Abstract
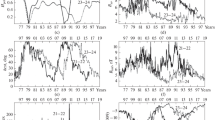
Monthly cosmic-ray data from Inuvik (0.16 GV) and Climax (2.96 GV) Neutron Monitor stations has been studied with the aid of solar activity parameters for the time period 1947–1995. Systematic differences in the overall shape of successive 11-year modulation cycles and similarities in the alternate 11-year cycles seem to be related to the polarity reversals of the polar magnetic field of the Sun. This suggests a possible effectiveness of the Hale cycle during even and odd solar activity cycles. Our results can be understood in terms of open and closed models of the heliosphere. Positive north pole of the Sun leads to open heliosphere where particles reach the Earth more easily when their access route is by the heliospheric oolar regions (even cycles) than when they gain access along the current sheet (odd cycles). In this case as the route of access becomes longer due to the waviness of the neutral sheet, the hysteresis effect of cosmic-rays is also longer. This interpretation is explained in terms of different contributions of convection, diffusion and drift mechanisms to the whole modulation process influencing cosmic-ray transport in the heliosphere.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahluwalia, H.S.: 1979,Proc. 19th ICRC (Paris)5, 182.
Ahluwalia, H.S.: 1995,Proc. 2nd SOLTIP Sym. 5, 247.
Babcock, H.W.: 1961,Astrophys. J. 133, 57.
Gnevyshev, M.N.: 1977,Sol. Phys. 51, 175.
Feminella, F. and Storini, M.: 1995,Proc. 9th Cambridge Workshop on Cool Stars, Stellar Systems and the Sun, (Florence).
Jokipii, J.R. and Thomas, B.: 1981,Astrophys. J. 243, 1115.
Marmatsouri, L., Vassilaki, A. and Mavromichalaki, H.: 1995,Adv. Space Res. 16, 245.
Mavromichalaki, H., Marmatsouri, E. and Vassilaki, A.: 1988,Earth, Moon and Planets 42, 233.
Nagashima, K. and Morishita, J.: 1980,Planet. Space Sci. 28, 195.
Otaola, J.R., Perez Enriquez, R. and Valdes-Galicia, J.F.: 1985, Proc. 19th ICRC (La Jolla)4, 93.
Smart, U.A. and Shea, D.F.: 1981, Adv. Space Res.1, 147.
Webber, W.R. and Lockwood, J.A.: 1988,J. Geophys. Res. 93, 8735.
Webber, W.R. and Lockwood, J.A.: 1993,J. Geophys. Res. 98, 21095.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mavromichalaki, H., Belehaki, A., Rafios, X. et al. Hale-cycle effects in cosmic-ray intensity during the last four cycles. Astrophys Space Sci 246, 7–14 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00637395
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00637395