Summary
The method is developed allowing to isolate the neuronal soma from the ganglia of snailHelix pomatia. The method is based on the preliminary treatment of ganglia by 1% trypsine. The surface membrane of isolated soma preserves a high input resistance, as well as normal values of resting and action potentials. Electromicroscopic study of the isolated neurones proved that the membrane is in direct contact with the surrounding medium.
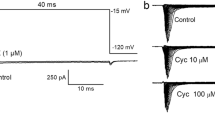
Voltage clamp technique was applied to measure the early inward current through the membrane of the isolated soma in different test solutions. In Na-free saline solution containing the normal amount of Ca (7 mM) the inward current decreased to 53±7% of the current measured in the normal saline. When Na in the external saline was replaced by an equivalent amount of Ca (53 mM), the inward current reached 129±8% of the maximum value in normal saline. Tetrodotoxin (5·10−6 M) did not cause any noticeable changes in the value of the inward current both in normal and “calcium” saline. CoCl2 or MnCl2 (10 mM) decreased considerably the inward current measured in both salines, but Co acted also unspecifically, increasing the leakage conductance.
The possibility of passing of both Ca and Na ions through the same system of channels is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baumgarten, R. von, Chen, C. F., Takeda, R.: Isolation of pacemaker neurones inAplysia californica. Fed. Proc.30, 490 Abs. (1971)
Chamberlain, S. G., Kerkut, G. A.: Voltage clamp analysis of the sodium and calcium inward currents in snail neurones. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.28, 787–801 (1969)
Geduldig, D., Gruener, R.: Voltage clamp of theAplysia giant neurone: early sodium and calcium currents. J. Physiol. (Lond.)211, 217–244 (1970)
Geletyuk, V. I., Veprintzew, B. N.: Electrical properties of neurones of the molluscLimnea stagnalis under conditions of tissue culture. Cytology14, 1133–1139 (1972)
Gerasimov, V. D., Kostyuk, P. G., Maiskii, V. A.: Influences of divalent cations on electrical characteristics of giant neurone membrane. Biofizika10, 447–453 (1965)
Jarelova, I. V., Krasts, I. V., Veprintzew, B. N.: The effect of sodium, calcium and magnesium on the amplitude of the action potential from giant neurones ofLimnea stagnalis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.40 A, 281–293 (1971)
Junge, D.: Multi-ionic action potentials in molluscan giant neurones. Nature (Lond.)215, 546–548 (1967)
Kerkut, G. A., Gardner, D. R.: The role of calcium ions in the action potentialsHelix aspersa neurones. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.20, 147–162 (1967)
Krishtal, O. A., Magura, I. S.: Calcium ions as inward current carriers in molluse neurones. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.35, 857–866 (1970)
Krishtal, O. A., Parkhomenko, N. T.: Effect of sodium-free solution on ionic currents of snail giant neurones. Neurophysiology (Kiev)2, 314–319 (1970)
Magura, I. S., Kiss, J., Krishtal, O. A.: Current-voltage relations of the giant neurone soma membrane ofLimnea stagnalis. Acta physiol. Acad. Sci. hung.40, 221–228 (1971)
Meves, H.: The ionic requirements for the production of action potentials inHelix pomatia neurones. Pflügers Arch.304, 215–241 (1968)
Moreton, R. B.: Ionic mechanism of the action potentials of giant neurones ofHelix aspersa. Nature (Lond.)219, 70–71 (1968)
Neher, E.: Two fast transient current components during voltage clamp on snail neurones. J. gen. Physiol.58, 36–53 (1971)
Oomura, Y., Ozaki, S., Maeno, T.: Electrical activity of a giant cell under abnormal conditions. Nature (Lond.)191, 1265–1267 (1961)
Wald, F.: Ionic differences between somatic and axonal action potentials in snail giant neurones. J. Physiol. (Lond.)220, 267–281 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kostyuk, P.G., Krishtal, O.A. & Doroshenko, P.A. Calcium currents in snail neurones. Pflugers Arch. 348, 83–93 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00586471
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00586471