Summary
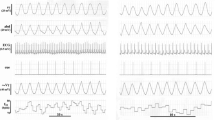
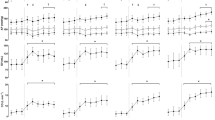
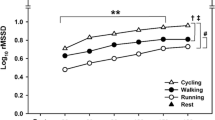
Significant increases in maximum oxygen consumption (\(\dot V{\text{O}}_{{\text{2max}}}\)) were noted in nine young track athletes following an 8-week high-intensity running period (P < 0.05).\(\dot V{\text{O}}_{{\text{2max}}}\) was measured, prior to and following the training program, using an on-line, open-circuit spirometry system. Parasympathetic activity was assessed using heart period variation (R-R interval in milliseconds) during carefully controlled breathing activity (R sinus arrhythmia). Following the training program, a 7.3% increase in aerobic capacity was associated with a 23.1% augmentation of efferent parasympathetic activity (P < 0.01). These data suggest that enhanced aerobic capacity increases efferent parasympathetic tone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barney JA, Ebert TJ, Groban L, Farrell PA, Hughes CV, Smith JJ (1988) Carotid baroreflex responsiveness in high-fit and sedentary young men. J Appl Physiol 65:2190–2194
Billman G, Schwartz P, Stone L (1984) The effects of exercise on susceptibility to sudden cardiac death. Circulation 64:1182–1187
Buchfuhrer MJ, Hansen JE, Robinson TE, Sue DY, Wasserman B, Whipp B (1983) Optimizing the exercise protocol for cardiopulmonary assessment. J Appl Physiol 55:1550–1564
De Meersman R, Faroudja N, Juris P, Higgins J, Gentile A (1990) Computerized noninvasive method for the measurement of parasympathetic activity. Comp Biol Med 20:74–94
De Schryver C, Herdt P, Lammerant J (1967) Effect of physical training on cardiac catecholamine concentrations. Nature 22:943–946
Eckberg DL (1983) Human sinus arrhythmia as an index of vagalcardiac outflow. J Appl Physiol 54:961–966
Ekblom B, Kilblom A, Soltysiak J (1973) Physical training, bradycardia and automatic nervous system. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 32:251–256
Fiocchi R, Fagard R, Vanhees L, Grauwels R, Amery A (1985) Carotid baroreflex sensitivity and physical fitness in cycling tourists. Eur J Appl Physiol 54:461–465
Fouad F, Tarazi R, Ferrario C, Fighaly S, Alicandri C (1984) Assessment of parasympathetic control of heart rate by noninvasive method. Am J Physiol 246:H838-H842
Katona PG, Mclean M, Doghton DH, Guz A (1982) Sympathetic and parasympathetic cardiac control in athletes and nonathletes at rest. J Appl Physiol 52:1652–1657
Kenney L (1985) Parasympathetic control of resting heart rate: relationship to aerobic power. Med Sci Sports Exerc 17:451–455
Lewis S, Nylander E, Gad P, Areskog NH (1980) Nonautonomic component in bradycardia of endurance trained men at rest and during exercise. Acta Physiol Scand 109:297–305
Maciel BC, Gallo L, Neto JA, Filho EC, Filho JT, Manco JC (1985) Parasympathetic contribution to bradycardia induced by endurance training in man. Cardiovasc Res 19:642–648
Mackay JD, Page M, Cambridge J, Watkins PJ (1980) Diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Diabetologia 18:471–478
Reiling MJ, Seals D (1988) Respiratory sinus arrhythmia and carotid baroreflex control of heart rate in endurance athletes and untrained controls. Clin Physiol 8:511–519
Smith ML, Hudson DL, Graitzer HM, Raven PB (1989) Exercise training bradycardia: the role of autonomic balance. Med Sci Sports Exerc 21:40–44
Tipton CM (1965) Training and bradycardia in rats. Am J Physiol 209:1089–1094
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Meersman, R.E. Respiratory sinus arrhythmia alteration following training in endurance athletes. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 64, 434–436 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00625063
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00625063