Summary
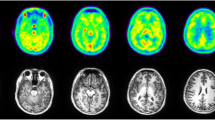
The in vivo distribution of the antileukemic agent busulfan labeled with the positron-emitting radionuclide carbon 11 was investigated in cynomolgus monkeys and in a human patient using positron emission tomography. After i.v. injection of the radiotracer, its regional uptake was monitored for about 1 h in the monkey's body and in a separate experiment, in the monkey's brain. The concentration of radioactivity in the liver, which showed the highest levels of all the organs scanned, increased throughout the experiment and was 9-fold that in the brain at the end of the experiment. [11C]-Busulfan rapidly crossed the blood-brain barrier. The radioactivity peaked in both the cortex and the white matter showing a ratio of 1.25, at 3 min but declined quickly to yield a ratio of approximately 1 after 30 min. In the human brain, radioactivity in the cerebellum, cortex, and white matter reached a maximum within 5 min showing a cortex:white matter ratio of 1.6. The activity in the cortex declined to yield a ratio of 1 within 30 min. Of the delivered dose, 20% penetrated into the brain.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CSF:
-
cerebrospinal fluid
- AML:
-
acute myelocytic leukemia
- BMT:
-
bone marrow transplantation
- PET:
-
positron emission tomography
- BBB:
-
blood-brain barrier
References
Anderson CC, Goldstone AH, Linch DC, Jones HM, Franklin IM, Boughton BJ, Cawley JC, Richards JDM (1987) Autologous bone marrow transplantation for patients with acute myeloid leukaemia and acute lymphoblastic leukaemia — a comparison. Bone Marrow Transplant 1: 271
Atkinson K, Biggs J, Noble G, Ashby M, Concannon A, Dodds A (1987) Preparative regimens for marrow transplantation containing busulphan are associated with haemorrhagic cystits and hepatic veno-occlusive disease but a short duration of leucopenia and little oro-pharyngeal mucositis. Bone Marrow Transplant 2: 385
Bergström M, Litton J, Eriksson L, Bohm C, Blomqvist G (1982) Determination of object contour from projections for attenuation correction in cranial positron emission tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr 6: 365
Ehrsson H, Hassan M (1984) Binding of busulfan to plasma proteins and blood cells. J Pharm Pharmacol 36: 694
Fitzsimmons WE, Ghalie R, Kaizer H (1990) The effect of hepatic enzyme inducers on busulfan neurotoxicity and myelotoxicity. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 27: 226
Gouyette A, Hartmann O, Pico J-L (1986) Pharmacokinetics of high-dose melphalan in children and adults. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 16: 184
Greig NH, Sweeney DJ, Rapoport SI (1988) Comparative brain and plasma pharmacokinetics and anticancer activities of chlorambucil and melphalan in the rat. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 21: 1
Hassan M, Ehrsson H (1987) Metabolism of [14C]-busulfan in isolated perfused rat liver. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 12: 71
Hassan M, Ehrsson H (1987) Urinary metabolites of busulfan in the rat. Drug Metab Dispos 15: 399
Hassan M, Ehrsson H, Wallin I, Eksborg S (1988) Pharmacokinetic and metabolic studies of busulfan in rat plasma and brain. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 13: 301
Hassan M, Ehrsson H, Smedmyr B, Tötterman T, Wallin I, Öberg G, Simonsson B (1989) Cerebrospinal fluid and plasma concentrations of busulfan during high-dose therapy. Bone Marrow Transplant 4: 113
Hassan M, öberg G, Ehrsson H, Ehrnebo M, Wallin I, Smedmyr B, Tötterman T, Eksborg S, Simonsson B (1989) Pharmacokinetic and metabolic studies of high-dose busulphan in adults. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 36: 525
Hassan M, Thorell J-O, Warne N, Stone-Elander S (1991)11C labelling of busulphan. Appl Radiat Isotopes 42: 1055
Kalifa C, Hartmann O, Vassal G, Valteau D, Lemerle J (1988) Preliminary results of a phase II study of high-dose busulfan and thiotepa in children with recurrent brain tumors. Pediatr Neurosci 14: 154
