Summary
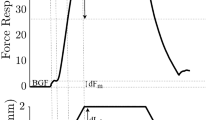
The effects of stretching the triceps surae muscle on the resting discharge of functionally isolated and identified γ-efferents in the medial gastrocnemius nerve were studied in intercollicular decerebrate cats. Extension of the muscle decreases the activity of 9 out of 25 γ-motoneurones. This inhibition becomes apparent at about 8 mm muscle length and increases with increasing extension. Only those γ-efferents exhibiting this length-dependent inhibition are found to be inhibited by repetitive antidromic stimulation of the ventral root or the homonymous muscle nerve. We suggest that inhibition of fusimotor neurones by muscle stretch is at least partly mediated by the recurrent collaterals of the α-motoneurones activated by the stretch. 11 γ-motoneurones were predominantly excited by muscle stretch applied to the detached Achilles tendon as well as by squeezing the tendon. Nociceptors within the tendon or surrounding fascia are probably responsible.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown, M. C., Lawrence, D. G., Matthews, P. B. C.: Antidromic inhibition of presumed fusimotor neurones by repetitive stimulation of the ventral root in the decerebrate cat. Experientia (Basel)24, 1210–1211 (1968a)
Brown, M. C., Lawrence, D. G., Matthews, P. B. C.: Reflex inhibition by Ia afferent input of spontaneously discharging motoneurones in the decerebrate cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.)198, 5–7P (1968b)
Diete-Spiff, K., Pascoe, J. E.: The spindle motor nerves to the gastrocnemius muscle of the rabbit. J. Physiol. (Lond.)149, 120–134 (1959)
Eccles, J. C., Eccles, R. M., Iggo, A., Lundberg, A.: Electrophysiological studies on gamma motoneurones. Acta physiol. scand.50, 32–40 (1960)
Eldred, E., Granit, R., Merton, P. A.: Supraspinal control of the muscle spindles and its significance. J. Physiol. (Lond.)122, 498–523 (1953)
Ellaway, P. H.: Antidromic inhibition of fusimotor neurones. J. Physiol. (Lond.)198, 39–40 P (1968)
Ellaway, P. H.: Recurrent inhibition of fusimotor neurones exhibiting background discharges in the decerebrate and the spinal cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.)216, 419–439 (1971)
Fromm, Chr., Haase, J.: Positionsempfindlichkeit und fusimotorische Aktivierung prätibialer Muskelspindelendigungen vor und nach Deafferentierung. Pflügers Arch.321, 242–252 (1970)
Granit, R.: Charles Scott Sherrington. An Appraisal. London: Nelson 1966
Granit, R., Pascoe, J. E., Steg, G.: The behaviour of tonic α and γ motoneurones during stimulation of recurrent collaterales. J. Physiol. (Lond.)138, 381–400 (1957)
Grillner, S.: The influence of Dopa on the static and the dynamic fusimotor activity to the triceps surae of the spinal cat. Acta physiol. scand.77, 490–509 (1969a)
Grillner, S., Supraspinal and segmental control of static and dynamic γ-motoneurones in the cat. Acta physiol. scand., Suppl.327, 1–34 (1969b)
Grillner, S., Hongo, T., Lund, S.: Descending monosynaptic and reflex control of γ-motoneurones. Acta physiol. scand.75, 592–613 (1969)
Hunt, C. C.: The reflex activity of mammalian small-nerve fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.)115, 456–469 (1951)
Hunt, C. C., Paintal, A. S.: Spinal reflex regulation of fusimotor neurones. J. Physiol. (Lond.)143, 195–212 (1958)
Matthews, P. B. C.: Muscle spindles and their motor control. Physiol. Rev.44, 219–288 (1964)
Noth, J.: Aktivitätsänderungen der Extensor-Fusimotoneurone der Katze infolge Reizung niedrigschwelliger Muskelafferenzen. Pflügers Arch.326, 231–239 (1971a)
Noth, J.: Recurrente Hemmung der Extensor-Fusimotoneurone? Pflügers Arch.329, 23–33 (1971b)
Pompeiano, O.: Alpha types of ‘release’ studied in tension-extension diagrams from cat's forelimb triceps muscle. Arch. ital. Biol.98, 92–117 (1960)
Proske, U., Lewis, D. M.: The effects of muscle stretch and vibration on fusimotor activity in the lightly anaesthetised cat. Brain Res.46, 55–69 (1972)
Voorhoeve, P. E., van Kanten, R. W.: Reflex behaviour of fusimotor neurones of the cat upon electrical stimulation of various afferent fibres. Acta physiol. pharmacol. neerl.10, 391–407 (1962)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fromm, C., Haase, J. & Noth, J. Length-dependent autogenetic inhibition of extensor γ-motoneurones in the decerebrate cat. Pflugers Arch. 346, 251–262 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00595711
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00595711