Abstract
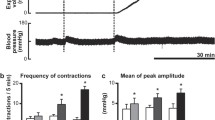
The present study revealed the site of origin and the possible function of a supraspinal descending-inhibitory influence over the lumbar sympathetic component of the recto-rectal reflex of guinea pigs. The recto-rectal reflex contraction was not changed by suprapontine transection. It completely disappeared after subpontine transection, but returned immediately after additional section of the colonic nerves, which contain the sympathetic inhibitory outflow to the rectum, i.e., subpontine transection with the lumbar colonic nerves transected did not suppress the recto-rectal reflex. These results indicate that a descending pathway which can inhibit the lumbar sympathetic component of the reflex may originate in the pons. On stimulation at sites within the pons of animals which had been spinalized at L4 we were able to evoke an increase of rectal motility and an inhibition of the lumbar colonic efferent discharges, thus producing a response which is comparable to the reflex response produced by afferent stimulation of the rectum.
The sites from which this effect could be evoked were mainly located in a band running rostrocaudally through the lateral reticular formation of the rostral part of the pons, medial to the sensory nucleus of the trigeminal nerve.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Groat WC, Lalley PM (1972) Reflex firing in the lumbar sympathetic outflow to activation of vesical afferent. J Physiol 226:289–309
De Groat WC, Krier J (1979) The central control of the lumbar sympathetic pathway to the large intestine of the cat. J Physiol 289:449–468
Fukuda H, Fukai K, Yamane M, Okada H (1981) Pontine reticular unit responses to pelvic nerve and colonic mechanical stimulation in the dog. Brain Res 207:59–71
Koppanyi T (1930) Studies on defecation with special reference to a medullary defecation center. J Lab Clin Med 16:225–238
Langworthy OR, Rosenberg SJ (1939) Control by the central nervous system of rectal smooth muscle. J Neurophysiol 2:356–360
Misu Y, Nishio H, Hosotani T, Hamano S (1976) A new guanidine derivative: dissociation of the adrenergic neuron blocking activity from local anesthetic activity. Jpn J Pharmacol 26:367–375
Nakayama S, Neya T, Yamasato T, Takaki M, Mizutani M (1978) Activity of the spinal defecation centre in the guinea pig. Ital J Gastroenterol 11:168–173
Okada H, Fukuda H, Yamane M (1976) On the localization of the pontine defecation reflex center of the dog. The Autonomic Nervous System 13:24–31 (in Japanese)
Rostad H (1973a) Colonic motility in the cat. III. Influence of hypothalamic and mesencephalic stimulation. Acta Physiol Scand 89:104–115
Rostad H (1973b) Colonic motility in the cat. IV. Peripheral pathways mediating the effects induced by hypothalamic and mesencephalic stimulation. Acta Physiol Scand 89:154–168
Takaki M, Neya T, Nakayama S (1980) Sympathetic activity in the recto-rectal reflex of the guinea pig. Pflügers Arch 388:45–52
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takaki, M., Neya, T. & Nakayama, S. Role and localization of a region in the pons which has a descending inhibitory influence on sympathetically mediated inhibition of the recto-rectal reflex of guinea pigs. Pflugers Arch. 398, 120–125 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00581058
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00581058