Summary
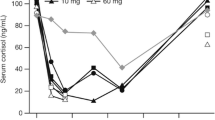
The pharmacokinetics of prednisolone have been studied in asthmatic patients following intravenous injection at three different doses and in normal volunteers at five oral doses. Plasma prednisolone concentrations were measured by radioimmunoassay. With increasing dose there is an increase in the apparent volume of distribution, plasma clearance and half life. The relationship between area under the plasma concentration time curve, maximum concentration and dose is linear but the regression lines do not pass through the origin. These findings following oral and intravenous administration confirm that prednisolone shows non-linear kinetics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chakraborty J, English J, Marks V, Dumasia MC, Chapman DJ (1976) A radioimmunoassay method for prednisolone. Comparison with competitive protein binding method. Br J Clin Pharmacol 3: 903–906
Feldman H, Robard D (1971) Mathematical theory of radioimmunoassay. In: Odell WD, Daughaday WH (eds) Principle of competitive protein-binding assays. JB Lippincott, Philadelphia PA, pp 158–199
Gibaldi M, Perrier D (1975) Pharmacokinetics. Marcel Dekker, New York
Green OC, Winter RJ, Kawahara FS, Philips LS, Lewy PR, Hart RL, Pachman LM (1978) Pharmacokinetic studies of prednisolone in children. J Paediat 93, 2: 299–303
Henderson RG, Wheatley T, English J, Chakraborty J, Marks V (1979) Variation in plasma prednisolone concentrations in renal transplant recipients given enteric coated prednisolone. Br Med J 1: 1534–1536
Kendall MG, Stuart A (1966) The advanced theory of statistics Vol 3: Design and analysis. Griffin, London, pp 44–45
Loo JCK, McGilveray IJ, Jordan N, Moffat J, Brien R (1978) Dose-dependent pharmacokinetics of prednisone and prednisolone in man. J Pharm Pharmacol 30: 736
Pickup ME, Lowe JR, Leatham PA, Rhind VM, Wright V, Downie WW (1977) Dose dependent pharmacokinetics of prednisolone. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 12: 213–219
Rocci LM, Johnson NF, Jusko WJ (1980) Serum protein binding of prednisolone in four species. J Pharm Sci 69: 977–978
Rose JQ, Yurachak AM, Jusko JW (1978) Dose dependent pharmacokinetics of prednisolone in man. Seventh International Congress of Pharmacology. Abstracts, Paris, p 400
Rose J, Jusko WJ, Nickelsen JA (1979) Prednisolone pharmacokinetics in relation to dose. J Paediat 94: 1014–1015
Tanner A, Bochner F, Caffin J, Halliday J, Powell L (1979) Dose dependent prednisolone kinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther 25: 571–578
Uribe M, Schalm S, Summerskill W, Go V (1978) Oral prednisolone for chronic active liver disease: Dose response and bioavailability studies Gut 19: 1131–1135
Wagner JG (1974) A modern view of pharmacokinetics. Teorell T, Dedrick RL, Condliffe PG (eds) Pharmacology and pharmacokinetics. Plenum Press, London, pp 27–67
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McAllister, W.A.C., Winfield, C.R. & Collins, J.V. Pharmacokinetics of prednisolone in normal and asthmatic subjects in relation to dose. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 20, 141–145 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00607151
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00607151