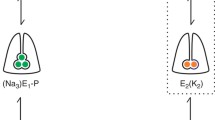Summary
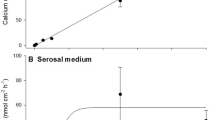
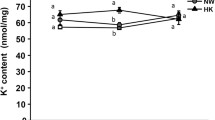
The ionic composition of the current crossing each membrane of the frog skin epithelia during a) the positive and transient current responses elicited by sudden addition of Na ions to the outer Na free medium b) the negative and transient current responses observed when Na loaded preparations are suddenly exposed to outer Na free solution was determined using isotopic techniques. It is shown that Na ions carry the current across the outer membrane while K ions are mainly involved in the transfert of charges across the inner membrane. The amount of Na accumulated by the epithelial cells during the responses is correlated to the area under the transient part of the current responses. Determinations of24Na uptake at different time of these transient positive responses show that the unidirectional Na influx across the outer membrane decreases as a function of time. It is suggested that the intracellular Na concentration might control the Na uptake mechanism across the outer membrane. During the negative responses, the Na efflux into the outer medium is highly correlated, either in time course or magnitude, to the current response. Both Na efflux and negative current are sensitive to amiloride, suggesting that the mechanism of Na uptake by the frog skin also is able to promote Na movement out of the epithelial cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biber, T. U. L.: Effect of change in transepithelial transport on the uptake of sodium across the outer surface of the frog skin. J. gen. Physiol.58, 131–144 (1971)
Biber, T. U. L., Cruz, L. J., Curran, P. F.: Sodium influx at the outer surface of frog skin. Evaluation of different extracellular markers. J. Membrane Biol.7, 365–376 (1972)
Biber, T. U. L., Curran, P. F.: Direct measurement of uptake of sodium at the outer surface of the frog skin. J. gen. Physiol.56, 83–99 (1970)
Bricker, N. S., Biber, T. U. L., Ussing, H. H.: Exposure of the isolated frog skin to high potassium concentration at the internal surface. I. Bioelectric phenomena and sodium transport. J. clin. Invest.42, 88–94 (1963)
Curran, P. F., Cereijido, M.: K fluxes in frog skin. J. gen. Physiol.48, 1011–1033 (1965)
Erlij, D., Smith, M. W.: Sodium uptake by frog skin and its modification by inhibitors of transepithelial sodium transport. J. Physiol. (Lond.)228, 221–239 (1973)
Garcia-Romeu, F., Ehrenfeld, J.: In vivo Na+ and Cl− independent transport across the skin of Rana Esculanta. Amer. J. Physiol. (in press, 1975)
Hansen, H. H., Zerahn, K.: Concentration of lithium, sodium and potassium in epithelial cells of the isolated frog skin during active transport of lithium. Acta physiol. scand.60, 189–196 (1964)
Herrera, F. C.: Inhibition of lithium transport across toad bladder by amiloride Amer. J. Physiol.222, 499–502 (1972)
Herrera, F. C., Egea, R., Herrera, A. M.: Movement of Li across toad urinary bladder. Amer. J. Physiol.220, 1501–1508 (1971)
Keynes, R. D.: Some further observations on the sodium efffux in frog muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.)178, 305–325 (1965)
Kirschner, L. B., Greenwald, L., Kerstetter, T. H.: Effect of amiloride on sodium transport across body surfaces of fresh water animals. Amer. J. Physiol.224, 832–837 (1973)
Leblanc, G.: The mechanism of lithium accumulation in isolated frog skin epithelium. Pflügers Arch.337, 1–18 (1972)
Morel, F., Leblanc, G.: Transient current changes and Na compartimentalization in frog skin epithelium. Pflügers Arch.358, 135–157 (1975)
Moreno, J. H., Reisin, I. L., Rodriguez-Boulan, E., Rotunno, C. A., Cereijido, M.: Barriers to sodium movement across frog skin. J. Membrane Biol.II, 99–115 (1973)
Vôute, C. L., Ussing, H. H.: Some morphological aspects of active sodium transport. The epithelium of the frog skin. J. Cell Biol.36, 625–638 (1968)
Zerahn, K.: Studies on the active transport of lithium in the isolated frog skin. Acta physiol. scand.33, 347–358 (1955)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leblanc, G., Morel, F. Na and K movements across the membranes of frog skin epithelia associated with transient current changes. Pflugers Arch. 358, 159–177 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00583925
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00583925