Abstract
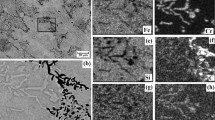
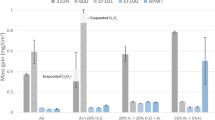
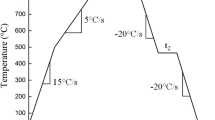
This paper reports an investigation into reducing the Cr concentration in commercial-grade stainless steels while maintaining oxidation protection at elevated temperatures. Aluminum and Si were added as partial substitute alloy elements to enhance the reduced operation protection resulting from Cr concentration reduced by approximately 50 pct of that found in stainless steels. The goal of this study was to determine the oxidation mechanism of such an Fe, Al-Si alloy: Fe-8Cr-14Ni-1Al-3.5Si-1Mn. During the initial oxidation period the protection resulted from a thin film of Al2O3 over an Fe and Cr spinel. Long-term oxidation protection resulted from the gradual formation of a Cr sesquioxide (Cr2O2) inner oxide layer. Eventually an outer oxide layer formed that was a mixed composition spinel of Cr and Mn (MnO · Cr2O3). The Al2O3, which was part of the original protective layer flaked off early in the oxide testing, and the aluminum oxide that formed later appeared as an internal oxide precipitate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Himmel, R. F. Mehl, and C. E. Birchenall, Self Diffusion of Iron in Iron Oxides and the Wagner Theory of Oxidation,Trans. AIME, J Met. XX, 827 (1953).
A. John, Sedriks,Corrosion of Stainless Steels (John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1979).
A. I. Kahveci and G. Welsch, High-Temperature Oxidation of Fe-3 wt pet Cr Alloy,Scripta Metall. 17, 121 (1983).
M. J. Graham, Thin Oxide Film Formation on Metals, High Temperature Corrosion. InInternational Corrosion Conference (NACE, Houston, TX, 1981), pp. 139–144.
W. E. Bogg, The High-Temperature Oxidation Resistance of Iron-Silicon-Aluminum Alloys,Oxid. Met. 10(4) 277–290 (1976).
S. Guruswamy, J. P. Hirth, and G. W. Powell, Oxidation Behavior of Fe-Si-Al Alloys at 1173–1373 K,Oxid. Met. 19(3/4), 77–98 (1983).
A. Kumar and D. L. Douglas, Modification of the Oxidation Behavior of High-Purity Austenitic Fe-14Cr-14Ni by the Addition of Silicon,Oxid. Met. 10(1), 1–22 (1970).
H. E. Evans, D. A. Hilton, R. A. Holm, and S. J. Weber, Influence of Silicon Additions on the Oxidation Resistance of a Stainless Steel,Oxid. Met. 19(1/2) 1–18 (1983).
R. G. Miner and V. Nagarajan, The Morphology of Oxidation of Alumina-Forming Iron-Base Chromium and Silicon,Oxid. Met. 16(3/4), 295–326 (1981).
A. Atkinson, M. L. O'Dwyer, and R. I. Taylor, Fe Diffusion in Magnetite Crystals at 550°C and its Relevance to Oxidation of Iron,J. Mat. Sci. 18, 2371 (1983).
T. E. Mitchell, D. A. Voss, and E. P. Butler, The Observation of Stress Effects During the High Temperature Oxidation of Iron,J. Mat. Sci. 17 1825 (1982).
O. Kubaschewski and B. E. Hopkins,Oxidation Metals and Alloys (Academic Press, Inc., London, 1953).
D. Caplan and M. Cohen,Nature 205, 690 (1965).
G. C. Wood and D. P. Whittle, Chromium Oxide Scale Growth on Iron-Chromium Alloys,J. Electrochem. Soc., Electrochemical Sci. 115(2), 126 (1968).
K. Ishiguro and T. Homma, Thin Oxide Films on a Ferritic and an Austenitic Alloy, InInternational Corrosion Conference (NACE, Houston, TX, 1981), pp. 28–34.
