Abstract
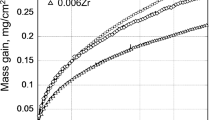
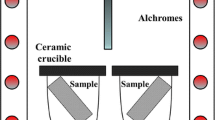
The oxidation behavior of Fe-40Al-1Hf, Fe-40Al-1Hf-0.4B, and Fe-40Al-0.1Zr-0.4B (at.%) alloys was characterized after 900°, 1000°, and 1100°C exposures. Isothermal tests revealed parabolic kinetics after a period of transitional θ-alumina scale growth. The parabolic growth rates for the subsequent α-alumina scales were about five times higher than those for NiAl+O.1Zr alloys. The isothermally grown scales showed a propensity toward massive scale spallation due to both extensive rumpling from growth stresses and to an inner layer of HfO2. Cyclic oxidation for 200 1-hr cycles produced little degradation at 900 or 1000°C, but caused significant spaliation at 1100°C in the form of small segments of the outer scale. The major difference in the cyclic oxidation of the three FeAl alloys was increased initial spallation for FeAl+Zr, B. Although these FeAl alloys showed many similarities to NiAl alloys, they were generally less oxidation-resistant. It is believed that this resulted from nonoptimal levels of dopants and larger thermal-expansion mismatch stresses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. Baker and D. J. Gaydosh,Mater. Sci. Eng. 96, 147 (1987).
W. C. Hagel,Corrosion 21, 316 (1965).
B. S. Ryl'nikov, G. V. Arkhangel'skaya, and L. V. Lyubetskaya,Protection Metals 17, 290 (1981).
C. A. Barrett,Oxid. Met. 30, 361 (1988).
F. Cosandey and J. Kandra,Metall. Trans. A 18, 1239 (1987).
E. M. Schulson, T. P. Weihs, I. Baker, H. J. Frost, and J. A. Horton,Acta Met. 34, 1395 (1986).
D. J. Gaydosh, S. L. Draper, and M. V. Nathal,Metall. Trans. A,20A, 1701 (1989).
G. C. Rybicki and J. L. Smialek,Oxid. Met. 31, 275 (1989).
J. K. Doychak, T. E. Mitchell, and J. L. Smialek,Ordered Intermetallic Alloys, MRS Symp. Proc. Vol. 39, C. C. Koch, C. T. Liu, and N. S. Stoloff, eds. (Materials Research Society, Pittsburgh, 1985), pp. 475–484.
J. L. Smialek,Metall. Trans. A,9, 309 (1978).
J. L. Smialek,Metall. Trans. A,18, 164 (1987).
J. L. Smialek, inOxidation of Metals and Associated Mass Transport, M. A. Dayananda, S. J. Rothman, and W. E. King, eds. (Metallurgical Society of AIME, 1986), pp. 297–313.
J. K. Doychak, J. L. Smialek, and C. A. Barrett, inOxidation of High-Temperature Intermetallics, T. Grobstein and J. Doychak, eds. (Metallurgical Society of AIME, 1988), pp. 41–56.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smialek, J.L., Doychak, J. & Gaydosh, D.J. Oxidation behavior of FeAl+Hf, Zr, B. Oxid Met 34, 259–275 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00665018
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00665018