Summary
Biosprolol is a new beta1-selective beta-blocking agent with a plasma half-time of 10–12 h and without partial agonist properties.
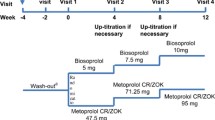
Forty-eight patients with essential hypertension were randomly treated with 5, 10, or 20 mg bisoprolol given once daily for 8 weeks. All measurements were made 24 hours after the last dose.
Bisoprolol had antihypertensive and beta-blocking properties both at rest and during exercise. The 20 mg dosage regimen was more effective than that of 5 mg and 10 mg.
The drug was well tolerated and all the 48 patients completed the trial.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frishman WH, Silverman R (1979) Clinical pharmacology of the new beta-adrenergic blocking drugs. 3. Comparative clinical experience and new therapeutic applications. Am Heart J 98: 119–131
A.M.A. Committee on hypertension (1973) Drug treatment of ambulatory patients with hypertension. J Am Med Assoc 225: 1647–1653
Caldwell JR, Cobb R, Dowling MD, Jough D (1979) The dropout problem in antihypertensive treatment. J Chronic Dis 22: 579–592
Rudd P, Beilstein B, Tul V, Howard J (1980) Once-daily regimen for propranolol anti-hypertensive therapy. Curr Ther Res 27: 29–39
Frithz G (1982) Once-a-day treatment of hypertension with pindolol. Am Heart J 104: 413–416
Franz IW, Lohmann FW (1979) The influence of a long-term cardioselective and non-cardioselective beta-receptor blockade on blood pressure, O2-uptake and carbohydrate metabolism. Z Kardiol 68: 503–509
Lager I, Blohmé G, Smith U (1979) Effect of cardioselective and non-selective beta-blockade on the hypoglycaémic response in insulin-dependent diabetics. Lancet 1: 458–462
Thiringer G, Svedmyr N (1976) Interaction of orally administered metoprolol, practolol and propranolol with isoprenaline in asthmatics. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 10: 163–170
Greefhorst APM, van Herwaarden CLA (1982) Ventilatory and haemodynamic effects of terbutaline infusion during beta1-selective blockade with metoprolol and acebutolol in asthmatic patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 23: 203–208
Manalan AS, Besch HR, Watanabe AM (1981) Characterization of3H (±) carazolol binding to beta-adrenergic receptors — application to study of beta-adrenergic subtypes in canine ventricular myocardium and lung. Circ Res 49: 326–336
Dorow P, Tönnesmann U (1984) Dose-response relationship of the beta-adrenoceptor antagonist bisoprolol in patients with coronary heart disease and chronic obstructive bronchitis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 27: 135–139
Leopold G, Pabst J, Ungethüm W, Bühring KU (1982) Phase I studies on EMD 33 512, a new beta1-selective adrenoceptor blocking agent. Clin Pharmacol Ther 31: 243–255
Åström H, Jonsson B (1976) Design of exercise test, with special reference to heart patients. Br Heart J 38: 289–296
Hypertension Detection and Follow-up Program Cooperative Group (1979) Five-year findings of the hypertension detection and follow-up program. I. Reduction in mortality of persons with high blood pressure, including mild hypertension. J Am Med Assoc 242: 2562–2577
Karch FE, Lasagna Z (1975) Adverse drug reactions. J Am Med Assoc 234: 1236–1241
Malahy B (1966) The effect of instruction and labelling on the number of medication errors made by patients at home. Am J Hosp Pharm 23: 283
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weiner, L., Frithz, G. Antihypertensive effects of bisoprolol during once daily administration in patients with essential hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 29, 517–521 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00635886
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00635886