Lajtha AL, Maker HS, Clarke DD (1981) Metabolism and transport of carbohydrates and amino acids. In: Siegel GJ, Albers RW, Agranoff BW, Katzman R (eds) Basic neurochemistry, 3rd edn. Little, Brown and Company, Boston, pp 329–353
Litton JE, Bergström M, Eriksson L, Bohm C, Blomqvist G, Kesselberg M (1984) Performance study of the PC-384 positron camera system for emission tomography of the brain. J Comput Assist Tomogr 8: 74
Litton JE, Holte S, Eriksson L (1990) Evaluation of the Karolinska new positron camera system; the Scanditronix PC2048-15B. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 37: 743
Marcus RE, Goldman JM (1984) Convulsions due to high-dose busulphan. Lancet II: 1463
Martell RW, Sher C, Jacobs P, Monteagudo FCP (1987) High-dose busulfan and myoclonic epilepsy. Ann Intern Med 106: 173
Peterson DW, Collins JF, Bradford HF (1983) Transmitter amino acids and their antagonists in epilepsy. In: Hertz L, Kvamme E, McGeer EG, Schousboe A (eds) Glutamine, glutamate, and GABA in the central nervous system, vol 7. Alan R. Liss, New York, pp 643–652
Roberts JJ, Warwick GP (1961) The mode of action of alkylating agents:III. The formation of 3-hydroxytetrahydrothiophene-1∶1-dioxide from 1∶4-dimethanesulphonyloxybutane (Myleran),S-β-l-alanyltetrahydydrothiophenium mesylate, tetrahydrothiophene and tetrahydrothiophene-1∶1-dioxide in the rat, rabbit and mouse. Biochem Pharmacol 6: 217
Santos GW, Tutshka PJ, Brookmeyer R, Saral R, Beschorner WE, Bias WB, Braine HG, Burns WH, Elfenbein GJ, Kaizer H, Mellits D, Sensenbrenner LL, Stuart RK, Yeager AM (1983) Marrow transplantation for acute nonlymphocytic leukemia after treatment with busulfan and cyclophosphamide. N Engl J Med 309: 1347
Schallier D, Impens N, Warson F, Van Belle S, De Wasch G (1983) Additive pulmonary toxicity with melphalan and busulfan therapy. Chest 84: 492
Shank RP, Campbell GL (1983) Metabolic precursors of glutamate and GABA. In: Hertz L, Kvamme E, McGeer EG, Schousboe A (eds) Glutamine, glutamate, and GABA in the central nervous system, vol 7. Alan R. Liss, New York, pp 355–369
Shapiro WR, Young DF, Mehta BM (1975) Methotrexate: distribution in cerebrospinal fluid after intravenous, ventricular and lumbar injections. N Engl J Med 293: 161
Siegers C-P, Bossen KH, Younes M, Mahlke R, Oltmanns D (1982) Glutathione and glutathione-S-transferases in the normal and diseased human liver. Pharmacol Res Commun 14: 61
Sureda A, Pérez de Oteyza J, García Laraña J, Odriozola J (1989) High-dose busulfan and seizures. Ann Intern Med 111: 543
Thomas AE, Patterson J, Prentice HG, Brenner MK, Ganczakowski M, Hancock JF, Pattinson JK, Blacklock HA, Hopewell JP (1987) Haemorrhagic cystitis in bone marrow transplantation patients: possible increased risk associated with prior busulphan therapy. Bone Marrow Transplant 1: 347
Trams EG, Nadkarni MV, DeQuattro V, Maengwyn-Davies GD, Smith PK (1959) Dimethanesulphonoxybutane (Myleran), preliminary studies on distribution and metabolic fate in the rat. Biochem Pharmacol 2: 7
Vassal G, Gouyette A, Hartmann O, Pico JL, Lemerle J (1989) Pharmacokinetics of high-dose busulfan in children. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 24: 386
Vassal G, Deroussent A, Hartmann O, Challine D, Benhamou E, Valteau-Couanet D, Brugiéres L, Kalifa C, Gouyette A, Lemerle J (1990) Dose-dependent neurotoxicity of high-dose busulfan in children: a clinical and pharmacological study. Cancer Res 50: 6203
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by grants from the Swedish Cancer Society (2805-B90-01X) and the Swedish Medical Research Council (B9012X0827603A and B9012P0843102B)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassan, M., öberg, G., Ericson, K. et al. In vivo distribution of [11C]-busulfan incynomolgus monkey and in the brain of a human patient. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 30, 81–85 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00686397
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00686397