Summary
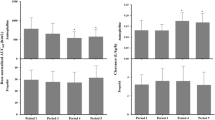
The effect of pentobarbital treatment in a mean dose of 30 mg/kg/day on the clearance of hexobarbital (Evipan) and dipyrone (Novalgin) has been evaluated in critical care patients receiving a large number of drugs as comedication. Eleven patients treated with pentobarbital showed a hexobarbital half-life of 2.79 h and a total plasma clearance of 9.80 ml·min−1·kg−1 as compared to 10 patients without pentobarbital administration in whom there was a significantly longer half life (6.92 h) and lower clearance (2.97 ml·min−1·kg−1). The kinetics of hexobarbital were correlated with the urinary excretion of D-glucaric acid, a non-invasive parameter of drug metabolising activity. In 10 patients on pentobarbital, the total plasma clearance of N-4-methylaminoantipyrine, the active form of dipyrone, did not differ from that in 8 patients not receiving pentobarbital. As drug kinetics show great variability in these patients, it is difficult to discriminate enzyme induction from other mechanisms, for example competitive inhibition or changes in volume of distribution. In the presence of pentobarbital, however, induction of drug metabolising enzymes should be considered as a possible reason for the higher clearance of hexobarbital.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bast A, Noordhoek J (1980) Inhibition of aminopyrine demethylation and binding to cytochrome P-450 by its main metabolites in rat liver microsomes. Br J Pharmacol 68: 121P-122P
Berman ML, Green OC (1971) Acute stimulation of cortisol metabolism by pentobarbital in man. Anesthesiology 34: 365–369
Breimer DD, Zilly W, Richter E (1975) Pharmacokinetics hexobarbital in acute hepatitis and after apparent recovery. Clin Pharmacol Ther 18: 433–440
Breimer DD, Honhoff C, Zilly W, Richter E, van Rossum JM (1975) Pharmacokinetics of hexobarbital in plasma of man after intravenous infusion. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 3: 1–11
Campos AR, Herraez FXV, Marcos RJ, Amer JG, Porcar RC, Lucia PI (1980) Drug use in an intensive care unit and its relation to survival. Intens Care Med 6: 163–168
Collste P, Seideman P, Borg K-O, Haglund K, von Bahr C (1979) Influence of pentobarbital on effect and plasma levels of alprenolol and 4-hydroxy-alprenolol. Clin Pharmacol Ther 25: 423–427
Heinemeyer G, Nigam S, Hildebrandt AG (1980) Hexobarbital binding, hydroxylation and hexobarbital dependent hydrogen peroxide production in hepatic microsomes from guinea pig, rat and rabbit. Arch Pharmacol 314: 201–210
Heinemeyer G, Roots I, Lestau P, Klaiber H-R, Dennhardt R (1986) D-glucaric acid excretion in critical care patients — comparison with 6β-hydroxycortisol excretion and serum γ-glutamyltranspeptidase activity and relation to multiple drug therapy. Br J Clin Pharmacol 21: 9–18
Heinemeyer G, Roots I, Dennhardt R (1986) Monitoring of pentobarbital plasma levels in critical care patients with increased intracranial pressure. Ther Drug Monit 8: 145–150
Hildebrandt AG, Roots I, Speck M, Saalfrank K, Kewitz H (1975) Evaluation of in vivo parameters of drug metabolizing enzyme activity in man after administration of clemastine, phenobarbital or placebo. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 8: 327–336
Marshall LF, Smith RW, Shapiro HM (1979) The outcome with aggressive treatment in severe head injuries. Part II: Acute and chronic barbiturate administration in the management of head injury. J Neurosurg 50: 26–30
Remmer H (1959) Die Beschleunigung der Evipanoxydation und der Demethylierung von Methylaminoantipyrin durch Barbiturate. Arch Exp Path Pharmakol 237: 296–307
Remmer H, Fleischmann RA, Kunz W (1979) Pharmacological consequences of induction of drug metabolizing enzymes. In: Estabrook RW, Lindenlaub E (eds) The induction of drug metabolism. Schattauer, Stuttgart New York, pp 555–581
Rietbrock I, Lazarus G, Richter E, Breimer DD (1981) Hexobarbitone disposition at different stages of intensive care treatment. Br J Anaesth 53: 283–293
Roots I, Holbe R, Ick AM, Heinemeyer G, Palme G, Hildebrandt AG (1978) Application of in vivo parameters of drug metabolizing enzyme activity in patients with liver cirrhosis. Boissier R (ed) 7th Internat Congr Pharmacol, Paris, Abstr. No. 2895. Pergamon Press, Oxford
Roots I, Holbe R, Hövermann W, Nigam S, Heinemeyer G, Hildebrandt AG (1979) Quantitative determination by HPLC of urinary 6β-hydroxycortisol, an indicator of enzyme induction by rifampicin and antiepileptic drugs. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 16: 63–71
Volz M, Kellner HM (1980) Kinetics and metabolism of pyrazolones (propyphenazone, aminopyrine and dipyrone). Br J Clin Pharmacol 10: 299S-308S
Zilly W, Breimer DD, Richter E (1978) Hexobarbital disposition in compensated and decompensated cirrhosis of the liver. Clin Pharmacol Ther 23: 525–534
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heinemeyer, G., Gramm, H.J., Simgen, W. et al. Kinetics of hexobarbital and dipyrone in critical care patients receiving high-dose pentobarbital. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 32, 273–277 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00607575
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00607575