Summary
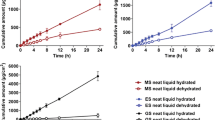
Results of measurements of the penetration rate of14C-labelled hydrocortisone butyrate (HCB) under varying conditions (cream or alcoholic solution as a vehicle, variation of the concentration and/or amount applied) are presented. Alcoholic solutions gave the highest penetration.
The amount of HCB present on the interface between the vehicle and the epidermis proved to be the rate-limiting factor under our experimental conditions.
Zusammenfassung
Die Penetrationsrate von14C-markiertem Hydrocortisonbutyrat (HCB) wurde unter verschiedenen Bedingungen (Creme oder alkoholische Lösung als Vehikel, unterschiedliche Konzentrationen und Mengen) gemessen. Alkoholische Lösungen zeigten die größte Penetrationsrate. Die an der Grenzzone zwischen Epidermis und Vehikel befindliche HCB-Menge erwies sich unter den verwandten Versuchsbedingungen als ausschlaggebend für die Penetrationsrate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, B. S., Fountain, R. B., Hadgraft, J. W., Sarkany, I.: Comparison of some physical properties of four vehicles used in dermatological preparations. Brit. J. Derm.81, 60–64 (1969).
Barett, C. W., Hadgraft, J. W., Caron, G. A., Sarkany, I.: The effect of particle size and vehicle on the percutaneous absorption of fluocinolone acetonide. Brit. J. Derm.77, 576–578 (1965).
Blank, I. H., Scheuplein, R. J., MacFarlane, D. J.: Mechanism of percutaneous absorption. III. The effect of temperature on the transport of non-electrolytes across the skin. J. invest. Derm.49, 582–589 (1967).
Burch, G. E., Winsor, T.: Rate of insensible perspiration locally through living and dead human skin. Arch. intern. Med.74, 437–444 (1946).
Crutcher, W., Maibach, H. I.: The effect of perfusion rate on in vitro percutaneous penetration. J. invest. Derm.53, 264–269 (1969).
Knight, A. G., Vickers, C. F. H., Percival, A.: The percutaneous absorption of antibacterial substances. Brit. J. Derm.81, Suppl. 4, 88–90 (1969).
Polano, M. K., Ponec, M., Smeenk, G., Hendrikse, J. C. M.: Factors influencing the penetration of corticosteroids through the epidermis. Advances in biology of skin, Vol. 12. Pharmacology and the skin, p. 325–338. New York: Appleton-Century-Crofts 1972.
Poulsen, B.: The use of models in estimating vehicle effects on the activity of topical corticosteroid formulation. Brit. J. Derm.82, Suppl. 6, 49–52 (1970).
Reinstein, J., Ostrenga, J., Haleblian, J., Shastri, S., Poulsen, B., Hatz, M.: Design of the optimal topical system for fluocinonide. Acta derm. Vol. 52 Suppl. 67, 13–17 (1972).
Sarkany, I., Hadgraft, J. W.: The influence of formulation on topical corticosteroid activity. Brit. J. Derm.81, Suppl. 4, 98–102 (1969).
Sarkany, I., Hadgraft, J. W., Caron, G. A., Barett, C. W.: The role of vehicles in the percutaneous absorption of corticosteroids. Brit. J. Derm.77, 569–575 (1965).
Scheuplein, R. J.: Mechanism of percutaneous absorption I. Routes of penetration and the influence of solubility. J. invest. Derm.45, 334–346 (1965).
Scheuplein, R. J.: Mechanism of percutaneous absorption II. Transient diffusion and the relative importance of various routes of skin penetration. J. invest. Derm.48, 79–88 (1967).
Scheuplein, R. J., Blank, I. H., Brauner, G. J., MacFarlane, D. J.: Percutaneous absorption of steroids. J. invest. Derm.52, 63–70 (1969).
Stoughton, R. B.: Vasoconstrictor activity and percutaneous absorption of glucocorticosteroids. Arch. Derm.99, 753–756 (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ponec, M., Polano, M.K. Hydrocortisone butyrate penetration through epidermis in vitro. Arch. Derm. Forsch. 245, 381–389 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00595642
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00595642