K. Kurroda, P. A. Labun, G. Welsch, and T. E. Mitchell, Oxide-Formation Characteristics in the Early Stages of Oxidation of Fe and Fe-Cr Alloys,Oxid. Met. 19(3/4), 117–128 (1983).
H. E. Evans, D. A. Hilton, R. A. Holm, and S. J. Webster, Influence of Silicon Additions on the Oxidation Resistance of a stainless Steel,Oxid. Met. 19(1/2), 1–18 (1983).
J. M. Francis, Influence of Minor Alloying Elements on Structure of Surface Oxides Forming During the High Temperature Oxidation of an Austenitic Steel,J. Iron and Steel Institute 910 (1966).
G. C. Wood and F. H. Scott, The Development and Growth of Protection Alpha-Al2O3 Scales on Alloys, InInternational Corrosion Conference (NACE, Houston, TX, 1981), pp. 227–250.
P. Tomaszewicz and G. R. Wallwork, Development of Oxidation Resistant Fe-Al Alloys, High Temperature Corrosion, InInternational Corrosion Conference (NACE, Houston, TX, 1981), pp. 258–266.
D. Delaunay, A. M. Huntz, and P. Lacombe, Impurities Influence on Oxidation Kinetics of Fe-Ni-Cr-Al Alloys,Corr. Sci. 24(1), 13 (1984).
F. Fitzer and J. Schlicting, Coatings, Containing Aluminum and Silicon for High Temperature Alloys. High Temperature Corrosion, InInternational Corrosion Conference (NACE, Houston, TX, 1981), pp. 604–614.
G. C. Wood, A. Richardson, M. G. Hobby, and J. Boustead, The Identification of the Thin Healing layers at the Base of Oxide Scales on Fe-Cr Based Alloys,Corr. Sci. 9, 659 (1969).
J. M. Francis and J. A. Jutson, Role of Silicon in Determining the Oxidation Resistance of an Austenitic Steel,Mat. Sci. Eng. 4, 84 (1969).
G. C. Wood, High-Temperature Oxidation of Alloys,Oxid. Met. 2(1), 11–57 (1970).
H. Hindam and D. P. Whittle, Microstructure, Adhesion, and Growth Kinetics of Protective Scales on Metals and Alloys,Oxid. Met. 18(5/6), 245–284 (1983).
A. Abba, A. Galarie, and M. Caillet, Protection Du Fer Contre L'Oxydation Par Siliciuration Superficielle,Mat. Chem. 5, 147 (1980).
M. L. Glenn, S. J. Bullard, D. E. Larson, and S. C. Rhoads,New Development in Stainless Steel Technology (ASM, Detroit, MI, 1984).
W. C. Hagel,Trans. of Metall. Soc. of AIME 236, 179 (1966).
K. Nohara and K. Hirano,Proceeding of the International Conference on Science Technology of Iron and Steel (Tokyo, Publisher, 1970).
A. W. Bowen and G. M. Leak,Met. Trans. 1(6), 1695 (1970).
A. M. Brown and M. F. Ashby, Correlations for Diffusion Constants,ACTA Metall. 28 1085 (1980).
Th. Heumann and R. Imu, The Development and Growth of Protection Alpha-Al2O3 Scales on Alloys,J. Phys. Chem. Solid 29 1613 (1968).
D. A. Porter and K. E. Easterling,Phase Transformations in Metals and Alloys (Van Nostrand Reinhold, Ltd., Berkshire, England, 1981), pp. 101–102.
Per. Kofstad, Oxidation Mechanism for Pure Metals in Single Oxidation Gases, High-Temperature Corrosion, InInternational Corrosion Conference (NACE, Houston, TX, 1981), pp. 123–138
J. A. Richardson, M. C. Hobby, and J. Boustead,Corr. Sci. 9, 659 (1969).
P. T. Mosley, G. Tappin, J. A. Crosley, and J. C. Riviere,Corr. Sci. 23, 901–920 (1983).
R. Freer, Diffusion in Silicate Materials and Glasses,Minerals Petrol. 76 449 (1981).