Abstract
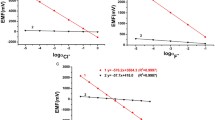
Current procedures for the manufacture of ionselective microelectrodes using liquid ion sensors result in two kinds of electrode, one with a short (10–100 μm) column of sensor at the tip and one with a long column (> 1 mm). We report here that the signal from a long-column microelectrode is very sensitive to small fluctuations in bath temperature and solution level when a recording is made above room temperature. This sensitivity is explained by the effects of temperature on the potentials developed at the interfaces between the ion sensor and the bordering aqueous solutions (the internal filling solution of the electrode and the test solution). If the temperature at the two interfaces is changed by different amounts, these interfacial potentials will also change by different amounts resulting in a change in the output of the electrode. Such an effect occurs for longcolumn electrodes because the column of sensor is usually not completely immersed in the heated test solution. Hence fluctuations in solution temperature and level will induce fluctuations in temperature along the column of sensor producing variations in the electrical signal from the electrode. In contrast, sensitivity to temperature and solution level is virtually absent in short-column microelectrodes since their column of sensor is fully immersed in the test solution and thereby at uniform temperature. In conclusion, in order to produce noise-free recordings of ion activities, the use of short-column microelectrodes is recommended for experiments performed above (or below) room temperature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cannell M, Lederer WJ (1986) A novel experimental chamber for single-cell voltage-clamp and patch-clamp applications with low electrical noise and excellent temperature and flow control. Pflügers Arch (in press)
Kaila K, Voipio J (1985) A simple method for dry-bevelling of micropipettes used in the construction of ion-selective microelectrodes. J Physiol 369:8P
Koryta J (1981) Theory of ion-selective electrodes. In: Syková E, Hnik P, Vyklický L (eds) Ion-selective microelectrodes and their use in excitable tissues. Plenum Press, New York London, p 3
Steiner RA, Oehme M, Amman D, Simon W (1979) Neutral carrier sodium-selective microelectrode for intracellular studies. Anal Chem 51:351–353
Thomas RC (1978) Ion-sensitive intracellular microelectrodes. How to make and use them. Academic Press, New York
Tsien RY (1983) Intracellular measurements of ion activities. Ann Rev Biophys Bioeng 12:91–116
Tsien RY, Rink TJ (1980) Neutral carrier ion-selective microelectrodes for measurement of intracellular free calcium. Biochem Biophys Acta 599:623–638
Vaughan-Jones RD (1979) Regulation of chloride in quiescent sheep-heart Purkinje fibres studied using intracellular chloride and pH-sensitive micro-electrodes. J Physiol 295:111–137
Walker JL (1971) Ion specific liquid ion exchanger microelectrodes. Anal Chem 43:89A-93A
Weingart R, Hess P (1984) Free calcium in sheep cardiac tissue and frog skeletal muscle measured with Ca2+-selective microelectrodes. Pflügers Arch 402:1–9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vaughan-Jones, R.D., Kaila, K. The sensitivity of liquid sensor, ion-selective microelectrodes to changes in temperature and solution level. Pflugers Arch. 406, 641–644 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00584033
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00584033