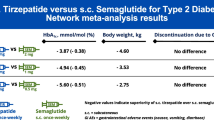
Summary
Pharmacokinetic data for diclofenac sodium has been well established in healthy volunteers, whereas in patients with rheumatoid arthritis very little information is available in the literature. A single oral dose of enteric-coated diclofenac sodium was given to 10 patients with active rheumatoid disease, adopting the same procedures used for a group of 10 healthy volunteers in whom pharmacokinetic data was already available. Plasma specimens were collected over a period of 8h following administration and concentrations of diclofenac determined by GLC. Resulting plasma concentration curves were similar to those obtained in the healthy subjects in that areas under curves and terminal half-lives were comparable. However, peak concentrations of diclofenac were significantly reduced in the rheumatoid patients. The lower peak concentrations were correlated with the lower serum albumin levels in the patients which are associated with active rheumatoid disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bayles TB (1962) Plasma salicylate levels in rheumatoid arthritis. In: Dixon A, Martin BK, Smith MJH, Wood PHN (eds) Salicylates, an international symposium. J & A Churchill, London, pp 43–46
Chalmers IM, Pohl JEF, Platt DS (1969) The evaluation in man of fenclozic acid (I.C.I. 54, 450: Myalex), a new anti-inflammatory agent. I. Serum concentration studies in healthy individuals and in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 28: 590–594
Champion GD, Graham GG (1978) Pharmacokinetics of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents. Aust NZ J Med 8: (Suppl 1) 94–100
Ciccolunghi SN, Chaudri HA, Schubiger BI, Reddrop R, (1978) Report on a long-term tolerability study of up to two years with diclofenac sodium (Voltaren). Scand J Rheumatol (Suppl 22) 86–96
Geiger UP, Degen PH, Sioufi A (1975) Quantitative assay of diclofenac in biological material by gas-liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr 111: 293–298
Kendall MJ, Thornhill DP, Willis JV (1979) Factors affecting the pharmacokinetics of diclofenac sodium. Rheumatol Rehabil (Suppl 2): 38–45
Ropes MW (1959) Diagnostic criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. 1958 Revision. Ann Rheum Dis 18: 49–51
Stierlin H, Faigle JW, Columbi A (1978) Pharmacokinetics of diclofenac sodium (Voltaren) and metabolites in patients with impaired renal function. Scand J Rheumatol (Suppl 22) 30–35
Wagner J, Sulc M (1979) Binding of diclofenac — Na (Voltaren) to serum proteins of different species and interactions with other drugs in protein binding. Aktuelle Rheumatol 4: 153
Willis JV, Kendall MJ (1978) Pharmacokinetic studies on diclofenac sodium in young and old volunteers. Scand J Rheumatol (Suppl 22): 36–41
Willis JV, Kendall MJ, Flinn RM, Thornhill DP, Welling PG (1979) The pharmacokinetics of oral and intravenous diclofenac sodium. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 16: 405–410
Willis JV, Kendall MJ, Jack DB (1980) A study of the effect of aspirin on the pharmacokinetics of oral and intravenous diclofenac sodium. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 18: 415–418
Willis JV, Kendall MJ, Jack DB (1981) The influence of food on the absorption of diclofenac after single and multiple oral doses. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 19: 33–37
Willis JV, Jack DB, Kendall MJ, John VA (1981) The influence of food on the absorption of diclofenac as determined by the urinary excretion of the unchanged drug and its major metabolites during chronic administration. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 19: 39–44
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Crook, P.R., Willis, J.V., Kendall, M.J. et al. The pharmacokinetics of diclofenac sodium in patients with active rheumatoid disease. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 21, 331–334 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00637622
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00637622