Summary
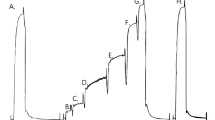
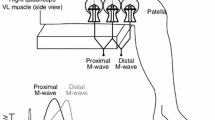
Contractile and histochemical properties of the triceps surae were compared in 16 males and 4 females aged 20 to 49 years. Surface electrical stimulation was used to determine twitch, tetanic and fatigue parameters. From these tests, twitch tension (Pt), time to peak tension (TPT), half relaxation time 1/2 RT), tetanic tensions at 10, 20 and 50 Hz and an index of fatigue (FI) were calculated. A maximal voluntary contraction (MVC) was also performed. Muscle samples from the belly of the lateral gastrocnemius were obtained using the needle biopsy technique. The samples were treated histochemically for myosin ATPase and NADH-tetrazolium reductase in order to classify the fibres as either Type I, slow twitch (ST) or Type II, fast twitch (FT) and to determine fibre areas. Correlations were performed between the grouped male and female contractile and histochemical variables. The results demonstrated significant positive relationships between percentage of ST fibres (%ST) and TPT (r=0.49), and %ST and the ratio of tetanic forces at 10 Hz to 50 Hz (Po10/Po50) (r=0.55). No significant relationships were obtained for Pt, 1/2 RT, MVC or FI with any histochemical parameter. The results suggest that fibre type distribution determined using myosin ATPase is related to electrically stimulated isometric contractile speeds and not to voluntary force generation (MVC) or electrically induced fatigue.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barany M (1967) ATPase activity of myosin correlated with speed of muscle shortening. J Gen Physiol 50:197–218
Bergstrom J (1962) Muscle electrolytes in man. Scand J Clin Lab Invest [Suppl] 68:11–13
Blomstrand E, Ekblom B (1982) The needle biopsy technique for fibre determination in human skeletal muscle — A methodological study. Acta Physiol Scand 116:437–442
Bosco C, Komi PV (1979) Mechanical characteristics and fibre composition of human leg extensor muscles. Eur J Appl Physiol 41:275–284
Brooke MH, Kaiser KK (1970) Three “myosin ATPase” systems: The nature of pH lability and sulfhydryl dependence. J Histochem Cytochem 18:670–672
Clarkson PM, Johnson J, Dextradeur D, Leszczynski W, Wai J, Melchionda A (1982) The relationships among isokinetic endurance, initial strength level and fibre type. Res Quart 53:15–19
Davies CTM, Mecrow IK, White MJ (1982) Contractile properties of the human triceps surae with some observations on the effects of temperature and exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 49:255–269
Eberstein A, Goodgold J (1968) Slow and fast twitch fibres in human skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol 215:535–541
Faulkner JA, Jones DA, Round JM, Edwards RHT (1980) Dynamics of energetic processes in human muscle. In: Cerretelli P, Whipp BJ (eds) Exercise bioenergetics and gas exchange. Elsevier/North-Holland Biomedical Press, pp 81–90
Froese EA, Houston ME (1985) Torque-velocity characteristics and muscle fibre type in human vastus lateralis. J Appl Physiol 59:309–314
Gatev V, Stefanova-Uzunova M, Stamatova L (1981) Influence of vertical posture development on the velocity properties of the triceps surae muscle in normal children. J Neurol Sci 52:85–90
Ivy JL, Withers RT, Brose G, Maxwell BD, Costill DL (1981) Isokinetic contractile properties of the quadriceps with relation to fibre type. Eur J Appl Physiol 47:247–255
Johnson MA, Polgar J, Weightman D, Appleton D (1973) Data on the distribution of fibre types in thirty-six human muscles: an autopsy study. J Neurol Sci 18:111–129
Kugelberg E, Thornell L (1983) Contraction time, histochemical type and terminal cisternae volume of rat motor units. Muscle Nerve 6:149–153
