Summary
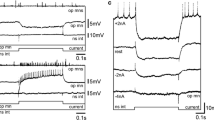
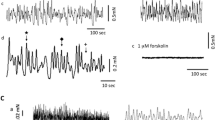
Intracellular microelectrodes were used to analyse the excitatory input to single cells of the mouse vas deferens. Excitatory junction potentials (EJP's) were evoked by both orthodromic and antidromic impulses in terminal axons lying within the musculature of the vas deferens, indicating that transmitter is released from the length of the terminal axon not just from the axon termination. The amplitude of the EJP was altered by altering the strength of stimulation. By using this variation, it was found that 15–22 nerve fibres gave a detectable contribution to the amplitude of the EJP in a single cell. The maximum amplitude of the EJP was 45 mV and the maximum depolarization caused by transmission from a single axon was 5 mV. By depolarizing the whole tissue with noradrenaline, the reversal potential for the EJP was found to be −20 to −15 mV. The EJP was not reversed when a single cell was depolarized with an intracellular current pulse. Extracellular electrodes failed to record any reversal of the EJP, corresponding to current sinks. It is concluded that the EJP in a single cell arises both from the action of transmitter, released from terminal varicosities, on its membrane and from potential changes electrically coupled from adjacent cells via low resistance connections between the smooth muscle cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett, M. R.: The effect of intracellular current pulses in smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig vas deferens at rest and during transmission. J. gen. Physiol.50, 2459–2475 (1967).
—, Burnstock, G.: Electrophysiology of the innervation of intestinal smooth muscle. In: Handbook of Physiology, sec. 6, vol. 4, ed. C. F. Code. Washington: Am. Physiol. Soc. 1968.
Burnstock, G.: Structure of smooth muscle and its innervation. In: Smooth Muscle, ed. E. Bülbring. London: Arnold 1969 (in press).
Burnstock, G., Holman, M. E.: The transmission of excitation from autonomic nerve to smooth muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.)155, 115–133 (1961).
——: Junction potentials at adrenergic synapses. Pharmacol. Rev.18, 481–493 (1966).
Colin, F., Vanwelkenhuyzen, P.: De l'activite electrique de la musculature du canal deferent. Acta urol. belg.35, 523–581 (1967).
Dewey, M. M., Barr, L.: Intercellular connections between smooth muscle cells: the nexus. Science137, 670–672 (1962).
Furness, J. B., Burnstock, G.: A comparative study of the spike potentials in response to nerve stimulation in the vas deferens of the mouse, rat and guinea-pig. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.31, 337–346 (1969).
Gillespie, J. S.: Spontaneous mechanical and electrical activity of stretched and unstretched intestinal smooth muscle cells and their responses to sympathetic nerve stimulation. J. Physiol. (Lond.)162, 54–75 (1962).
Hillarp, N.-Å.: Structure of the synapse and the peripheral innervation apparatus of the autonomic nervous system. Acta anat. (Basel) Suppl.4, 1–153 (1946).
—: Peripheral autonomic mechanisms. In: Handbook of Physiology, ed. Field, Magoun and Hall, sect. 1, vol. 2, pp. 976–1006. Washington: Am. Physiol. Soc. 1960.
Holman, M. E.: Some electrophysiological aspects of transmission from autonomic nerves to smooth muscle. Circulat. Res. Suppl.3, 71–82 (1967).
—: Introduction to electrophysiology of visceral smooth muscle. In: Handbook of Physiology, sec. 6, vol. 4, pp. 1665–1708. Ed. C. F. Code. Washington: Am. Physiol. Soc. 1968.
Lane, B. P., Rhodin, J. A. G.: Cellular interrelationships and electrical activity in two types of smooth muscle. J. Ultrastruct. Res.10, 470–488 (1964).
Malmfors, T.: Studies on adrenergic nerves. Acta physiol. scand.64, Suppl. 248, 1–93 (1965).
Martin, A. R., Pilar, G.: An analysis of electrical coupling at synapses in the avian ciliary ganglion. J. Physiol. (Lond.)171, 454–475 (1964).
Merrillees, N. C. R., Burnstock, G., Holman, M. E.: Correlation of fine structure and physiology of the innervations of smooth muscle in the guinea-pig vas deferens. J. Cell Biol.19, 529–550 (1963).
Nagai, T., Prosser, C. L.: Patterns of conduction in smooth muscle. Amer. J. Physiol.204, 910–914 (1963).
Thaemert, J. C.: Ultrastructure interrelationships of nerve processes and smooth muscle cells in three dimensions. J. Cell Biol.28, 37–49 (1966).
Tomita, T.: Electrical responses of smooth muscle to external stimulation in hypertonic solution. J. Physiol. (Lond.)183, 450–468 (1966).
—: Current spread in the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig vas deferens. J. Physiol. (Lond.)189, 163–176 (1967).
Yamauchi, A., Burnstock, G.: Post-natal development of the innervation of the mouse vas deferens. A fine structural study. J. Anat. (Lond.)104, 17–32 (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by grants from the Australian Research Grants Committee and the National Heart Foundation of Australia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Furness, J.B. The excitatory input to a single smooth muscle cell. Pflugers Arch. 314, 1–13 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00587042
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00587042