Summary
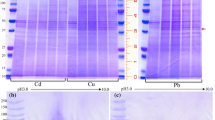
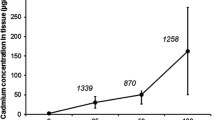
Three species of terrestrial Helicidae (Helix pomatia, Cepaea hortensis andArianta arbustorum) were fed cadmium-rich diet in the laboratory. The snails accumulated high amounts of the metal in their hepatopancreas. Most cadmium and some zinc were found, after centrifugation, in the soluble fractions from which a cadmium-binding protein was isolated for each species by ion exchange and gel chromatography. The proteins contained different amounts of cadmium, but little or no zinc, and showed high absorption at 254 nm indicating the presence of cadmium-mercaptide bonds. After gel filtration, a molecular weight of 12000 was found for cadmium-binding proteins fromHelix pomatia andArianta arbustorum, whereas a molecular weight of 10 000 was found for a cadmium-binding protein fromCepaea hortensis. SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis showed one single band for each protein fromHelix pomatia andArianta arbustorum and suggested a molecular weight of 11000 for both species. Amino acid analysis revealed, for each protein, high amounts of cysteine (12–20%), glycine (15–19%), and serine (12–14%), and moderately elevated contents of lysine (9–13%) and alanine (4–8%), but no methionine and only traces, if any, of aromatic amino acids. The ratios of cadmium to cysteine were 1:5, 1:10 and 1:3 in the proteins fromHelix pomatia,Cepaea hortensis andArianta arbustorum, respectively. Some features of the isolated proteins resembled mammalian metallothioneins. Most characteristics, however, differed from true metallothioneins and were similar to cadmium-binding proteins found in some marine molluscs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kägi JHR, Nordberg M: Metallothionein and other low molecular weight metal-binding proteins. Experientia Suppl 34:41–124, 1979
Stone HC, Overnell J: Minireview. Non-metallothionein cadmium binding proteins. Comp Biochem Physiol 80C:9–14, 1985
Hamer DH: Metallothionein. Ann Rev Biochem 55:913–951, 1986
Margoshes M, Vallee BL: A cadmium protein from equine kidney cortex. J Am Chem Soc 79:4813–4814, 1957
Fowler BA, Hildebrand CE, Kojima Y, Webb M: Nomenclature of metallothionein. In: Kägi JHR and Kojima Y (eds) Metallothionein II. Birkhäuser Verlag, Zürich, 1987, pp 19–22
Roesijadi G: The significance of low molecular weight, metallothionein-like proteins in marine invertebrates. Current status. Mar Environ Res 4:167–179, 1980
Hamilton SJ, Mehrle PM: Metallothionein in fish: Review of its importance in assessing stress from metal contaminants. Trans Am Fish Soc 115:596–609, 1986
Stone HC, Wilson SB, Overnell J: Cadmium binding components of scallop (Pecten maximus) digestive gland. Partial purification and characterization. Comp Biochem Physiol 85C:259–268, 1986
Langston WJ, Zhou M: Evaluation of the significance of metal-binding proteins in the gastropodLittorina littorea. Mar Biol 92:505–515, 1986
Dallinger R, Carpene E, Dalla Via GJ, Cortesi P: Effects of cadmium onMurex trunculus from the Adriatic Sea. I. Accumulation of metal and binding to a metallothionein-like protein. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 1988, in press
Engel DW, Brouwer M: Trace metal-binding proteins in marine molluscs and crustaceans. Mar Environ Res 13:177–194, 1984
Benson WH, Birge WJ: Detection of cadmium-binding proteins in fish chronically exposed to heavy metals. Environ Toxicol Chem 6:623–626, 1987
Schoetti G, Seiler HG: Uptake and localisation of radioactive zinc in the visceral complex of the land pulmonate,Arion rufus. Experientia 26:1212–1213, 1970
