Abstract
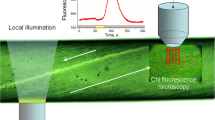
When prothalli ofAdiantum capillus-veneris L. were kept for 2 d in the dark, chloroplasts gathered along the anticlinal walls (Kagawa and Wada, 1994, J Plant Res 107: 389–398). In these dark-adapted prothallial cells, irradiation with a microbeam (10 gm in diameter) of red (R) or blue light (B) for 60 s moved the chloroplasts towards the irradiated locus during a subsequent dark period. Chloroplasts located less than 20 gm from the center of the R microbeam (18 J·m−2) moved towards the irradiated locus. The higher the fluence of the light, the greater the distance from which chloroplasts could be attracted. The B microbeam was less effective than the R microbeam. Chloroplasts started to move anytime up to 20 min after the R stimulus, but with the B microbeam the effect of the stimulus was usually apparent within 10 min after irradiation. The velocity of chloroplast migration was independent of light-fluence in both R and B and was about - 0.3 μm·min−1 between 15 min and 30 min after irradiation. Whole-cell irradiation with far-red light immediately after R- and B-microbeam irradiations demonstrated that these responses were mediated by phytochrome and a blue-light-absorbing pigment, respectively. Sequential treatment with R and B microbeams, whose fluence rates were less than the threshold values when applied separately, resulted in an additive effect and induced chloroplast movement, strongly suggesting that signals from phytochrome and the blue-light-absorbing pigment could interact at some point before the induction of chloroplast movement.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- B:
-
blue light
- FR:
-
far-red light
- IR:
-
infrared light
- R:
-
red light
References
Bowler C, Neuhaus G, Yamagata H, Chua N-H (1994) Cyclic GMP and calcium mediate phytochrome phototransduction. Cell 77: 73–81
Gabryś H, Walczak T, Zurzycki J (1981) Chloroplast translocations induced by light pulses. Planta 152: 533–556
Haupt W (1959) Die Chloroplastendrehung beiMougeotia: I. Über den quantitativen und qualitativen Lichtbedarf der Schwachlitbewegung. Planta 53: 484–501
Haupt W (1982) Light-mediated movement of chloroplasts. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 33: 205–233
Haupt W, Mider D-P (1994) Photomovement. In: Kendrick RE, Kronenberg GHM (eds) Photomorphogenesis in plants (2nd edn). Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht Boston London, pp 707–732
Haupt W, Schönfeld I (1963) Die Wirkung von kurzwelliger Strahlung auf die Schwachlichtvewegung desMougeotia-Chloroplasten. Z Bot 51: 17–31
Haupt W, Mörtel G, Winkelnkemper I (1969) Demonstration of different dichroic orientation of phytochrome Pr and Pfr. Planta 88: 183–186
Izutani Y, Takagi S, Nagai R (1990) Orientation movements of chloroplasts inVallisneria epidermal cells: different effects of light at lowand high-fluence rate. Photochem Photobiol 51: 105–111
Kadota A, Wada M (1992) Photoorientation of chloroplasts in protonemal cells of the fern Adiantum as analyzed by use of a videotracking system. Bot Mag Tokyo 105: 265–279
Kagawa T, Wada M (1993) Light-dependent nuclear migration in prothallial cells ofAdiantum capillus-veneris L. Protoplasma 177: 82–85
Kagawa T, Wada M (1994) Brief irradiation with red or blue light induces orientational movement of chloroplasts in dark-adapted prothallial cells of the fernAdiantum. J Plant Res 107: 389–398
Kagawa T, Kadota A, Wada M (1994) Phytochrome-mediated photoorientation of chloroplasts in protonemal cells of the fernAdiantum can be induced by brief irradiation with red light. Plant Cell Physiol 37: 371–377
Kraml M, Büttner G, Haupt W, Herrmann H (1988) Chloroplast orientation inMesotaenium: the phytochrome effect is strongly potentiated by interaction with blue light. Protoplasma Suppl 1: 172–179
Shacklock PS, Read ND, Trewavas AJ (1992) Cytosolic free calcium mediates red light-induced photomorphogenesis. Nature 358: 753–755
Shimmen T (1988) Characean actin bundles as a tool for studying actomyosin based motility. Bot Mag Tokyo 101: 533–544
Tlalka M, Gabryś H (1993) Influence of calcium on blue-light-induced chloroplast movement inLemna trisulca L. Planta 189: 491–198
Wada M, Furuya M (1970) Photocontrol of the orientation of cell division inAdiantum. I. Effects of the dark and red periods in the apical cell of gametophytes. Dev Growth Diff 12: 109–118
Wagner G, Klein K (1978) Differential effect of calcium on chloroplast movement inMougeotia. Photochem Photobiol 27: 137–140
Wagner G, Haupt W, Laux A (1972) Reversible inhibition of chloroplast movement by cytochalasin B in the green algaMougeotia. Science 176:808–809
White PR (1963) The cultivation of animal and plant cells 2nd edn. Ronald Press, New York.
Yatsuhashi H, Wada M (1990) High-fluence rate responses in the lightoriented chloroplast movement inAdiantum protonemata. Plant Sci 68: 87–94
Yatsuhashi H, Kadota A, Wada M (1985) Blue- and red-light action in photoorientation of chloroplasts inAdiantum protonemata. Planta 165: 43–50
Zurzycki J (1967a) Properties and localization of the photoreceptor active in displacements of chloroplasts inFunaria hygrometrica. I. Action spectrum. Acta Soc Bot Pol 36: 133–142
Zurzycki J (1967b) Properties and localization of the photoreceptor active in displacements of chloroplasts inFunaria hygrometrica. II. Studies with polarized light. Acta Soc Bot Pol 36: 143–152
Zurzycki J (1980) Blue light-induced intracellular movements. In: Senger H (ed) The blue light syndrome. Springer-Verlag Berlin, pp. 50–68
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kagawa, T., Wada, M. Phytochrome- and blue-light-absorbing pigment-mediated directional movement of chloroplasts in dark-adapted prothallial cells of fernAdiantum as analyzed by microbeam irradiation. Planta 198, 488–493 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00620067
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00620067