Abstract
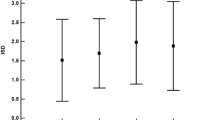
Elderly normal volunteers (N=12, mean age 70.4 years) were administered placebo or diazepam 2.5, 5, 10 mg in four consecutive sessions separated by at least a 1-week interval. Memory and psychomotor performance and plasma diazepam concentrations were assessed at baseline and at 1 and 3 h following drug administration. Significant impairments were found in response to all doses of diazepam. The maximum impairment occurred at 1 h, which coincided with the highest plasma concentration of the drug.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berchou R, Block RI (1983) Use of computerized psychomotor testing in determining CNS effects of drugs. Percept Mot Skills 57:691–700
Briggs RS, Castleden CM, Kraft CA (1980) Improved hypnotic treatment using chlormethiazole and temazepam. Br Med J 1:601–604
Brown J, Lewis V, Brown MW, Horn G, Bowes JB (1978) Amnesic effects of intravenous diazepam and lorazepam. Experientia 34:501–502
Buschke H (1973) Selective reminding for analysis of memory and learning. J Verbal Learn Verbal Behav 12:543–550
Clark EO, Glanzer M, Turndorf H (1979) The pattern of memory loss resulting from intravenously administered diazepam. Arch Neurol 36:296–300
Clarke PRF, Eccersley PS, Frisby JP, Thornton JA (1970) The amnesic effect of diazepam (Valium). Br J Anaesth 42:690–697
Ghoneim MM, Mewaldt SP, Thatcher JW (1975) The effect of diazepam and fentanyl on mental, psychomotor and electroencephalographic functions and their rate of recovery. Psychopharmacologia 44:61–66
Ghoneim MM, Mewaldt SP (1975) Effects of diazepam and scopolamine on storage, retrieval and organizational processes in memory. Psychopharmacologia 44:257–262
Ghoneim MM, Mewaldt SP (1977) Studies on human memory: The interactions of diazepam, scopolamine, and physostigmine. Psychopharmacology 52:1–6
Ghoneim MM, Korttila K, Chiang CK, Jacobs L, Schoenwald RD, Mewaldt SP, Kayaba KO (1981) Diazepam effects and kinetics in Caucasians and Orientals. Clin Pharmacol Ther 29:749–756
Ghoneim MM, Mewaldt SP, Berie JL, Hinrichs JV (1981) Memory and performance effects of single and 3-week administration of diazepam. Psychopharmacology 73:147–151
Greenblatt DJ, Ochs HR, Lloyd BL (1980) Entry of diazepam and its major metabolite into cerebrospinal fluid. Psychopharmacology 70:89–93
Greenblatt DJ, Sellers EM, Shader RI (1982) Drug disposition in old age. N Engl J Med 306:1081–1088
Grundstrom R, Holmberg G, Hansen T (1978) Degree of sedation obtained with various doses of diazepam and nitrazepam. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 43:13–18
Hartley L (1980) Diazepam: Human learning of different materials. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol 4:193–197
Hinrichs JV, Mewaldt SP, Ghoneim MM, Berie JL (1982) Diazepam and learning: Assessment of acquisition deficits. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 17:165–170
Jones DM, Lewis MJ, Spriggs TLB (1978) The effects of low doses of diazepam on human performance in group-administered tasks. Br J Clin Pharmacol 6:333–337
Kleinknecht RA, Donaldson D (1975) A review of the effects of diazepam on cognitive and psychomotor performance. J Nerv Ment Dis 161:399–411
Linnoila M, Mattila MJ (1973) Drug interaction on driving skills as evaluated by laboratory tests and by a driving simulator. Pharmacopsychiatria 6:127–132
Linnoila M, Viukari M, Lamminsivu U, Auvinen J (1980) Efficacy and side effects of lorazepam, oxazepam, and temazepam as sleeping aids in psychogeriatric inpatients. Int Pharmacopsychiatry 15:129–135
McNair DM, Lorr M, Droppleman LF (1971) Manual for the Profile of Mood States. Educational and Industrial Testing Service, San Diego
Petersen RC, Ghoneim MM (1980) Diazepam and human memory: Influence on acquisition, retrieval, and state-dependent learning. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol 4:81–89
Reidenberg MM, Levy M, Warner H, Coutinho CB, Schwartz MA, Yu G, Cheripko J (1978) Relationship between diazepam dose, plasma level, age, and central nervous system depression. Clin Pharmacol Ther 23:371–374
Salzman C, Shader RI, Harmatz J, Robertson L (1975) Psychopharmacologic investigations in elderly volunteers: Effect of diazepam in males. J Am Geriatr Soc 23:451–457
Smith JM, Misiak H (1976) Critical flicker frequency (CFF) and psychotropic drugs in normal human subjects: A review. Psychopharmacology 47:175–182
Thompson TL II, Moran MG, Nies AS (1983) Psychotropic drug use in the elderly (first of two parts). N Engl J Med 308: 134–138
Weber A, Jermini C, Grandjean EP (1975) Relationship between objective and subjective assessment of experimentally induced fatigue. Ergonomics 18:151–156
Wittenborn JR (1979) Effects of benzodiazepines on psychomotor performance. Br J Clin Pharmacol 7:61S-67S
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pomara, N., Stanley, B., Block, R. et al. Adverse effects of single therapeutic doses of diazepam on performance in normal geriatric subjects: Relationship to plasma concentrations. Psychopharmacology 84, 342–346 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00555210
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00555210