Summary
-
1.
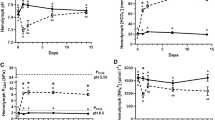
Hemolymph acid-base balance (pH,P CO 2 and bicarbonate concentration) was measured in shore crabs,Carcinus maenas, exposed first for 17–18 h to normoxic seawater at three levels of titration alkalinity, TAw 0.95, 2.5 and 4.5 meq·l−1, either at low (ca. 0.3 Torr) or at high (ca. 4.3 Torr) ambientP CO 2 (PwCO 2), and subsequently exposed acutely for 2 h to hyperoxia in the same ambient acid-base conditions. WaterP CO 2 was controlled with a pH-CO2-stat system in all experiments.
-
2.
At low constantPwCO 2 (0.3 Torr), decreased TAw led to an uncompensated hypercapnic acidosis with hemolymphP CO 2 increased and hemolymph pH decreased. At highPwCO 2 (4.3 Torr) however, hemolymph acid-base state was independent of TAw.
-
3.
Acute hyperoxia induced hypercapnic acidosis in all conditions. At lowPwCO 2, the hyperoxia-induced hypercapnia was more marked at low than at high TAw whereas at highPwCO 2 it was of the same magnitude whatever the TAw.
-
4.
The internal acid-base state thus depends on TAw at constant low inspiredPwCO 2, probably via related changes of the water CO2 capacitance coefficient, ΔCwCO 2/ΔPwCO 2, due to buffering of excreted CO2 by carbonate ions at high water pH. Therefore, all the acid-base properties of the ambient water, pH,P CO 2 and carbonate alkalinity, must be taken into account in studying acid-base balance of water-breathers.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CA :
-
carbonate alkalinity
- PwO 2,PwCO 2O2, CO2 :
-
partial pressure of water phase
- TAw :
-
titration alkalinity of water
- v :
-
mixed venous blood (pH,P CO 2 etc.)
References
Burnett LE, Johansen K (1981) The role of branchial ventilation in blood acid-base changes in the shore crab,Carcinus maenas, during hypoxia. J Comp Physiol 141:489–494
Cameron JN (1978) Regulation of blood pH in teleost fish. Respir Physiol 33:129–144
Dejours P (1981) Principles of comparative respiratory physiology, 2nd Edn. Elsevier North Holland Biomedical Press, Amsterdam
Dejours P, Armand J (1980) Hemolymph acid-base balance of the crayfishAstacus leptodactylus as a function of the oxygenation and acid-base balance of the ambient water. Respir Physiol 41:1–11
Dejours P, Armand J, Verriest G (1968) Carbon dioxide dissociation curves of water and gas exchange of water-breathers. Respir Physiol 5:23–33
Dejours P, Armand J, Gendner JP (1978) Importance de la régulation de l'équilibre acide-base de l'eau ambiante pour l'étude des échanges respiratoires et ioniques des animaux aquatiques. CR Acad Sci 287:1397–1399
Dejours P, Armand J, Gendner JP (1980) Carbon dioxide in aquatic biotopes. In: Lahlou B (ed) Epithelial transport in the lower vertebrates. Cambridge University Press, pp 105–113
Giraud MM (1981) Carbonic anhydrase activity in the integument of the crabCarcinus maenas during the intermoult cycle. Comp Biochem Physiol 69A:381–387
Jouve A, Truchot JP (1978) Influence de l'oxygénation de l'eau sur la consommation d'oxygène et la ventilation branchial e du crabeCarcinus maenas (L.). CR Acad Sci 286:331–334
Jouve-Duhamel A, Truchot JP (1983) Ventilation in the shore crabCarcinus maenas (L.) as a function of ambient oxygen and carbon dioxide: field and laboratory studies. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 70:281–296
McMahon BR, Butler PJ, Taylor EW (1978) Acid-base changes during recovery from disturbances and during long term hypoxic exposure in the lobsterHomarus vulgaris. J Exp Zool 205:361–370
Piiper J, Dejours P, Haab P, Rahn H (1971) Concepts and basic quantities in gas exchange physiology. Respir Physiol 13:292–304
Skirrow G (1975) The dissolved gases: carbon dioxide. In: Riley JP, Skirrow G (eds) Chemical Oceanography, vol 2. Academic Press, New York, pp 1–181
Strickland JDH, Parsons TR (1965) A manual of seawater analysis. Fisheries Res Board Canada Bull no 125, Ottawa
Truchot JP (1975a) Action de l'hypercapnie sur l'état acide-base du sang chez le crabeCarcinus maenas (L.) (Crustacé Décapode). CR Acad Sci 280:311–314
Truchot JP (1975b) Blood acid-base changes during experimental emersion and reimmersion of the intertidal crab,Carcinus maenas (L.). Respir Physiol 23:351–360
Truchot JP (1975c) Changements de l'état acide-base du sang en fonction de l'oxygénation de l'eau chez le crabeCarcinus maenas (L.). J Physiol (Paris) 70:583–592
Truchot JP (1976) Carbon dioxide combining properties of the blood of the shore crabCarcinus maenas (L.): carbon dioxide solubility coefficient and carbonic acid dissociation constants. J Exp Biol 64:45–57
Truchot JP (1981a) L'equilibre acido-basique extracellulaire et sa régulation dans les divers groupes animaux. J Physiol (Paris) 77:529–580
Truchot JP (1981b) The effect of water salinity and acid-base state on the blood acid-base balance in the euryhaline crab,Carcinus maenas (L.). Comp Biochem Physiol 68A:555–561
Truchot JP (1983) Regulation of acid-base balance. In: Mantel LH (ed). The biology of crustacea, vol 5. Academic Press, New York, pp 431–457
Truchot JP, Duhamel-Jouve A (1980) Oxygen and carbon dioxide in the marine intertidal environment: diurnal and tidal changes in rockpools. Respir Physiol 31:241–254
Truchot JP, Toulmond A, Dejours P (1980) Blood acid-base balance as a function of water oxygenation: a study at two different ambient CO2 levels in the dogfish,Scyliorhinus canicula. Respir Physiol 41:13–28
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Truchot, J.P. Water carbonate alkalinity as a determinant of hemolymph acid-base balance in the shore crab,Carcinus maenas: a study at two different ambientP CO 2 andP O 2 levels. J Comp Physiol B 154, 601–606 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00684414
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00684414