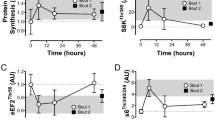
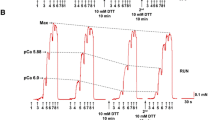
Abstract
Chronic administration of an anabolic hormone, nandrolone phenylpropionate, in sedentary female rats for 6 weeks gave a 20% increase in body weight and the same proportional increase in all muscles sampled (heart, diaphragm, soleus, TA, EHP and EDL), such that the muscle/body weight ratio was unchanged. Cardiac muscle was unresponsive to treatment. Acute stimulation of EDL via lateral popliteal nerve gave similar values for contraction time, 1/2 relaxation time and twitch: tetanus ratio in both groups suggesting no slowing of the muscle. Fatigue resistance of EDL was improved with 0.29±0.029 vs. 0.46±0.071 of maximum isometric twitch tension being developed after 10 min repetitive stimulation at 4 Hz. This improved endurance was not accompanied by any increase in strength and could not be explained on the basis of cellular hypertrophy, but appears to reflect an increased aerobic capacity of skeletal muscle. The proportion of FOG fibres in EDL increased, 38±1.1% vs. 46±1.1%, and this was paralleled in the other skeletal muscles. Specific hypertrophy of FOG and FG fibres could be conclusively demonstrated in soleus and TA, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alén M, Häkkinen K, Komi PV (1984) Changes in neuromuscular performance and muscle fibre characteristics of elite power athleties self-administering androgenic and anabolic steroids. Acta Physiol Scand 122:535–544
Boris A, Stevenson RH, Trmal T (1970) Comparative androgenic, myotrophic and antigonadotrophic properties of some anabolic steroids. Steroids 15:61–71
Breuer CB, Florini JR (1965) Amino acid incorporation into protein by cell-free systems from rat skeletal muscle. Biochemistry 4:1544–1550
Chaudry MAQ, James KC, Ng CT, Nicholls PJ (1976) Anabolic and androgenic activities, in rats, of some nandrolone and androstandone esters. J Pharm Pharmacol 28:882–885
Dahlberg E, Snochowski M, Gustafsson J-Å (1981) Regulation of the androgen and glucocorticoid receptors in rat and mouse skeletal muscle cytosol. Endocrinology 108:1431–1440
Döhler KD, Wuttke W (1975) Changes with age in levels of serum gonadotropins, prolactin, and gonadal steroids in pre-pubertal male and female rats. Endocrinology 97:898–907
Egginton S (1986) Effects of an anabolic hormone on performance and composition of rat skeletal muscle. J Physiol 373:35P
Egginton S (1987) Effects of an anabolic hormone on aerobic capacity of rat striated muscle. Pflügers Arch 410:356–361
Exner GU, Staudte HW, Pette D (1973a) Isometric training of rats — effects upon fast and slow muscle and modification by an anabolic hormone (nandrolone decanoate). I. Female rats. Pflügers Arch 345:1–14
Exner GU, Staudte HW, Pette D (1973b) Isometric training of rats — effects upon fast and slow muscle and modification by an anabolic hormone (nandrolone decanoate). II. Male rats. Pflügers Arch 345:15–22
Fahley TD, Brown CH (1973) The effects of an anabolic steroid on the strength, body composition and endurance of college males when accompanied by a weight training program. Med Sci Sprots Exerc 5:272–276
Freed DLJ, Banks AJ, Longston D, Burley DM (1975) Anabolic steroids in athletes: crossover double-blind trial on weight-lifters. Br Med J 2:477–473
Goldberg AL, Tischler M, DeMartino G, Griffin G (1980) Hormonal regulation of protein degradation and synthesis in skeletal muscle. Fed Proc 39:31–36
Gustafsson J-Å, Saartok T, Dahlberg E, Snochowski M, Häggmark T, Eriksson E (1984) Studies on steroid receptors in human and rabbit skeletal muscle — clues to the understanding of the mechanism of action of anabolic steroids. In: Gurpide E, Calandra LC, Soto RJ (eds) Hormones and Cancer. Liss, New York, pp 261–290
Hanzliková V, Gutman E (1974) The absence of androgen-sensitivity in the grafted soleus muscle innervated by the pudendal nerve. Cell Tiss Res 154:121–129
Hervey GR, Hutchinson I (1973) The effects of testosterone on body weight and composition in the rat. J Endocrinol 57:XXIV
