Summary
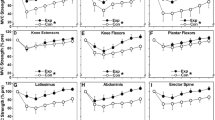
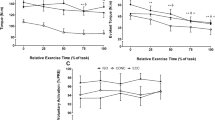
The effects of performing a second eccentric exercise bout prior to and after recovery from the first bout were compared. Twenty subjects performed 70 eccentric actions with the forearm flexors. Group A (n = 9) and group B (n = 11) repeated the same exercise 5 and 14 days after the initial bout, respectively. Dependent variables included muscle soreness, elbow joint angles, isometric strength, and serum creatine kinase (SCK). Subjects were tested pre-exercise and up to day 5 following each bout. The first bout produced significant changes in all measures for both groups (P < 0.01). Values remained significantly different from baseline on day 5 when group A repeated the exercise (P < 0.01) but were back to normal when group B performed bout 2. For both groups an adaptation occurred; significantly smaller changes in dependent variables were produced by the second bout, and recovery time was faster whether or not muscles were fully restored (P < 0.01). The repeated bout did not exacerbate soreness, performance decrements, and elevation of SCK when performed by affected muscles that had not fully recovered from the first bout. Thus, the results suggest that an adaptation response had taken place prior to full recovery and restoration of muscle function following the initial eccentric exercise bout.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong RB, Oglivie RW, Schwane JA (1983) Eccentric exercise-induced injury to rat skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 54:80–93
Brody IA (1969) Muscle contracture induced by exercise. N Engl J Med 281:187–192
Byrnes WC, Clarkson PM, White JS, Hsieh SS, Frykman PN, Maughan RJ (1985) Delayed onset muscle soreness following repeated bouts of downhill running. J Appl Physiol 59:710–715
Clarkson PM, Tremblay I (1988) Rapid adaptation to exercise induced muscle damage. J Appl Physiol 65:1–6
Clarkson PM, Apple FS, Byrnes WC, McCormick KM, Triffletti P (1987a) Creatine kinase isoforms following isometric exercise. Muscle Nerve 10:41–44
Clarkson PM, Byrnes WC, Gillisson E, Harper E (1987b) Adaptation to exercise-induced muscle damage. Clin Sci 73:383–386
Davies CTM, Barnes C (1972) Negative (eccentric) work. I. Effects of repeated exercise. Ergonomics 15:3–14
Davies CTM, White MJ (1981) Muscle weakness following eccentric work in man. Pflugers Arch 392:168–171
Friden J, Sjostrom M, Ekblom B (1983a) Myofibrillar damage following intense eccentric exercise in man. Int J Sports Med 4:170–176
Friden J Seger J, Sjostrom M, Ekblom B (1983b) Adaptive response in human skeletal muscle subjected to prolonged eccentric training. Int J Sports Med 4:177–183
Hoppeler H (1986) Exercise-induced ultrastructural changes in skeletal muscle. Int J Sports Med 7:187–204
Howell JN, Chila AG, Ford G, David D, Gates T (1985) An electromyographic study of elbow motion during postexercise muscle soreness. J Appl Physiol 58:1713–1718
Hunter JB, Critz JB (1971) Effect of training on plasma enzyme levels in man. J Appl Physiol 31:20–23
Jones DA, Newham DJ, Round JM, Tolfree SEJ (1986) Experimental human muscle damage: morphological changes in relation to other indices of damage. J Physiol 375:435–448
Jones DA, Newham DJ, Clarkson PM (1987) Skeletal muscle stiffness and pain following eccentric exercise of the elbow flexors. Pain 30:233–242
Newham DJ, Mills KR, Quigley BM, Edwards RHT (1983a) Pain and fatigue after concentric and eccentric muscle contractions. Clin Sci 64:55–62
Newham DJ, Jones DA, Edwards RHT (1983b) Large delayed plasma creatine kinase changes after stepping exercise. Muscle Nerve 6:380–385
Newham DJ, McPhail G, Mills KR, Edwards RHT (1983c) Ultrastructural changes after concentric and eccentric contractions of human muscle. J Neurol Sci 61:109–122
Newham DJ, Jones DA, Clarkson PM (1987) Repeated high force eccentric exercise: effects on muscle pain and damage. J Appl Physiol 63:1381–1386
Nuttall FQ, Jones B (1968) Creatine kinase and glutamic oxalacetic transaminase activity in serum: kinetics of change with exercise and effect of physical conditioning. J Lab Clin Med 71:847–854
Schwane JA, Armstrong RB (1983) Effect of training on skeletal muscle injury from downhill running in rats. J Appl Physiol 55:969–975
Schwane JA, Johnson SR, Vandenakker CB, Armstrong RB (1983) Delayed-onset muscular soreness and plasma CPK and LDH activities after downhill running. Med Sci Sports Exerc 15:51–56
Szasz G, Gruber W, Bernt E (1976) Creatine kinase in serum. I. Determination of optimum reaction conditions. Clin Chem 22:650–656
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ebbeling, C.B., Clarkson, P.M. Muscle adaptation prior to recovery following eccentric exercise. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 60, 26–31 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00572181
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00572181