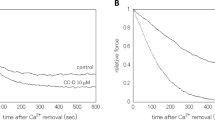
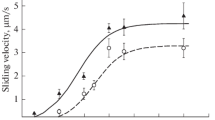
Abstract
During smooth muscle activation the calcium calmodulin complex interacts with myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) whereby activating it. A synthetic peptide analogue (RS20) corresponding to the calmodulin recognition sequence of MLCK has been synthesized and previously found to inhibit the calmodulin stimulated light chain kinase activity. Here we studied the effect of this peptide on skinned fibers from guinea pig taenia coli. Maximal contractions induced by 30 μM Ca2+ at 0.1 μM calmodulin could be completely relaxed by the peptide at 1 μM. The inhibitory effect was accompanied by partial dephosphorylation only of the regulatory myosin light chain. Relaxation could be reversed by addition of calmodulin which also increased the extent of light chain phosphorylation.The calmodulin concentration required for reversing the inhibition depended on the concentration of the inhibitory peptide suggesting that the peptide competed with MLCK for the calmodulin binding site. As the calcium-calmodulin-peptide mixture constitutes a calmodulin buffer, our results suggest, that the peptide is a calmodulin antagonist unique in terms of its potency and that less than nanomolar concentrations of free calmodulin may be required for inducing smooth muscle contractions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asano M, Stull JT (1985) Effects of calmodulin antagonists on smooth muscle contraction and myosin phosphorylation. In: Hidaka H, Hartshorne DJ (eds) Calmodulin antagonists and cellular physiology. Orlando, pp 225–260
Biajolan C, Rüegg JC, Takai A (1988) Effects of okadaic acid on isometric tension and myosin phosphorylation of chemically skinned guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol 398:81–95
Cassidy P, Hoar PE, Kerrick WGL (1979) Irreversible thiophosphorylation and activation in functionally skinned rabbit ileum strips by35(S)-ATPγS. J Biol Chem 254:11148–11153
Fabiato A, Fabiato F (1979) Calculator programs for computing the composition of solution containing multiple metals and ligands used for experiments in skinned muscle cells. J Physiol (Paris) 75(5):463–505
Ishikawa T, Chijiwa T, Hagiwara M, Mamiya S, Saitoh M, Hidaka H (1988) ML-9 inhibits the vascular contraction via the inhibition of myosin light chain phosphorylation. Mol Pharmacol 33:598–603
Kemp B, Pearson RB, Guerriero V Jr, Bagchi IC, Means AR (1987) The calmodulin binding domain of chicken smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase contains a pseudosubstrate sequence. J Biol Chem 262:2542–2548
Lukas TJ, Burgess WH, Prendergast FG, Lau W, Watterson DM (1986) Calmodulin binding domains: characterization of a phosphorylation and calmodulin binding site from myosin light chain kinase. Biochemistry 25:1458–1464
Meisheri KD, Rüegg JC, Paul RJ (1985) Studies on skinned fiber preparations. In: Daniels EE, Grover AK (eds) Calcium and contractility. Humana Press, New Jersey, pp 191–224
Saitoh M, Ishikawa T, Matsushima S, Naka M, Hidaka H (1987) Selective inhibition of catalytic activity of smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase. J Biol Chem 262:7796–7801
Smith CWJ, Pritchard K, Marston SB (1987) The mechanism of Ca2+ regulation of vascular smooth muscle thin filaments by caldesmon and calmodulin. J Biol Chem 262:116–122
Sparrow MP, Mrwa U, Hofmann F, Rüegg JC (1981) Calmodulin is essential for smooth muscle contraction. FEBS Lett 125:141–145
Takai A, Biajolan C, Troschka M, Rüegg JC (1987) Smooth muscle myosin phosphatase inhibition and force enhancement by black sponge toxin. FEBS Lett 217:81–84
Wagner J, Rüegg JC (1986) Skinned smooth muscle: Calciumcalmodulin activation independent of myosin phosphorylation. Pflügers Arch 407:569–571
Zimmer M, Hoffmann F (1984) Calmodulin antagonists inhibit activity of myosin light chain kinase independent of calmodulin. Eur J Biochem 142:393–397
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rüegg, J.C., Zeugner, C., Strauss, J.D. et al. A calmodulin-binding peptide relaxes skinned muscle from guinea-pig taenia coli. Pflugers Arch. 414, 282–285 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00584627
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00584627