Summary
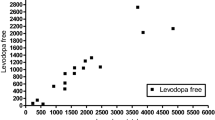
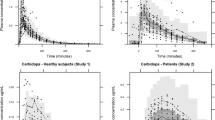
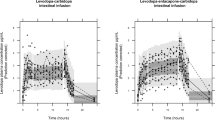
Previous studies have suggested that the absorption of L-dopa in the elderly Parkinsonian patient might be unusually efficient. In the present investigation, the systemic availability of L-dopa was examined in 5 elderly Parkinsonian patients (mean age=77 years) and 6 young, healthy volunteers (mean age=26 years) following a single oral 300 mg dose of L-dopa. Quantitation of plasma levels of intact L-dopa was effected by ion-exchange column chromatography and spectrofluorimetry. The L-dopa plasma concentration-time profiles obtained confirmed the considerable intersubject variability in the absorption of L-dopa previously reported in the literature. Maximum plasma concentrations of L-dopa generally occurred within 60 min of administration of the dose. The existence of more than one plasma peak of L-dopa concentration was displayed in 45% of the subjects studied. This characteristic was not confined exclusively to either subject group. There was a significantly larger (P<0.02) area under the plasma L-dopa concentration-time curve (AUC ∞o ) in the elderly Parkinsonian patients (mean=234.69 µg · min/ml; SD=84.70) compared to the young, healthy volunteers (mean=82.33 µg · min/ml; SD=31.00). A significant (P<0.01) correlation existed between AUC ∞o and age (r=0.7970; n=11) among the subjects studied. The apparent elimination phase plasma half-life of L-dopa in the elderly Parkinsonian patients (mean=66.0 min; SD=11.1) was not significantly different to that observed in the young, healthy volunteers (mean=74.0 min; SD=18.1). These results suggest that there may be an age-related alteration to the disposition of orally administered L-dopa in the elderly Parkinsonian patient.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrams, W. B., Coutinho, C. B., Leon, A. S., Spiegel, H. E.: Absorption and metabolism of levodopa. J. Am. Med. Assoc.218, 1912–1914 (1971)
Bianchine, J. R., Rivera-Calimlim, L., Morgan, J. P., Dujovne, C. A., Lasagna, L.: Metabolism and absorption of L-3, 4-dihydroxyphenylalanine in patients with Parkinson's disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci.179, 126–140 (1971)
Bianchine, J. R., Sunyapridakul, L.: Individualization of levodopa therapy. Med. Clin. North. Am.58, 1071–1081 (1974)
Broe, G. A., Caird, F. I.: Levodopa for Parkinsonism in elderly and demented patients. Med. J. Aust.1, 630–635 (1973)
Chiou, W. L.: Critical evaluation of the potential error in pharmacokinetic studies of using the linear trapezoidal rule method for the calculation of the area under the plasma level-time curve. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm.6, 539–546 (1978)
Cotler, S., Holazo, A., Boxenbaum, H. G., Kaplan, S. A.: Influence of route of administration on physiological availability of levodopa in dogs. J. Pharm. Sci.65, 822–827 (1976)
Curzon, G., Kantamaneni, B. D., Trigwell, J.: A method for the determination of Dopa and 3-O-methyldopa in the plasma of parkinsonian patients. Clin. Chim. Acta37, 335–341 (1972)
Dixon, W. J., Massey, J. J.: Correlation problems. In: Introduction to statistical analysis, pp. 202–216. Tokyo: McGraw-Hill Kogakusha 1969
Dunner, D. L., Goodwin, F. K., Brodie, H. K. H., Spiegel, H. E.: Plasma DOPA response to levodopa administration in man: Effects of a peripheral decarboxylase inhibitor. Clin. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.12, 212–216 (1971)
Geissbuehler, F.: Méthode de dosage fluorométrique de la DOPA plasmatique à des taux submicromolaires. Clin. Chim. Acta45, 423–427 (1973)
Gibaldi, M., Perrier, D.: In: Pharmacokinetics, J. Swarbrick, (ed.), pp. 293–296. New York: Marcel Dekker 1975
Goldstein, A.: The two sample rank test: A simple alternative to the t-test. In: Biostatistics: An introductory text, pp. 55–58. New York: Macmillan 1964
Grad, B., Wener, J., Rosenberg, G., Wener, S. W.: Effects of levodopa therapy in patients with Parkinson's disease: Statistical evidence for reduced tolerance to levodopa in the elderly. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc.22, 489–494 (1974)
Granerus, A. K., Jagenburg, R., Rodjer, S., Svanborg, A.: Absorption of L-phenylalanine and L-dopa with reference to age. In: Proceedings 4th European symposium on basic research in gerontology, A Vridite (ed.), p. 84 (Abstract) 1973
Granerus, A. K., Jagenburg, R., Rodjer, S., Svanborg, A.: Variations in L-dopa absorption. Acta Med. Scand.196, 459–463 (1974)
Granerus, A. K., Steg, G., Svanborg, A.: Clinical analyses of factors influencing L-Dopa treatment of the parkinsonian syndrome. Acta Med. Scand.192, 1–11 (1972)
Kuruma, I., Bartholini, G., Tissot, R., Pletscher, A.: The metabolism of 3-O-methyldopa, a precursor of DOPA in man. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.12, 678–682 (1971)
Mearrick, P. T., Graham, G. G., Wade, D. N.: The role of the liver in the clearance of L-Dopa from plasma. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm.3, 13–23 (1975)
Mearrick, P. T., Wade, D. N., Birkett, D. J., Morris, J.: Metoclopramide, gastric emptying and L-Dopa absorption. Aust. N. Z. J. Med.4, 144–148 (1974)
Rivera-Calimlim, L., Dujovne, C. A., Morgan, J. P., Lasagna, L., Bianchine, J. R.: L-dopa absorption and metabolism by the human stomach. Pharmacologist12, 269 (Abstract) (1970a)
Rivera-Calimlim, L., Dujovne, C. A., Morgan, J. P., Lasagna, L., Bianchine, J. R.: L-dopa treatment failure: Explanation and correction. Br. Med. J.4, 93–94 (1970b)
Rivera-Calimlim, L., Morgan, J. P., Dujovne, C. A., Bianchine, J. R., Lasagna, L.: L-dopa absorption and metabolism by the human stomach. J. Clin. Invest.49, 79a (Abstract) (1970c)
Shindo, H., Komai, T., Kawai, T.: Studies on the metabolism of D- and L-isomers of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA). V. Mechanism of intestinal absorption of D-and L-DOPA-14C in rats. Chem. Pharm. Bull.9, 2031–2038 (1973)
Tyce, G. M., Muenter, M. D., Owens, C. A.: Dihydroxyphenylalanine (Dopa) in plasma during dopa treatment of patients with Parkinson's disease. Mayo Clin. Proc.45, 438–443 (1970)
Vignalou, J., Beck, H.: La L-dopa chez 122 Parkinsoniens de plus de 70 ans. Gerontol. Clin.15, 50–64 (1973)
Wade, D. N., Mearrick, P. T., Birkett, D. J., Morris, J.: Variability of L-dopa absorption in man. Aust. N. Z. J. Med.4, 138–143 (1974)
Wade, D. N., Mearrick, P. T., Morris, J. L.: Active transport of L-dopa in the intestine. Nature242, 463–465 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Evans, M.A., Triggs, E.J., Broe, G.A. et al. Systemic availability of orally administered L-dopa in the elderly Parkinsonian patient. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 17, 215–221 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00561903
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00561903