Summary
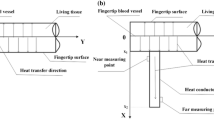
Local heat clearance probes containing two measuring points each surrounded by a heating system, thus enabling an alternative heating of both points, were tested in model experiments and in the measuring of human muscle flood flow. Measurements with alternative heating of both measuring points at the same probe position allow the determination of the degree of homogeneity of local blood flow. Thus inhomogeneity errors in estimating the local heat clearance (heat transport index, HTI), which arise from the fact that the reference measuring point is always slightly coheated, can be avoided. With this modified technique, the chances of finding suitable probe, positions for the measurement of human muscle blood flow are significantly increased.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aschoff, J.: Grundversuche zur Temperaturregulation. Über vergleichende Meßwerte zur Beurteilung der Wärmeabgabe an Wasser. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.247, 469–479 (1944).
Felix, R., Golenhofen, K.: Wärmeleitmessung im menschlichen Muskel mit alternativ heizbaren Wärmeleitsonden und der Effekt lokaler Histaminapplikation. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.289 R99-R100 (1966).
Gibbs, F. A.: A thermoelectric blood flow recorder in the form of a needle. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N.Y.)31, 141–146 (1933).
Golenhofen, K.: Blood flow of muscle and skin studied by the local heat clearance technique (Wärmeleitmessung). Scand. J. clin. Lab. Invest.19, (Suppl. 99) 79–85 (1967).
—, Hensel, H., Hildebrandt, G.: Durchblutungsmessung mit Wärmeleitelementen. Stuttgart: G. Thieme 1963.
———: Recent developments in the measurement of muscle blood flow in man with heated thermocouples. J. Physiol. (Lond.)170, 58P-59P (1964).
—, Hildebrandt, G.: Das Verfahren der Wärmeleitmessung und seine Bedeutung für die Physiologie des menschlichen Muskelkreislaufes. Arch. Kreisl.-Forsch.38, 23–70 (1962a).
——: Weiterentwicklung der Wärmeleitsonde zur Messung der menschlichen Muskeldurchblutung. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.274, 615–623 (1962b).
Hensel, H.: Neue Wärmeleitsonden zur Durchblutungsregistrierung. Naturwissenschaften50, 155–156 (1963).
—, Ruef, J.: Fortlaufende Registrierung der Muskeldurchblutung am Menschen mit einer Calorimetersonde. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.259, 267–280 (1954).
Merguet, P., Golenhofen, K.: Lokal-mechanische Regulation der menschlichen Muskelstrombahn (“myogene Reaktion”, “Bayliss-Effekt”). Pflügers Arch ges. Physiol.297, R36 (1967).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Golenhofen, K., Felix, R. Local heat clearance probes with alternative heating and their application in the measuring of human muscle blood flow. Pflugers Arch. 331, 145–152 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00587257
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00587257