burris HA III, Fields SM (1994) Topoisomerase I inhibitors: an overview of the camptothecin analogs. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 8: 333–355
Burris HA, III, Hanauske A-R, Johnson RK, Marshall MH, Kuhn JG, Hilsenbeck SG, Von Hoff DD (1992) Activity of topotecan, a new topoisomerase I inhibitor, against human tumor colony-forming units in vitro. J Natl Cancer Inst 84: 1816
Collins JM, Dedrick RL (1983) Distributed model for drug delivery to CSF and brain tissue. Am J Physiol 245: R303-R310
DArgenio DZ, Schumitzky A (1992) ADAPT II users guide, Biomedical Simulations Resource, USC, Los Angeles, CA
Fassberg J, Stella VJ (1992) A kinetic and mechanistic study of the hydrolysis of camptothecin and some analogues. J Pharm Sci 81: 676–684
Friedman HS, Houghton PJ, Schold C, Keir S, Bigner DD (1994) Activity of 9-dimethylaminomethyl-10-hydroxycamptothecin against pediatric and adult central nervous system tumor xenografts. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 34: 171–174
Gibaldi M, Perrier D (1982) Multicompartment models. In: Swarbrick J (ed) Pharmacokinetics, 2nd edn. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 45–111
Grochow LB, Rowinsky EK, Johnson R, Ludeman S, Kaufmann SH, McCabe FL, Smith BR, Hurowitz L, DeLisa A, Donehower RC, Noe DA (1992) Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of topotecan in patients with advanced cancer. Drug Metab Dispos Biol Fate Chem 20: 706–713
Haas NB, LaCreta FP, Walczak J, Hudes GR, Brennan JM, Ozols RF, ODwyer PJ (1994) Phase I/pharmacokinetic study of topotecan by 24-hour continuous infusion weekly. Cancer Res 54: 1220–1226
Hande KR, Wedlund PJ, Noone RM, Wilkinson GR, Greco FA, Wolff SN (1984) Pharmacokinetics of high-dose etoposide (VP-16-213) administered to cancer patients. Cancer Res 44: 379–382
Heideman RL, Cole DE, Balis F, Sato J, Reaman GH, Packer RJ, Singher LJ, Ettinger LJ, Gillespie A, Sam J, Poplack DG (1989) Phase I and pharmacokinetic evaluation of thiotepa in the cerebrospinal fluid and plasma of pediatric patients: evidence for dose-dependent plasma clearance of thiotepa. Cancer Res 49: 736–741
Hochster H, Liebes L, Speyer J, Sorich J, Taubes B, Oratz R, Wernz J, Chachoua A, Raphael B, Vinci RZ, Blum RH (1994) Phase I trial of low-dose continuous topotecan infusion in patients with cancer: an active and well-tolerated regimen. J Clin Oncol 12: 553–559
Kantarjian HM, Beran M, Ellis A, Zwelling L, OBrien S, Cazenave L, Koler C, Rios MB, Plunet W, Keating MJ, Estey EH (1993) Phase I study of topotecan: a new topoisomerase I inhibitor, in patients with refractory or relapsed acute leukemia. J Clin Oncol 81: 1146–1151
Poplack DG, Bleyer WA, Horowitz ME (1980) Pharmacology of antineoplastic agents in cerebrospinal fluid. In: Wood JH (ed) Neurobiology of cerebrospinal fluid, vol. II. Plenum Press, New York, pp 561–578
Potmesil M (1994) Camptothecins: from bench research to hospital wards. Cancer Res 54: 1431–1439
Pratt CB, Stewart C, Santana VM, Bowman L, Furman W, Ochs J, Marina N, Kuttesch JF, Heideman R, Sandlund JT, Avery L, Meyer WH (1994) Phase I study of topotecan for pediatric patients with malignant solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 12: 539–543
Rowinsky EK, Grochow LB, Hendricks CB, Ettinger DS, Forastiere AA, Hurowitz LA, McGuire WP, Sartorius SE, Lubejko BG, Kaufmann SH, Donehower RC (1992) Phase I and pharmacologic study of topotecan: a novel topoisomerase I inhibitor. J Clin Oncol 10: 647–656
Saltz L, Sirott M, Young C, Tong W, Niedzwiecki D, Tzy-Jyun Y, Tao Y, Trochanowski B, Wright P, Barbosa K, Toomasi F, Kelsen D (1993) Phase I clinical and pharmacology study of topotecan given daily for 5 consecutive days to patients with advanced solid tumors, with attempt at dose intensification using recombinant granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. J Natl Cancer Inst 85: 1499–1507
Shapiro WR, Young DF, Mehta BM (1975) Methotrexate: distribution in cerebrospinal fluid after intravenous, ventricular and lumbar injections. N Engl J Med 293: 161–166
Slichenmyer WJ, Rowinsky EK, Donehower RC, Kaufmann SH (1993) The current status of camptothecin analogues as antitumor agents. J Natl Cancer Inst 85: 271–291
Stewart CF, Baker SD, Heideman RL, Jones D, Crom WR, Pratt CB (1994) Clinical pharmacodynamics of continuous infusion topotecan in children: systemic exposure predicts hematologic toxicity. J Clin Oncol 12: 1946–1954
Sung C, Blaney SM, Cole DE, Balis FM, Dedrick RL (1994) A pharmacokinetic model of topotecan clearance from plasma and cerebrospinal fluid. Cancer Res 54: 5118–5122
Underberg WJM, Goossen RMJ, Smith BR, Beijnen JH (1990) Equilibrium kinetics of the new experimental antitumor compound SK&F 104864-A in aqueous solution. J Pharm Biomed Anal 8: 681–683
Verweij J, Lund B, Beijnen J, Planting A, de Boer-Dennert M, Koier I, Rosing H, Hansen H (1993) Phase I and pharmacokinetics study of topotecan, a new topoisomerase I inhibitor. Ann Oncol 4: 673–678
Wall JG, Burris HA III, Von Hoff DD, Rodriguez G, Kneuper-Hall R, Shaffer D, ORourke T, Brown T, Weiss G, Clark G, McVea S, Brown J, Johnson R, Friedman C, Smith B, Mann WS, Kuhn J (1992) A phase I clinical and pharmacokinetic study of the topoisomerase I inhibitor topotecan (SK&F 104864) given as an intravenous bolus every 21 days. Anticancer Drugs 3: 337–345
Zimm S, Collins JM, Miser J, Chatterji D, Poplack DG (1984) Cytosine arabinoside cerebrospinal fluid kinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther 35: 826–830
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baker, S.D., Heideman, R.L., Crom, W.R. et al. Cerebrospinal fluid pharmacokinetics and penetration of continuous infusion topotecan in children with central nervous system tumors. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 37, 195–202 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00688317
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00688317