Abstract
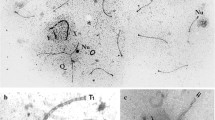
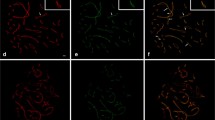
The development of meiotic prophase in pollen mother cells ofLilium longiflorum is presented through photomicrographs of squashes and sections and through electron micrographs of thick and thin sections. Emphasis is placed on the first appearance of axial cores, the participation of axial cores in the formation of synaptinemal complexes, the fine structure of the complex and the fate of the complex at the end of pachytene. It is shown that axial cores are formed in early meiotic prophase chromosomes and that the two axial cores of a set of homologous chromosomes participate in the formation of a synaptinemal complex. It is proposed that the transverse filaments of each axial core meet and interdigitate and so produce the transverse filaments of the complex. It is shown that the complex is axial to the pachytene bivalent and that the association of the complex with chromosomal material is terminated at the end of pachytene. The pairing affinity of the cores in homologous and non-homologous chromosome associations is discussed. The zygotene stage is defined in terms of the occurrence of synaptinemal complexes and the attachment of the nucleolus to the nuclear membrane during this stage is noted.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, T. G., andL. L. Franchi: The structure of the chromosomes in human primordial oocytes. Chromosoma (Berl.)22, 358–377 (1967).
Barker, K. R., andR. W. Riess: An electron microscope study of spermateleosis in the hemipteran (Oncopeltus fasciatus). Cellule66, 41–54 (1966).
Barry, E. G.: Abstract: Cytological considerations bearing on the time of crossing over inNeurospora. Genetics54, 321 (1966); - Chromosome aberrations inNeurospora, and the correlation of chromosomes and linkage groups. Genetics55, 21–32 (1967).
Callan, H. G.: The organization of genetic units in chromosomes. J. Cell Sci.2, 1–7 (1967).
Coleman, J. R., andM. J. Moses: DNA and the fine structure of synaptic chromosomes in the domestic rooster (Gallus domestieus). J. Cell Biol.23, 63–78 (1964).
Erickson, R. O.: Cytological and growth correlations in the flower bud and anther ofLilium longiflorum. Amer. J. Bot.35, 729–739 (1948).
Fawcett, D. W.: The fine structure of chromosomes in the meiotic prophase of vertebrate spermatocytes. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol.2, 403–406 (1956).
Ford, E. H., andD. H. M. Woollam: The fine structure of the sex vesicle and sex chromosome association in spermatocytes of mouse, golden hamster and field vole. J. Anat. (Lond.)100, 787–799 (1966).
Hastings, P. J., andH. L. K. Whitehouse: A polaror model of genetic recombination by the formation of hybrid DNA. Nature (Lond.)201, 1052–1054 (1964).
Koch, E. A., andR. C. King: The origin and early differentiation of the egg chamber ofDrosophila melanogaster. J. Morph.119, 283–304 (1966).
—,P. A. Smith, andR. C. King: The division and differentiation ofDrosophila cystocytes. J. Morph.121, 55–70 (1967).
Luft, J. H.: Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol.9, 409 (1961).
Maguire, M. P.: Evidence for homologous pairing of chromosomes prior to meiotic prophase in maize. Chromosoma (Berl.)21, 221–231 (1967).
Martin, J.: Meiosis in inversion heterozygotes inChironomidae. Canad. J. Genet. Cytol.9, 255–268 (1967).
McClintock, B.: The association of non-homologous parts of chromosomes in the mid-prophase of meiosis inZea mays. Z. Zellforsch.19, 191–237 (1933); - -Neurospora. I. Preliminary observations of the chromosomes ofNeurospora crassa. Genetics34, 493–507 (1945).
McLeish, J., andB. Snoad: Looking at chromosomes, 4th ed. New York: Macmillan & Co. 1966.
Menzel, M. Y., andJ. M. Price: fine structure of synapsed chromosomes in F1 Lycopersicon esculentum — Solanum lycopersicoides and its parents. Amer. J. Bot.53, 1079–1086 (1966).