Hickson RC, Hensner WW, Van Huss WD, Taylor JF, Carrow RE (1976) Effects of an anabolic steroid and sprint training on selected histochemical and morphological observations in rat skeletal types. Eur J Applied Physiol 35:251–259
Hickson RC, Galassi TM, Kurowski TT, Daniels DG, Chatterton RT (1984) Androgen and glucocorticoid mechanisms in exereise-induced cardiac hypertrophy. Am J Physiol 246:H761-H767
Hudlická O, Dodd L, Renkin EM, Gray SD (1982) Early changes in fibre profiles and capillary density in long-term stimulated muscles. Am J Physiol 243:H528-H535
Hutchinson IWW, Schantz P, Åstrand P-O, Bevan L (1983) Muscle fibre type distribution, muscle cross-sectional area and serum androgens. Med Sci Sports Exerc 15:176
James KC, Nicholls PJ, Roberts M (1969) Biological half-lives of [4-14C] testosterone and some of its esters after injection into the rat. J Pharm Pharmacol 21:24–27
Johnson LC, O'Shea JP (1969) Anabolic steroid effects on strength development. Science 164:957–959
Kelly FJ, McGrath JA, Goldspink DF, Cullen MJ (1986) A morphological/biochemical study on the actions of corticosteroids on rat skeletal muscle. Muscle Nerve 9:1–10
Keul J, Deus B, Kindermann W (1976) Anabole Hormone: Schädigung, Leistungsfähigkeit und Stoffwechsel. Med Klin 71:497–503
Kuhn FE, Max SR (1985) Testosterone and muscle hypertrophy in female rats. J Appl Physiol 59:24–27
Max SR, Rance NE (1984) No effect of sex steroids on compensatory muscle hypertrophy. J Appl Physiol 56:1589–1593
Millward DJ, Garlick PJ, Nnanyelugo DO (1976) The relative importance of muscle protein synthesis and breakdown in the regulation of muscle mass. Biochem J 156:185–188
Müntener M (1979) Variable pH dependence of the myosin-ATPase in different muscles of the rat. Histochemistry 62:299–304
Nachlas MM, Tsou K, Desonsa G, Cheng C, Seligman A (1957) Cytochemical demonstration of SDH by the use of a new p-nitrophenol substituted derivative. J Histochem Cytochem 5:420–436
Overbeek GA, van der Vies J, de Visser J (1969) The so-called “pure” anabolic agents. J Am Med Wom Assoc 24:54–59
Papanicolaou GN, Falk EA (1938) General muscular hypertrophy induced by androgenic hormone. Science 87:238–239
Pearse AGE (1968) Histochemistry, theoretical and applied. 3rd edn, Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh London New York
Pullen AH (1977) The distribution and relative sizes of fibre types in the extensor digitorum longus and soleus muscles of the adult rat. J Anat 123:467–486
Rothstein JM, Rose SJ (1982) Muscle mutability. Part 2 Adaption to drugs, metabolic factors and aging. Phys Ther 62:1788–1798
Ryan AJ (1981) Anabolic steroids are fool's gold. Fed Proc 40:2682–2688
Saartok T, Dahlberg E, Gustafsson J-Å (1984) Relative binding affinity of anabolic and androgenic steroids: comparison of the binding to the androgen receptors in skeletal muscle and in prostate, as well as to sex-hormone binding globulin. Endocrinology 114:2100–2106
Salmons S (1983) Myotrophic effects of anabolic steroids. Vet Res Commun 7:19–26
Stone MH, Lipner H (1978) Responses to intensive training and methandrostenelone administration. I. Contractile and performance variables. Pflügers Arch 375:141–146
Tóth M, Zakár T (1982) Relative binding affinities of testosterone, 19-nortestosterone and their 5α-reduced derivatives to the androgen receptor and to other androgen-binding proteins. J Steroid Bichem 17:653–660
van der Vies J (1970) Model studies in vitro with long-acting hormonal preparations. Acta Endocrinol 64:656–669
Viru A, Korge P (1979) Role of anabolic steroids in the hormonal regulation of skeletal muscle adaption. J Steroid Biochem 11:931–932
Wright JE (1980) Anabolic steroids and athletes. In: Hutton RS, Miller DI (eds) Exercise and Sport Sciences Reviews, vol 8. Franklin Institute Press, Philadelphia, PA, pp 149–202
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Egginton, S. Effects of an anabolic hormone on striated muscle growth and performance. Pflugers Arch. 410, 349–355 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00586510
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00586510