Summary
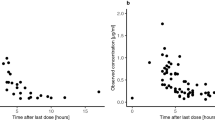
Penetration of etoposide into the cerebrospinal fluid, brain tumor, and brain tissue after intravenous administration was investigated in patients presenting with malignant brain tumors. A relatively low dose (55–65 mg/m2) was used to compare intravenous with oral administration. High-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection was used to evaluate drug levels. Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid levels of etoposide after oral administration (50–150 mg/day) were also studied so as to determine the adequate oral dose for the treatment of malignant brain tumors. The peak plasma concentration after intravenous administration ranged from 7.01 to 10.47 μg/ml, varying in proportion to the injected dose, whereas that after oral administration was lower, namely, 1.44–4.99 μg/ml, and was unstable when the oral dose was 150 mg daily. The peak cerebrospinal fluid level following either intravenous or oral administration was much lower than the plasma concentration and was influenced by the peak plasma level and the sampling site. The etoposide concentration in cerebrospinal fluid taken from the subarachnoid space and ventricle of patients displaying no tumor invasion and of those presenting with meningeal carcinomatosis and in cerebrospinal fluid taken from the dead space after tumor resection was 0.7%±0.5%, 3.4%±1.0%, and 7.2% ± 8.5%, respectively, of the plasma concentration. Serial oral administration did not result in the accumulation of etoposide in cerebrospinal fluid. The tumor concentration (1.04–4.80 μg/g) was 14.0%±2.9% of the plasma level after intravenous administration, was related to the injected dose, and was approximately twice the concentration detected in the brain tissue. Therefore, a relatively low dose of etoposide injected intravenously penetrates the brain tumor at an efficacious concentration. Our results indicate than an oral dose of 100 mg etoposide be given for malignant brain tumors, as limited penetration of the drug into the intracranial region was observed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carney DN, Grogan L, Smit EF, Harford P, Berendsen HH, Postmus PE (1990) Single-agent oral etoposide for elderly small cell lung cancer patients. Semin Oncol 17:49
Creaven PJ (1982) The clinical pharmacology of VM 26 and VP 16-213. A brief overview. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 7:133
D'Incalci M, Sessa C, Rosso C, Roviaro G, Mangioni C (1985) Pharmacokinetics of etoposide in gestochoriocarcinoma. Cancer Treat Rep 69:69
Feun LG, Lee Y-Y, Yung W-KA, Savaraj N, Qallace S (1987) Intracarotid VP-16 in malignant brain tumors. J Neurooncol 4:397
Finn GP, Bozek T, Souhami RL, Slevin ML, Thomas DGT (1985) High-dose ctoposide in the treatment of relapsed primary brain tumors. Cancer Treat Rep 69:603
Giannone L, Wolff SN (1987) Phase II treatment of central nervous system gliomas with high-dose etoposide and autologous bone marrow transplantation. Cancer Treat Rep 71:759
Haaxma-Reiche H, Berendsen HH, Postmus PE (1988) Podophyllotoxins for brain metastases of small cell lung cancer. J Neurooncol 6:231
Hainsworth JD, Johnson DH, Frazier SR, Greco FA (1989) Chronic daily administration of oral etoposide. A phase I trial. J Clin Oncol 7:396
Hande KR, Wedlund PJ, Noone RM, Wilkinson GR, Greco FA, Wolff SN (1984) Pharmacokinetics of high-dose etoposide (VP-16-213) administration to cancer patients. Cancer Res 44:379
Holthuis JJM, Postmus PE, Oort WJV, Hulshoff B, Verleun H, Sleijfer DT, Mulder NH (1986) Pharmacokinetics of high dose etoposide (VP16-213). Eur J Cancer Oncol 22:1149
Idzu G, Yazawa Y, Tachibana M, Terada T, Hashimoto Y, Shimazu T (1989) Determination of etoposide in plasma by high performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. Clin Rep 23:479
Kleisbauer JPP, Lena-Nosny N, Vesco D (1987) Taux seriques dans le liquide cephalo-rachidien apres forte dose d'etopside administree par voie intraveineuse. Bull Cancer 74:631
Kleisbauer JP, Vesco D, Orehek J, Blaive B, Clary C, Poirier R, Saretto S, Carles P, Dongay G, Guerin JC, Martinat Y (1988) Treatment of brain metastases of lung cancer with high doses of etoposide (VP16-213). Cooperative study of the Groupe Français Pneumo Cancérologie. Eur J Cancer Oncol 24:131
Kobayashi T, Yoshida J, Ishiyama J, Noda S, Kito A, Kida Y (1989) Combination chemotherapy with cisplatin and etoposide for malignant intracranial germ-cell tumors. An experimental and clinical study. J Neurosurg 70:676
Lee SJ, Murphy WK, Glisson BS, Dhinga HM, Holoye PY, Hong WK (1989) Primary chemotherapy of brain metastasis in small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 7:916
Lu K, Savraj N, Feun L, Leaven M, Loo TL (1982) Clinical pharmacology and intracerebral tumor penetration of 4′-demethyl epipodophyllotoxin 9-(4,6-O-ethylidene-β-d-glucopyranoside) (VP-16, NSC-141 540). Clin Pharmacol Ther 31:245
Postmus PE, Holthuis JJM, Haaxma-Reiche H, Mulder NH, Vencken LM, Oort WJ, Sleijfer DT, Sluiter HJ (1984) Penetration of VP16-213 into cerebrospinal fluid after high-dose intravenous administration. J Clin Oncol 2:215
Postmus PE, Haaxma-Reiche H, Sleijfer DT, Kirkpatriek A, McVie JG, Kleisbauer JP, for the EORTC Lung Cooperative Group (1989) High dose etoposide for brain metastasis of small cell lung cancer. A phase II study. Br J Cancer 59:254
Slevin ML (1991) The clinical pharmacology of etoposide. Cancer 67:319
Stewart DJ, Richard M, Hugenholtz H, Dennery J (1983) VP-16 (VP) and VM-26 (VM) penetration into human brain tumors (BT). Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res 24:133
Stewart DJ, Richard M, Hugenholtz H, Dennery JM, Belanger R, Gerin-Lajoie J, Montpetit V, Nundy D, Prior J, Hopkins HS (1984) Penetration of VP-16 (etoposide) into human intracerebral and extracerebral tumors. J Neurooncol 2:133
Takeda S, Takada S, Kojima T, Kinoshita K, Sakamoto S (1990) Oral etoposide therapy in stage III–IV ovarian carcinoma. J Jpn Soc Cancer Ther 25:2562
Tirelli U, D'Incalci M, Canetta R, Tumolo S, Franchin G, Veronesi A, Galligiono E, Trovo MG, Rossi C, Grigoletto E (1984) Etoposide (VP-16-213) in malignant brain tumors: a phase II study. J Clin Oncol 2:432
Viens P, Lagrange J-L, Thyss A, Ayela P Frenay M, Schneider M (1988) Brain metastases of lung cancer: excessive toxicity of high dose VP 16213. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol 24:1905
Yuki K, Kodama Y, Emoto K, Yukawa O, Onda J, Uozumi T (1989) A case report of advanced malignant mixed germ cell tumor of parasellar origin indicating marked efficacy of a salvage combined chemotherapy of CDDP and etoposide and subsequent chemotherapy using oral etoposide. Jpn J Cancer Chemother 16:2651
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kiya, K., Uozumi, T., Ogasawara, H. et al. Penetration of etoposide into human malignant brain tumors after intravenous and oral administration. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 29, 339–342 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00686001
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00686001