Abstract
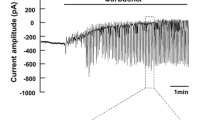
Single cells isolated from rat lacrimal glands were studied with the tight-seal whole-cell recording technique. It was found that furosemide (1 mM, applied externally) selectively blocked one part of the electrical response elicited by muscarinic agonists. This component of the response had been shown in a previous work (Marty et al. 1984) to be due to Ca-dependent Cl channels.
The action of furosemide was further studied on cells which were dialysed with a high-Ca, high-Na solution, and which mainly displayed the Ca-dependent Cl conductance. In these experiments, furosemide (1 mM) was again found to depress the Ca-dependent Cl current.
The present findings offer an explanation for previous reports that furosemide blocks ion fluxes and electrolyte secretion in exocrine glands without necessarily involving the neutral Na-K-Cl carrier usually assumed to be affected by the drug.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Case RM, Hunter M, Novak I, Young JA (1984) The anionic basis of fluid secretion by the rabbit mandibular salivary gland. J Physiol 349: 619–630
Findlay I (1984) A patch-clamp study of potassium channels and whole-cell currents in acinar cells of the mouse lacrimal gland. J Physiol 350: 179–195
Ginsborg BL, House CR (1980) Stimulus-response coupling in gland cells. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng 9: 55–80
Hamill OP, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth FJ (1981) Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflügers Arch 391: 85–100
Katchman AN, Zeimal EV (1982) Ionic mechanisms of the rapid (nicotinic) phase of acetylcholine response in identifiedPlanobarius corneus neurones. Brain Res 241: 95–103
Martell AE, Smith RM (1974) Critical stability constants. Amino acids, vol 1. Plenum Press, New York
Martinez JR, Cassity N (1983) Effect of transport inhibitors on secretion by perfused rat submandibular gland. Am J Physiol 245: G711-G716
Martinez JR, Cassity N (1985)36Cl fluxes in dispersed rat submandibular acini: effects of acetylcholine and transport inhibitors. Pflügers Arch 403: 50–54
Marty A, Tan YP, Trautmann A (1984) Three types of calcium-dependent channel in rat lacrimal glands. J Physiol 357: 293–325
Nicoll RA (1978) The blockade of GABA mediated responses in the frog spinal cord by ammonium ions and furosemide. J Physiol 283: 121–132
Palfrey HC, Silva P, Epstein FH (1984) Sensitivity of cAMP-stimulated salt secretion in shark rectal gland to “loop” diuretics. Am J Physiol 246: C242–246
Petersen OH (1980) The electrophysiology of gland cells. Academic Press, New York
Petersen OH, Maruyama Y (1984) Calcium-activated potassium channels and their role in secretion. Nature 307: 693–696
Poulsen JH, Kristensen LO (1982) Is stimulation-induced uptake of sodium in rat parotid acinar cells mediated by a sodium/chloride co-transport system? In: Case RM, Garner A, Thurnberg LA, Young JA (eds) Electrolyte and water transport across gastrointestinal epithelia. Raven Press, New York, p 157
Putney JW Jr (1979) Stimulus-permeability coupling: role of calcium in the receptor regulation of membrane permeability. Pharmacol Rev 30: 209–245
Singh J (1984a) Inhibition of ACh-evoked Rb efflux by furosemide and chloride removal in isolated mouse pancreas. J Physiol 346: 113P
Singh J (1984b) Effects of acetylcholine and caerulein on86Rb+ efflux in mouse pancreatic acinar cells: Evidence for a sodium-potassium-chloride-co-transport system. Biochim Biophys Acta 775: 77–85
Trautmann A, Marty A (1984) Activation of Ca-dependent K channels by carbamylcholine in rat lacrimal glands. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81: 611–615
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Evans, M.G., Marty, A., Tan, Y.P. et al. Blockage of Ca-activated Cl conductance by furosemide in rat lacrimal glands. Pflugers Arch. 406, 65–68 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00582955
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00582955