Summary
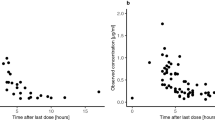
The pharmacokinetics of carboplatin in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and plasma was studied in five children with brain tumors (four medulloblastomas and one ependimoblastoma) who underwent preirradiation treatment with carboplatin. Carboplatin pharmacokinetics was studied following the administration of 600 mg/m2 as a 1-h infusion. Four children were treated a few weeks after surgery, whereas one child with an unresectable tumor was treated prior to surgery. All patients had a ventricular-peritoneal CSF shunt connected to a subcutaneous reservoir. Total platinum and free carboplatin were measured. The mean AUC values for free carboplatin in CSF and plasma were 2.29±1.20 and 8.18±1.27 mg ml−1 min, respectively. The mean ratio of CSF AUC to plasma AUC was 0.28 (range, 0.17–0.46). Both plasma peak levels and AUC values showed limited interpatient variability. On the other hand, carboplatin levels in CSF showed substantial interpatient variability, with a>5-fold difference in peak levels and a 3-fold difference in AUC values being recorded. The interpatient difference in CSF pharmacokinetics may have been related at least in part to the different anatomical alterations induced by the surgical procedures or by the presence of a large tumor mass. In the four evaluable patients exhibiting macroscopic residual tumor, we observed one complete remission (CR) and two partial remissions (PR) following two cycles that consisted of two doses of 600 mg/m2 carboplatin given on 2 consecutive days (total dose, 1200 mg/m2) and were separated by a l-month interval. These results may give some indication as to the optimal dose and schedule for carboplatin administration in the treatment of primitive neuroectodermic tumors (PNET).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen JC, Walker R, Luks E, Jennings M, Barfoot S, Tan C (1987) Carboplatin and recurrent childhood brain tumors. J Clin Oncol 5:459
Blasberg R, Groothuis D (1986) Chemotherapy of brain tumors. Physiological and pharmacokinetic considerations. Semin Oncol 13:70
Boven E, Vijgh WJF van der, Nauta MM, Schluper HMM, Pinedo HM (1985) Comparative activity and distribution studies of five platinum analogues in nude mice bearing human ovarian carcinoma xenografts. Cancer Res 45:86
El-Yazigi A, Al-Saleh I (1986) Rapid determination of platinum by flameless atomic absorption spectrophotometry following the administration of cisplatin to cancer patients. Ther Drug Monit 8:318
Gaver RC, Deeb G (1986) High-performance liquid chromatographic procedures for the analysis of carboplatin in human plasma and urine. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 16:201
Gaynon P, Ettinger LJ, Baum E, Siegel S, Krailo M, Hammond GD (1990) Carboplatin in childhood brain tumors. A children's Cancer Study Group phase II trial. Cancer 66:2465
Gibaldi M, Perrier D (1975) Pharmacokinetics. Marcel Dekker, New York
Gore Me, Calvert AH, Smith IE (1987) High dose carboplatin in the treatment of lung cancer and mesothelioma: a phase I dose escalation study. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol 23:1391
Gormley PE, Gangji D, Wood JH, Poplack DG (1981) Pharmacokinetic study of cerebrospinal fluid penetration ofcis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II). Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 5:257
Hill BT, Whelan RDH, Hosking LK (1988) Use of human neuroblastoma continuous cell lines for in vitro drug sensitivity screening. Invest New Drugs 6:11
Levin VA, Freeman MA, Landahl HD (1975) The permeability characteristics of brain adjacent to intracerebral rat tumors. Arch Neurol 32:785
Newell DR, Siddik ZH, Gumbrell LA, Boxall FE, Gore ME, Smith IE, Calvert AH (1987) Plasma free platinum pharmacokinetics in patients treated with high dose carboplatin. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol 23:1399
Riccardi R, Riccardi A, Tartaglia RL, Carelli G, Lasorella A, Tornesello A, Ceddia A, Mastrangelo R (1991) Pharmacokinetics of carboplatin in children (abstract). Proceedings, 23rd SIOP Meeting, Rhodes, 1–4 October, 1991, Med Ped, Oncol
Stewart DJ, Leavens M, Maor M, Feun L, Luna M, Bonura J, Caprioli R, Loo TL, Benjamin RS (1982) Human central nervous system distribution ofcis-diamminedichloroplatinum and its use as a radiosensitizer in malignant brain tumors. Cancer Res 42:2474
Van der Vijgh WJF, Klein I (1986) Protein binding of five platinum compounds. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 18:129
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was partially supported by the AIRC
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Riccardi, R., Riccardi, A., Di Rocco, C. et al. Cerebrospinal fluid pharmacokinetics of carboplatin in children with brain tumors. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 30, 21–24 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00686480
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00686480