Summary
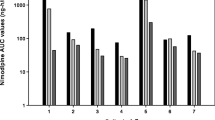
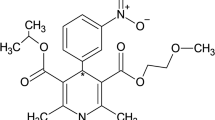
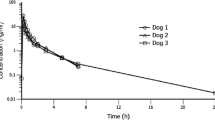
Patients with a ruptured supratentorial aneurysm undergoing early surgery after the subarachnoid haemorrhage were treated postoperatively with nimodipine to prevent delayed ischaemic dysfunction. It was given first as a continuous intravenous infusion 2 mg/h (mean dose 0.5 µg/kg/min) for at least 7 days, and then orally (45 mg × 6) for at least a further 7 days. During the i.v. infusion, the mean plasma concentration was 26.6±1.8 ng/ml. The plasma clearance ranged from 0.57 to 1.77 l/kg/h and was negatively correlated with the age of the patient. Immediately prior to successive oral doses, the mean plasma concentration was 13.2 ng/ml (range<3–38.8 ng/ml). The peak level was usually found after 1 h; it ranged from 7.0–96.0 ng/ml. Mean bioavailability was 15.9%. The nitropyridine metabolite was found in measurable concentrations only after oral treatment with nimodipine. In some cases, the concentration of metabolite exceeded that of the parent compound. The three patients investigated who developed delayed ischaemic dysfunction had plasma concentrations well within the range in patients who did not, so it seems unlikely that the therapeutic failure could be attributed to individual deviations in the pharmacokinetics of the drug.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fisher CM, Kistler JP, Davis JM (1980) Relation of cerebral vasopasm to subarachnoid hemorrhage visualized by computerized tomographic scanning. Neurosurgery 6: 1–9
Brandt L, Andersson KE, Bengtsson B, Edvinsson L, Ljunggren B, MacKenzie ET (1979) Effects of nifedipine on pial arteriolar calibre: An in vivo study. Surg Neurol 12: 349–352
Kazda S, Towart R (1982) Nimodipine: A new calcium antagonistic drug with a preferential cerebrovascular action. Acta Neurochirurgica 63: 259–265
Allen GS, Ahn HS, Preziose TJ, Battje R, Boone SC, Chou SN, Kelly DL, Weir BK, Crabbe RA, Lavik PJ, Rosenbloom SB, Dorsey FC, Ingram CR, Mellits DE, Bertsch LA, Boisvert DPJ, Hundley MB, Johnson RK, Strom JA, Transou CR (1983) Cerebral arterial spasm — a controlled trial of nimodipine in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. N Engl J Med 308: 619–624
Auer LM (1984) Acute operation and preventive nimodipine improve outcome in patients with ruptured cerebral aneurysms. Neurosurgery 15: 57–66
Ljunggren B, Brandt L, Säveland H, Nilsson PE, Cronqvist S, Andersson KE, Vinge E (1984) Outcome in 60 consecutive patients treated with early aneurysm operation and intravenous nimodipine. J Neurosurg 61: 864–873
Bach PR, and the Clinical Investigation of Duchenne Dystrophy Group (1983) Determination of nifedipine in serum or plasma by reversed-phase liquid chromatography. Clin Chem 29: 1344–1348
Krol GJ, Noe AJ, Yeh SC, Rämsch KD (1984) Gas and liquid chromatographic analyses of nimodipine calcium antagonist in blood plasma and cerebrospinal fluid. J Chromatogr 305: 105–118
Rämsch KD, Ahr G, Tettenborn D, Auer LM (1985) Overview on pharmacokinetics of nimodipine in healthy volunteers and in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurochirurgia 28 [Suppl 1]: 74–78
Kirch W, Rämsch KD, Dührsen U, Ohnhaus EE (1984) Clinical pharmacokinetics of nimodipine in normal and impaired renal function. Int J Clin Pharm Res 4: 381–384
Towart R, Wehinger E, Meyer H, Kazda S (1982) The effects of nimodipine, its optical isomers and metabolites on isolated vascular smooth muscle. Arzneimittelforsch/Drug Res 32: 338–346
Ljunggren B, Säveland H, Brandt L (1983) Causes of unfavorable outcome after early aneurysm operation. Neurosurgery 13: 629–633
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vinge, E., Andersson, K.E., Brandt, L. et al. Pharmacokinetics of nimodipine in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 30, 421–425 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00607954
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00607954