Abstract
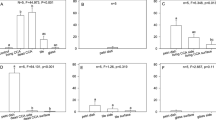
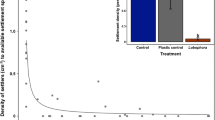
The larval settlement rate of the Indo-Pacific reef coral,Pocillopora damicornis, on bare glass was compared with the rate on glass covered with measured amounts and area of fine sediment. Larval settlement in all sediment treatments was significantly less than on bare glass. Sediment cover of 95% completely prevented settlement. There was no increase in settlement when sediment cover was reduced from 90% to 50% of the glass surface area. If planulae of many coral species behave in a similar fashion in nature, sedimentation at a level that only partially covers the substrate and that is not directly harmful to adult colonies could significantly reduce larval recruitment by inhibiting settlement.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babcock RC (1988) Fine-scale spatial and temporal patterns in coral recruitment. Proc 6th Int Coral Reef Symp 2:635–639
Bak RPM (1978) Lethal and sublethal effects of dredging and corals. Mar Pollut Bull 9:14–16
Birkeland C, Rowley D, Randall RH (1982) Coral recruitment patterns at Guam. Proc 4th Int Coral Reef Symp 2:339–344
Carleton JH, Sammarco PW (1987) Effects of substratum iregularity on success of coral settlement: quantification by comparative geomorphological techniques. Bull Mar Sci 40:85–98
Cortes J, Risk M (1985) A reef under siltation stress: Cahuita, Costa Rica. Bull Mar Sci 36:339–356
Fitzhardinge R (1985) Spatial and temporal variability in coral recruitment in Kaneohe Bay (Oahu, Hawaii). Proc 6th Int Coral Reef Symp 4:373–378
Fitzhardinge RC, Bailey-Brock JH (1989) The colonization of artificial reef materials by corals and other sessile organisms. Bull Mar Sci 44:567–579
Goreau NI, Goreau TJ, Hayes RL (1981) Settling, survivorship and spatial aggregation in planulae and juveniles of the coralPorites porites. Bull Mar Sci 31:424–435
Hadfield MG (1986) Settlement and recruitment of marine invertebrates: a perspective and some proposals. Bull Mar Sci 39:418–425
Harrigan JF (1972) The planula larva ofPocillopora damicornis: Lunar periodicity of swarming and substratum selection behavior. Ph D dissertation, Department of Zoology, University of Hawaii, Honolulu
Harriott VJ (1985) Recruitment patterns of scleractinian corals at Lizard Island, Great Barrier Reef. Proc 6th Int Coral Reef Symp 4:367–372
Heyward A, Yamazato K, Yeemin T, Minei M (1987) Sexual reproduction of corals in Okinawa. Galaxea 6:331–343
Hida Y (1932) A note of the earlier stage of colony formation with the coral,Pocillopora caespitosa Dana. Sci Rep Tohoku Imp Univ 4:425–431
Hixon MA, Brostoff WN (1985) Substrate characteristics, fish grazing, and epibenthic reef assemblages off Hawaii. Bull Mar Sci 37:200–213
Hodgson G (1985) Abundance and distribution of planktonic coral larvae in Kaneohe Bay, Oahu, Hawaii. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 26:61–71
Hodgson G (1989) The Effects of Sedimentation on Indo-Pacific Reef Corals. Ph D dissertation, Department of Zoology, University of Hawaii, Honolulu
Hodgson G, Dixon JA (1988) Logging versus fisheries and tourism in Palawan. Environment and Policy Institute, East-West Center, Honolulu, Hawaii, occasional paper
Lewis JB (1974) The settlement behaviour of planulae larvae of the hermatypic coralFavia fragum (Esper): J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 15:165–172
Maragos JE (1972) A study of the ecology of Hawaiian reef corals. Ph D dissertation. Department Oceanography, University of Hawaii, Honolulu
Marshall SM, Orr AP (1931) Sedimentation on Low Isles reef and its relation to coral growth. Scientific Report of the Great Barrier Reef Expedition 1928–29. Br Mus Nat Hist 1:93–133
Salvat B (1987) Human impacts on coral reefs: facts and recommendations. Antenne Museum EPHE, French Polynesia
Wallace CC, Bull GD (1982) Patterns of juvenile recruitment on a reef front during a spring-summer spawning period. Proc 4th Int Coral Reef Symp 2:344–350
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hodgson, G. Sediment and the settlement of larvae of the reef coralPocillopora damicornis . Coral Reefs 9, 41–43 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00686720
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00686720