Summary
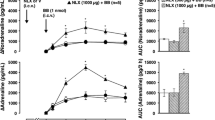
Effects of dynorphin-(1–13), Leu5-enkephalin,d-Ala2,d-Leu5-enkephalin (DADLE), and for comparison bremazocine, on plasma noradrenaline concentration and mean arterial pressure (MAP) were studied in pithed rabbits. In the first series of experiments, the sympathetic outflow was stimulated electrically via the pithing rod at 2 Hz twice for 3 min each (S1, S2). Drugs were administered before S2. Bremazocine 10 μg/kg+2μg/kg/h and 100 μg/kg+20 μg/kg/h, dynorphin 1 and 3 μg/kg/min, Leu5-enkephalin 100 μg/kg/min and DADLE 10 and 30 μg/kg/min all diminished the electrically-evoked increase in plasma noradrenaline and MAP. The effects were antagonized by naloxone. In the second series, an infusion of noradrenaline (2 μg/kg/min) was given twice for 3 min each (N1, N2). Drugs were administered before N2. Bremazocine 100 μg/kg+20 μg/kg/h slightly enhanced the pressor effect of exogenous noradrenaline, whereas dynorphin 3 μg/kg/min, Leu5-enkephalin 100 μg/kg/min and DADLE 30 μg/kg/min caused no significant change. In the third series, the sympathetic outflow was stimulated continuously at 2 Hz, and the interaction of dynorphin and DADLE was studied. Dynorphin 1 μg/kg/min and DADLE 10μg/kg/min initially decreased MAP to a similar extent. The effect of DADLE faded with time. When, during continuous infusion of DADLE 10 μg/kg/min, and after return of MAP to the pre-DADLE level, dynorphin 1 μg/kg/min or DADLE 10 μg/kg/min was infused additionally, the effect of dynorphin was unchanged, whereas that of DADLE was almost abolished. We conclude that the opioid peptides as well as bremazocine decrease action potential-evoked release of noradrenaline and, secondarily, blood pressure. They act at peripheral sites, presumably prejunctional opioid receptors at postganglionic sympathetic axons. Dynorphin on the one hand, and Leu5-enkephalin and DADLE on the other hand, appear to act at different receptors, dynorphin probably at a ϰ- and DADLE and Leu5-enkephalin at a δ-receptor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Corbett AD, Paterson SJ, McKnight AT, Magnan J, Kosterlitz HW (1982) Dynorphin1–8 and dynorphin1–9 are ligands for the ϰ-subtype of opiate receptor. Nature 299:79–81
Ensinger H, Hedler L, Schurr C, Starke K (1984) Ethylketocyclazocine decreases noradrenaline release and blood pressure in the rabbit at a peripheral opioid receptor. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 328:20–23
Ensinger H, Hedler L, Szabo B, Starke K (1986) Bremazocine causes sympatho-inhibition and hypotension in rabbits by activating peripheral ϰ-receptors. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol (in press)
Eulie PJ, Rhee HM (1984) Reduction by phentolamine of the hypotensive effect of methionine enkephalin in anaesthetized rabbits. Br J Pharmacol 83:783–790
Feuerstein G, Faden AI (1982) Differential cardiovascular effects of μ, δ and ϰ opiate agonists at discrete hypothalamic sites in the anesthetized rat. Life Sci 31:2197–2200
Fuder H, Rothacher G (1984) Etorphine inhibits3H-noradrenaline release from field-stimulated guinea-pig atria by activation of opioid receptors. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 325:R71
Gaddis RR, Dixon WR (1982) Modulation of peripheral adrenergic neurotransmission by methionine-enkephalin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 221:282–288
Gautret B, Schmitt H (1985) Central and peripheral sites for cardiovascular actions of dynorphin-(1–13) in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 111:263–266
Henderson G, Hughes J, Kosterlitz HW (1979) Modification of catecholamine release by narcotic analgesics and opioid peptides. In: Paton DM (ed) The release of catecholamines from adrenergic neurons. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 217–228
Illes P, Pfeiffer N, v. Kügelgen I, Starke K (1985a) Presynaptic opioid receptor subtypes in the rabbit ear artery. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 232:526–533
Illes P, Ramme D, Starke K (1985b) Inhibition of neuroeffector transmission in the rabbit mesenteric artery by [Met5]enkephalin. Eur J Pharmacol 107:397–398
James IF, Goldstein A (1984) Site-directed alkylation of multiple opioid receptors. I. Binding selectivity. Mol Pharmacol 25:337–342
Knoll J (1976) Neuronal peptide (enkephalin) receptors in the ear artery of the rabbit. Eur J Pharmacol 39:403–407
Konishi S, Tsunoo A, Otsuka M (1979) Enkephalins presynaptically inhibit cholinergic transmission in sympathetic ganglia. Nature 282:515–516
v. Kügelgen I, Illes P, Wolf D, Starke K (1985) Presynaptic inhibitory opioid δ- and ϰ-receptors in a branch of the rabbit ileocolic artery. Eur J Pharmacol (in press)
Laubie M, Schmitt H, Vincent M, Remond G (1977) Central cardiovascular effects of morphinomimetic peptides in dogs. Eur J Pharmacol 46:67–71
Laurent S, Schmitt H (1983) Central cardiovascular effects of ϰ agonists dynorphin-(1–13) and ethylketocyclazocine in the anaesthetized rat. Eur J Pharmacol 96:165–169
Ledda F, Mantelli L (1982) Possible presynaptic inhibitory effect of etorphine on sympathetic nerve terminals of guinea-pig heart. Eur J Pharmacol 85:247–250
Lundberg JM, Hökfelt T, Änggård A, Uvnäs-Wallensten K, Brimijoin S, Brodin E, Fahrenkrug J (1980) Peripheral peptide neurons: distribution, axonal transport, and some aspects on possible function. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol 22:25–36
Majewski H, Hedler L, Starke K (1982) The noradrenaline release rate in the anaesthetized rabbit: facilitation by adrenaline. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 321:20–27
Montel H, Starke K (1973) Effects of narcotic analgesics and their antagonists on the rabbit isolated heart and its adrenergic nerves. Br J Pharmacol 49:628–641
Ramme D, Illes P (1985) Presynaptic opioid receptors in rabbit mesenteric arteries. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 329:R76
Sander GE, Giles TD, Kastin AJ, Quiroz AC, Kaneish A, Coy DH (1981) Cardiopulmonary pharmacology of enkephalins in the conscious dog. Peptides 2:403–407
Schadt JC, Gaddis RR (1985) Endogenous opiate peptides may limit norepinephrine release during hemorrhage. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 232:656–660
Starke K (1977) Regulation of noradrenaline release by presynaptic receptor systems. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 77:1–124
Starke K, Schöffel E, Illes P (1985) The sympathetic axons innervating the sinus node of the rabbit possess presynaptic opioid ϰ- but not μ- or δ-receptors. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 329:206–209
Weihe E, McKnight AT, Corbett AD, Kosterlitz HW (1985) Proenkephalin- and prodynorphin-derived opioid peptides in guinea-pig heart. Neuropeptides 5:453–456
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Szabo, B., Hedler, L., Ensinger, H. et al. Opioid peptides decrease noradrenaline release and blood pressure in the rabbit at peripheral receptors. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 332, 50–56 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00633196
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00633196