Abstract
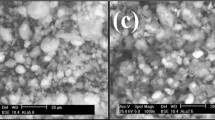
The effects of the addition of aluminium orthophosphate (Al/P=1) to sepiolite were investigated with respect to texture, porosity, surface chemistry and catalytic performance. The AlPO4-sepiolite catalysts, containing different weight compositions, were prepared by precipitation of AlPO4 (Al/P=1) with propylene oxide or aqueous ammonia on to commercial natural sepiolite. Sepiolite inhibits the AlPO4 crystallization which is found when pure AlPO4 is calcined at 873 K.
The surface acid-basic properties have been studied gas-chromatographically through the irreversible adsorption of organic acids and bases at temperatures in the range 473 to 673 K. In addition, the cyclohexene skeletal isomerization (CSI) acid catalysed test reaction to 1- and 3-methylcyclopentenes (1- and 3-MCP), was used to test catalyst performance. Catalytic activity, as an apparent rate constant, fits the Bassett-Habgood kinetic model for first-order processes. Marked changes were found in their catalytic properties as a function of the preparation method and the AlPO4 to sepiolite ratio.
AlPO4 addition induced acidity by increasing the strength of acid sites which resulted in a higher conversion which was accompanied by a greater selectivity for 1-MCP. The incorporation of AlPO4 to sepiolite also inhibited the loss of activity with the prolonged use of the catalyst which was found for reference pure natural sepiolite.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. A. Aramendia, J. M. Campelo, S. Esteban, C. Jimenez, J. M. Marinas andJ. V. Sinisterra,Rev. Mex. Petrol. 12 (1980) 61.
J. M. Campelo, A. Garcia, D. Luna andJ. M. Marinas,Can. J. Chem. 61 (1983) 2567.
J. M. Campelo, J. M. Marinas, S. Mendioroz andJ. Pajares,J. Catal. 101 (1986) 484.
J. M. Campelo, A. Garcia, J. M. Gutierrez, D. Luna andJ. M. Marinas,J. Colloid Interface Sci. 95 (1983) 544.
J. M. Campelo, A. Garcia, D. Luna andJ. M. Marinas,J. Catal. 111 (1988) 106.
Idem., ibid. 102 (1986) 299.
Idem., in “Preparation of Catalysts IV” (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1987) p. 199.
J. M. Campelo, J. M. Marinas andR. Perezossorio,An. Quim. 74 (1978) 86.
J. M. Campelo andJ. M. Marinas,Afinidad 38 (1981) 333.
J. M. Campelo, A. Garcia, D. Luna andJ. M. Marinas,Mater. Phys. 24 (1989) 51.
Idem., J. Colloid Interface Sci. 118 (1987) 98.
Idem., Bull. Soc. Chim. Fr. (1988) 283.
Idem., J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans I 85 (1989) 2535.
A. Blanco, J. M. Campelo, A. Garcia, D. Luna, J. M. Marinas andM. S. Moreno,Appl. Catal. 53 (1989) 135.
K. Brauner andA. Preisinger,Tschermaks Miner. Petrog. Mitt. 6 (1956) 120.
R. H. S. Robertson,Chem. Ind. (1957) 1492.
Idem., Silicates Industriels 38 (1973) 33.
J. M. Garcia-Segura, C. Cid, J. Martin De Llano andJ. G. Gavilanes,British Polym J. 19 (1987) 517.
A. J. Dandy andM. S. Nadiye-Tabbiruka,Clays Clay Miner. 30 (1982) 347.
M. N. Fernandez-Hernandez andT. Fernandez-Alvarez,An. Quim. 79 (1983) 342.
F. Rey-Bueno, M. Villafranca-Sanchez, E. Gonzalez-Pradas andJ. D. Lopez-Gonzalez,ibid. 81B (1985) 18.
M. Villafranca-Sanchez, E. Gonzalez-Pradas, J. D. Lopez-Gonzalez andF. Rey-Bueno,ibid. 81B (1985) 158.
M. Villafranca-Sanchez, A. Valverde-Garcia, E. Gonzalez-Pradas andF. Rey-Bueno,ibid. 83B (1987) 151.
E. Gonzalez-Pradas, A. Valverde-Garcia, M. Villafranca-Sanchez andF. Rey-Bueno,ibid. 83B (1987) 162.
J. M. Campelo, A. Garcia, D. Luna andJ. M. Marinas,Reactiv. Solids 3 (1987) 263.
H. Pines, in “The Chemistry of Catalytic Hydrocarbon Conversions” (Academic Press, New York, 1981) p. 9.
J. D. Lopez-Gonzalez, A. Ramirez-Saenz, F. Rodriguez-Reinoso, C. Valenzuela-Calahorro andL. Zurita-Herrera,Clay Miner. 16 (1981) 103.
J. L. Bonilla, J. D. Lopez-Gonzalez, A. Ramirez-Saenz, F. Rodriguez-Reinoso andC. Valenzuela-Calahorro,ibid. 16 (1981) 173.
F. Rodriguez-Reinoso, A. Ramirez-Saenz, J. D. Lopez-Gonzalez, C. Valenzuela-Calahorro andL. Zurita-Herrera,ibid. 16 (1981) 315.
L. Gonzalez-Hernandez, L. Ibarra-Rueda, A. Rodriguez-Diaz andC. Chamorro-Anton,Angew. Makromol. Chem. 103 (1982) 51.
L. Gonzalez-Hernandez, L. Ibarra-Rueda, A. Rodriguez-Diaz, J. S. Moya andF. J. Valle,Clay Miner. 19 (1984) 93.
L. Gonzalez-Hernandez, L. Ibarra-Rueda, A. Rodriguez-Diaz andC. Chamorro-Anton,J. Colloid Interface Sci. 109 (1986) 150.
A. Corma, J. Perez-Pariente, V. Fornes andA. Mifsud,Clay Miner. 19 (1984) 673.
A. Corma andJ. Perez-Pariente,Clay Miner. 22 (1987) 423.
S. Brunauer, P. H. Emmett andE. Teller,J. Amer. Chem. Soc,60 (1938) 309.
E. P. Barret, L. G. Joyner andP. Halenda,ibid. 73 (1951) 373.
A. Lecloux andJ. Pirard,J. Colloid Interface Sci. 70 (1979) 265.
A. Preisinger,Clays Clay Miner. 10 (1963) 365.
S. Brunauer, L. S. Deming, W. S. Deming andE. Teller,J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 62 (1940) 1723.
A. V. Kiselev andY. I. Yashin, in “Gas Adsorption Chromatography” (Plenum, New York, 1969).
V. R. Choudhary andL. K. Doraiswamy,Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev. 10 (1971) 218.
A. K. Gosh andG. Curthoys,J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans I,79 (1983) 2569.
D. Bassett andH. W. Habgood,J. Phys. Chem. 64 (1960) 769.
D. Best andH. W. Wojciechowski,ibid. 47 (1977) 11.
A. N. Ko andH. W. Wojciechowski,Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 15 (1983) 1249.
A. Wheeler,Adv. Catal. 3 (1951) 250.
P. M. Viruela-Martin, I. Nebot, R. Viruela-Martin andJ. Planelles,J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans II (1986) 1053.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Campelo, J.M., Garcia, A., Luna, D. et al. New AlPO4-sepiolite systems as acid catalysts, I. Preparation, texture, surface-chemical properties and cyclohexene skeletal isomerization conversion. J Mater Sci 25, 2513–2519 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00638052
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00638052