Summary
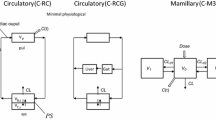
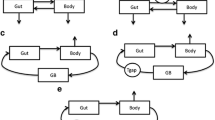
Assessment of pharmacokinetics in terms of circulatory drug transport is proposed using the methods of linear system theory. In this model-independent approach drug distribution and disposition are characterized by the total extraction ratio, the mean residence time in the body and the volume of distribution at steady state. In analyzing concentration(c)-time(t) data, the procedure requires calculation only of the areas under the c(t)-and c(t)×t-curves to estimate kinetic parameters, and for prediction of the steady state concentration following continuous infusion or multiple doses. Pulmonary clearance of drugs is included in the theory.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bassingthwaighte, J. B.: Blood flow and diffusion through mammalian organs. Science167, 1347 (1970)
Benowitz, N. L., Meister, W.: Pharmacokinetics in patients with cardiac failure. Clin. Pharmacokinet.1, 389 (1976)
Benowitz, N. L., Forsyth, R. P., Melmon, K., Rowland, M.: Lidocaine disposition kinetics in monkey and man. I. Prediction by a perfusion model. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.16, 87 (1974)
Chen, C. N., Coleman, D. L., Andrade, J. D., Temple, A. R.: Pharmacokinetic model for salicylate in cerebrospinal fluid, blood, organs and tissues. J. Pharm. Sci.67, 38 (1978)
Dedrick, R. L.: Animal scale-up. In: Pharmacology and pharmacokinetics. Teorell, T., Dedrick, R. L., and Condliffe, P. G. (eds.) pp. 117–145. New York: Plenum Press, 1974
Dienes, J. K.: The mathematics of recirculation and the measurement of cardiac output. Math. Biosci.32, 141 (1976)
Gillette, J. R., Pang, K. S.: Theoretic aspects of pharmacokinetic drug interactions. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.22, 623 (1977)
Harrison, L. I., Gibaldi, M.: Physiologically based pharmacokinetic model for digoxin disposition in dogs and its preliminary application to humans. J. Pharm. Sci.66, 1679 (1977)
Homer, L. D., Small, A.: A unified theory for estimation of cardiac output, volumes of distribution and renal clearances from indicator dilution curves. J. Theor. Biol.64, 535 (1977)
Rescigno, A., Segre, G.: Drug and Tracer Kinetics. Waltham: Blaisdell 1966
Roberts, G. W., Larson, K. B., Spaeth, E. E.: The interpretation of mean transit time measurements for multiphase tissue systems. J. Theor. Biol.39, 447 (1973)
Segre, G.: Mathematical models in the study of drug kinetics. In: Mathematical Models in Medicine. Lecture Notes in Biomathematics. Berger, J., Bühler, W. (eds.), Vol. 11, pp. 204–225. Berlin - Heidelberg - New York: Springer 1976
Sziegoleit, W., Weiss, M., Pönicke, K., Förster, W.: Pharmakokinetische Kenngrößen von N,N′-Bis-[3-(2′-äthoxyphenoxy-2-hydroxypropyl-äthylendiamin (FalirytminR) bei Gesunden. Dtsch. Gesundheitswes.31, 331 (1976)
Wagner, J. G.: Fundamentals of Clinical Pharmacokinetics. Hamilton: Drug Intelligence Publ. 1975
Wagner, J. G.: Linear pharmacokinetic equations allowing direct calculation of many needed pharmacokinetic parameters from the coefficients and exponents of polyexponential equations which have been fitted to the data. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm.4, 443 (1976)
Weiss, M., Förster, W.: Pharmacokinetics of prostaglandins: Prediction of steady state concentrations during intravenous infusion. Int. J. clin. Pharmacol., in press
Wilkinson, G. R.: Pharmacokinetics of drug disposition: Hemodynamic considerations. Ann. Rev. Pharmacol.15, 11 (1975)
Yeh, K. C., Kwan, K. C.: A comparison of numerical integration algorithms by trapezoidal, lagrange, and spline approximation. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm.6, 79 (1978)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weiss, M., Förster, W. Pharmacokinetic model based on circulatory transport. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 16, 287–293 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00608408
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00608408