Meyer, G. F.: The fine structure of spermatocyte nuclei ofDrosophila melanogaster. Proc. Europ. Reg. Conf. El. Microscopy2, 951–954 (1961); - A possible correlation between the submicroscopic structure of meiotic chromosomes and crossing over. Electron Microscopy 1964 (M. Titlbach, ed.), vol. B. 1964.
Millonig, G.: A modified procedure for lead staining of thin sections. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol.11, 736–739 (1961).
Moens, P. B.: A new interpretation of meiotic prophase inLycopersicon esculentum (tomato). Chromosoma (Berl.)15, 231–242 (1964).
Moses, M. J.: Chromosomal structures in crayfish spermatocytes. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol.2, 215–218 (1956);- The relation between the axial complex of meiotic prophase chromosomes and chromosome pairing in a salamander (Plethodon cinereus). J. biophys. biochem. Cytol.4, 633–638 (1958).
-, andJ. R. Coleman: Structural patterns and the functional organization chromosomes. In: The role of chromosomes in development (M. Locke, ed.), p. 11–49. 23rd Symp. Soc. Stud. Growth and Develop. 1964.
Nebel, B. R., andE. M. Coulon: The fine structure of chromosomes in pigeon spermatocytes. Chromosoma (Berl.)13, 272–291 (1962); - Enzyme effects on pachytene chromosomes of the male pigeon evaluated with the electron microscope. Chromosoma (Berl.)13, 292–299 (1962).
Roth, T. F.: Changes in the synaptinemal complex during meiotic prophase in mosquito oöcytes. Protoplasma (Wien)61, 346–386 (1966).
Schin, K. S.: Meiotische Prophase und Spermatidenreifung beiGryllus domesticus mit besonderer Berücksichtigung der Chromosomenstruktur. Z. Zellforsch.65, 481–513 (1965).
Singleton, J. R.: Chromosome morphology and the chromosome cycle in the ascus ofNeurospora crassa. Amer. J. Bot.40, 124–144 (1953).
Solari, A. J., andL. L. Tres: The ultrastructure of the human sex vesicle. Chromosoma (Berl.)22, 16–31 (1967).
Sotelo, J. R., andO. Trujillo-Cenoz: Submicroscopic structure of meiotic chromosomes. Exp. Cell Res.14, 1–8 (1958); - Electron microscope study on spermatogenesis (Chromosome morphogenesis at the onset of meiosis (Cyte I) and nuclear structure of early and late spermatids). Z. Zellforsch.51, 243–277 (1960).
—, andR. Wettstein: Electron microscope study on meiosis. The sex chromosome in spermatocytes, spermatids and oöcytes ofGryllus argentinus. Chromosoma (Berl.)15, 389–415 (1964).
Taylor, J. H., andR. D. McMaster: Autoradiographic and microphotometric studies of desoxyribose nucleic acid during microgametogenesis inLilium longiflorum. Chromosoma (Berl.)6, 489–521 (1954).
Westergaard, M., andD. von Wettstein: The meiotic cycle in an ascomycete. The effects of ionizing radiations on meiotic systems. Panel Proceedings Series, Int. Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna 1967.
Whitehouse, H. L. K.: A cycloid model for the chromosome. J. Cell Sci.2, 9–22 (1967).
—, andP. J. Hastings: The analysis of genetic recombination on the polaron hybrid DNA model. Genet Res.6, 27–92 (1965).
Wolstenholme, D. R., andG. F. Meyer: Some facts concerning the nature and formation of axial core structure in spermatids ofGryllus domesticus. Chromosoma (Berl.)18, 272–286 (1966).
Woollam, D. H. M., andE. H. K. Ford: The fine structure of the mammalian chromosome in meiotic prophase with special reference to the synaptinemal complex. J. Anat. (Lond.)98, 163–173 (1966).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moens, P.B. The structure and function of the synaptinemal complex inLilium longiflorum sporocytes. Chromosoma 23, 418–451 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00625287
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00625287