Summary
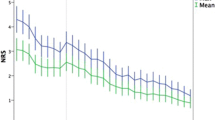
A double-blind randomized trial was carried out in 90 male patients suffering from pain after meniscectomy. The patients received a single dose of paracetamol 1 000 mg plus codeine 60 mg, paracetamol 1 000 mg, codeine 60 mg, or placebo. The tablets were taken when needed after surgery and the postoperative pain was recorded on a visual analogue scale. Over a period of 4 h the efficacy of the drugs was calculated in terms of pain intensity, pain intensity difference and percentage pain reduction. The greatest effect was obtained in patients taking the paracetamol plus codeine combination. Statistical analysis was carried out by use both of parametric and non-parametric procedures. The results suggest that pain reduction is a valuable measurement of analgesic efficacy and that non-parametric assumptions are preferable in the statistical analysis of analgesic activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huskisson EC (1974) Measurement of pain. Lancet 2: 1127–1131
Kremer E, Atkinson JH, Ignelzi RJ (1981) Measurement of pain: Pain preference does not confund pain measurement. Pain 10: 241–248
Scott J, Huskisson EC (1976) Graphic representation of pain. Pain 2: 175–184
Ohnhaus EE, Adler R (1975) Methodological problems in the measurement of pain: A comparison between the verbal rating scale and the visual analogue scale. Pain 1: 379–384
Revill SI, Robinson JO, Rosen M, Hogg MIJ (1976) The reliability of a linear analogue for evaluating pain. Anaesthesia 31: 1191–1198
Maxwell C (1978) Sensitivity and accuracy of the visual analogue scale: a psychophysical classroom experiment. Br J Clin Pharmacol 6: 15–24
Welch BL (1947) The generalization of student's problem when several different population variances are involved. Biometrika 34: 28
Carmer SG, Swanson MR (1973) An evaluation of ten pair-wise multiple comparison procedures by monte carlo methods. J Am Stat Assoc 68: 66–74
Eddy NB, Friebel H, Hahn K-J, Halbach H (1970) Codeine and its alternatives for pain and cough relief. World Health Organisation, Geneva, p 26
Quiding H, Oksala E, Happonen R-P, Lehtimäki K, Ojala T (1981) The visual analogue scale in multiple dose evaluations of analgesics. J Clin Pharmacol 21: 424–429
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quiding, H., Häggquist, S.O. Visual analogue scale and the analysis of analgesic action. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 24, 475–478 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00609889
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00609889