Summary
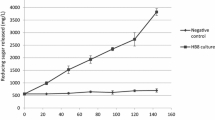
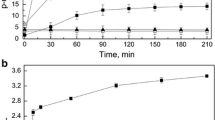
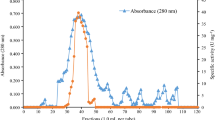
The production of amylolytic enzymes by a thermophilic cellulolytic fungus,Myceliophthora thermophila D14 was investigated by batch cultivation in Czapek-Dox medium at 45° C. Among various nitrogenous compounds used, NaNO3 and KNO3 were found to be the best for amylase production. Starch, cellobiose and maltose induced the synthesis of amylase while glucose, fructose, galactose, lactose, arabinose, xylose, sorbitol, mesoinositol and sucrose did not. Calcium ions had the most stimulating effect on enzyme formation amongst many ions investigated. The synthesis of amylolytic enzymes was dependent on growth and occurred predominantly in the mid-stationary phase. The enzyme was active in a broad temperature range (50° C–60° C) and displayed activity optima at 60° C and pH 5.6.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aunstrup K (1977) Production of industrial enzymes. FEMS/Symp 4:157–171
Bernfeld P (1955) Amylases, alpha and beta. Methods Enzymol 1:149–150
Clementi F, Rossi J, Costamagna L, Rossi J (1980) Production of amylase(s) bySchwanniomyces castelli andEndomycopsis filbuligera. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek J Microbiol 46:399–405
Davis BJ (1964) Disc electrophoresis II. Ann N Y Acad Sci 121:404–427
Fogarty WM (1983) Microbial enzymes and biotechnology. Applied Science Publishers, London, pp 1–77
Fogarty WM, Kelly CT (1980a) Amylases, amyloglucosidases and related glucanases. In Rose AH (ed) Economic microbiology —microbial enzymes and bioconversions vol 5. Academic Press, New York, pp 115–170
Fogarty WM, Kelly CT (1980b) Amylases, amyloglucosidases of microbial origin. Prog Ind Microbiol 15:87–150
Hyun HH, Zeikus JG (1985) Regulation and genetic enhancement of glucoamylase and pullulanase production inClostridium thermohydrosulfuricum. J Bacteriol 164:1146–1152
Ingle MB, Boyer EW (1976) Microbiology (Schlessinger D). American Society of Microbiology, Washington, DC, p 420
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Norman B (1979) In: Berkeley RCW, Gooday GW, Ellwood DC (eds) Microbial polysaccharides and polysaccharases. Academic Press, London, p 339
Palmer TJ (1975) Glucose sirups in food and drink. Process biochem 10:19–20
Roy SK, Raha SK, Dey SK, Chakrabarty SL (1988) Induction and catabolite repression of β-glucosidase synthesis inMyceliophthora thermophila D14 (=ATCC 48 104). Appl Environ Microbiol 54:2152–2153
Roy SK, Raha SK, Dey SK, Chakrabarty SL (1989) Immobilization of β-glucosidase fromMyceliophthora thermophila D14. Enzyme Microb Technol 11:431–435
Ruttloff HA, Taefel A, Zickler F (1979) Glucoamylase aus Endomycopsis bispora. I. Zur Produktion des Enzymes in Schüttelkultur. Z Alg Mikrobiol 19:195–201
Saito N (1973) A thermophilic extracellular β-amylase fromBacillus licheniformis. Arch Biochem Biophys 155:290–298
Sen S, Abraham TK, Chakrabarty SL (1981) Cellulase activity ofMyceliophthora thermophila D14. Curr Sci 50:598–600
Sen S, Abraham TK, Chakrabarty SL (1982) Characteristics of cellulase produced byM. thermophila D14. Can J Microbiol 28:271–277
Sen S, Abraham TK, Chakrabarty SL (1983) Induction of cellulase inMyceliophthora thermophila D14. Can J Microbiol 29:1258–1260
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sadhukhan, R.K., Manna, S., Roy, S.K. et al. Thermostable amylolytic enzymes from a cellulolytic fungusMyceliophthora thermophila D14 (ATCC 48 104). Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 33, 692–696 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00604940
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00604940