Meincke KF, Schaller KH: Über die Brauchbarkeit der Weinbergschnecke (Helix pomatia L.) im Freiland als Indikator für die Belastung der Umwelt durch die Elemente Eisen, Zink und Blei. Oecologia 15:393–398, 1974
Coughtrey PJ, Martin MH: The distribution of Pb, Zn, Cd and Cu within the pulmonate molluscHelix aspersa Müller. Oecologia 23:315–322, 1976
Cooke M, Jackson A, Nickless G, Roberts DJ: Distribution and speciation of cadmium in the terrestrial snail,Helix aspersa. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 23:445–451, 1979
Ireland MP: Uptake and distribution of cadmium in the terrestrial slugArion ater L. Comp Biochem Physiol 68A:37–41, 1981
Dallinger R, Wieser W: Patterns of accumulation, distribution and liberation of Zn, Cu, Cd and Pb in different organs of the land snailHelix pomatia L. Comp Biochem Physiol 79C:117–124, 1984
Dallinger R, Wieser W: Molecular fractionation of Zn, Cu, Cd and Pb in the midgut gland ofHelix pomatia L. Comp Biochem Physiol 79C:125–129, 1984
Chan KM, Davidson WS, Fletcher GL: Hepatic metallothionein mRNA in the winter flounder (Pseudopleuronectes americanus). Can J Zool 65:472–480, 1987
Andersen RD, Weser U: Partial purification, characterization and translationin vitro of rat liver metallothionein messenger RNA. Biochem J 175:841–852, 1978
Laemmli UK: Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature (London) 227:680–685, 1970
Nordberg GF, Nordberg M, Piscator M, Vesterberg O: Separation of two forms of rabbit metallothionein by isoelectric focusing. Biochem J 126:491–498, 1972
Hirs CHW: Determination of cysteine as cysteic acid. In: Hirs CHW (ed) Methods of Enzymology, Vol 11, Academic Press, New York, 1967, pp 59–65
Moore S, Stein WH: Chromatography of amino acids on sulfonated polystyrene resins. J Biol Chem 192:663–681, 1951
Spackman DH, Stein WH, Moore S: Automatic recording apparatus for use in the chromatography of amino acids. Anal Chem 30:1190–1206, 1958
Berger B, Dallinger R, Wieser W. Cadmium balance and metallothionein inArianta arbustorum L. In: Velthuis HHW (ed) Proceedings of the Third European Congress of Entomology, part 2, Amsterdam, 1986, p 325
Frazier JM, George SS, Overnell J, Coombs TL, Kögi J: Characterization of two molecular weight classes of cadmium binding proteins from the mussel,Mytilus edulis. Comp Biochem Physiol 80C:257–262, 1985
Kägi JHR, Vallee BL: Metallothionein: a cadmium and zinccontaining protein from equine renal cortex. J Biol Chem 236:2435–2442, 1961
Kägi JHR, Nordberg M: Metallothionein and other low molecular weight metal-binding proteins: In: Kägi JHR and Nordberg M (eds) Proceedings on first international meeting on metallothionein and other low molecular weight proteins, Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel, 1979, pp 41–136
Kägi JHR, Himmelhoch SR, Whanger PD, Bethume JL, Vallee BL: Equine hepatic and renal metallothioneins. Purification, molecular weight, amino acid composition and metal content. J Biol Chem 249:3537–3542, 1974
Minkel DT, Poulsen K, Wielgus S, Shaw CF, Petering DH: On the sensitivity of metallothioneins to oxidation during isolation. Biochem J 191:475–485, 1980
Finger JM, Smith JD: Molecular association of Cu, Zn, Cd and210Po in the digestive gland of the squidNototodarus gouldi Mar Biol 95:87–91, 1987
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dallinger, R., Berger, B. & Bauer-Hilty, A. Purification of cadmium-binding proteins from related species of terrestrial helicidae (gastropoda, mollusca): A comparative study. Mol Cell Biochem 85, 135–145 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00577109
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00577109