Larsson L, Gransberg L, Knutsson E (1985) Torgue-velocity relations in the quadriceps muscle of smoking — discordant twins with different fibre type proportions. Acta Physiol Scand 123:515–518
Lexell J, Taylor C, Sjostrom M (1985) Analysis of sampling errors in biopsy techniques using data from whole muscle cross sections. J Appl Physiol 59:1228–1235
Mahon M, Toman A, William PLT, Bagnall KM (1984) Variability of histochemical and morphometric data from needle biopsy specimens of human quadriceps femoris muscle. J Neurol Sci 63:85–100
Maughan RJ, Nimmo MA (1984) The influence of variations in muscle fibre composition on muscle strength and crosssectional area in untrained males. J Physiol 351:299–311
Maughan RJ, Nimmo MA, Harmon M (1985) The relationship between muscle myosin ATPase activity and isometric endurance in untrained male subjects. Eur J Appl Physiol 54:291–296
Moulds RFW, Young A, Jones DA, Edwards RHT (1977) A study of contractility, biochemistry and morphology of an isolated preparation of human skeletal muscle. Clin Sci Mol Med 52:291–297
Novikoff AB, Shin W, Drucker J (1961) Mitochondrial localization of oxidative enzymes: staining results with two tetrazolium salts. J Biophys Biochem Cytol 9:47–61
Nygaard E, Houston M, Zuzuki Y, Jorgensen K, Saltin B (1983) Morphology of the brachial biceps muscle and elbow flexion in man. Acta Physiol Scand 117:287–292
Padykula HA, Herman E (1967) The specificity of the histochemical method of adenosine triphosphatase. J Histochem Cytochem 3:170–195
Round JM, Jones DA, Chapman SJ, Edwards RHT, Ward PS, Fodden L (1984) The anatomy and fibre type composition of the human adductor pollicis in relation to its contractile properties. J Neurol Sci 66:263–292
Sale D, Quinlan J, Marsh E, McComas AJ, Belanger AY (1982) Influence of joint position on ankle plantarflexion in humans. J Appl Physiol 52:1636–1642
Saltin B, Gollnick PD (1983) Skeletal muscle adaptability. Peachy LD (ed) In: Handbook of physiology, Sect 10. American Physiological Society Bethesda MD, pp 555–631
Sandow A (1965) Excitation — contraction coupling in skeletal muscle. Pharmacol Rev 17:265–320
Schantz P, Randall-Fox E, Hutchinson W, Tyden A, Astrand PO (1983) Muscle fibre type distribution, muscle cross sectional area and maximal voluntary strength in humans. Acta Physiol Scand 117:219–226
Sjoholm H, Sahlin K, Edstrom L, Hultman E (1983) Quantitative estimation of anaerobic and oxidative energy metabolism and contraction characteristics in intact human skeletal muscle in response to electrical stimulation. Clin Physiol 3:227–239
Tesch P, Karlsson J (1978) Isometric strength performance and muscle fibre type distribution in man. Acta Physiol Scand 103:47–51
Tesch P, Karlsson J (1985) Muscle fibre types and sizes in trained and untrained muscles of elite athletes. J Appl Physiol 59:1716–1720
Tsunoda N, MacDougall D, Sale D, O'Hagan F, Garner S, Moroz J (1986) Structural and contractile properties of human elbow flexion muscles. C J Appl Sp Sci 11:46P
Vandervoort AA, McComas AJ (1983) A Comparison of the contractile properties of the human gastrocnemius and soleus muscles. Eur J Appl Physiol 51:435–440
Wiles CM, Young A, Jones DA, Edwards RHT (1979) Muscle relaxation rate, fibre type composition and energy turnover in hyper- and hypo thyroid patients. Clin Sci 57:375–384
Young A (1984) The relative isometric strength of type I and type II muscle fibres in the human quadriceps. Clin Physiol 4:23–32
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rice, C.L., Cunningham, D.A., Taylor, A.W. et al. Comparison of the histochemical and contractile properties of human triceps surae. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 58, 165–170 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00636621
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00636621