Abstract
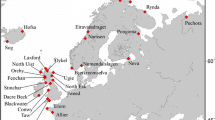
It has been reported that Atlantic tomcod (Microgadus tomcod) from the Hudson River exhibit an extremely high incidence of liver tumors. More than 90% of spawning 2-year-old fish display hepatocellular carcinomas. In contrast, representatives of this species from a relatively pristine environment show a much lower incidence of tumors. Genomic DNA and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) were isolated from tomcod from the Hudson River, New York, and the Saco River and Royal River, Maine. We found a statistically significant difference in the frequency ofPstI-generated restriction fragment length polymorphisms in theabl cellular oncogene between Hudson and Maine tomcod. Allelic variation was observed at two of the threeabl domains scored. A single composite genotype seen in approximately 40% of Hudson River fish was seen in only one Maine fish. This polymorphism enabled us to differentiate a Hudson River population from that encountered in the Maine rivers. This is the first demonstration of a population-specific polymorphism at a cellular oncogene locus in any species. In contrast, no restriction site polymorphisms were seen in mtDNA between the populations. The lack of mtDNA diversity in these fish is consistent with the geological history of the area. In combination, these results suggest that the genetic diversity observed at the c-abl oncogene locus must have been a fairly recent event and that oncogene loci may be particularly sensitive to mutational change.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam, D., Wittbrodt, J., and Schartl, M. (1988). RFLP for an EGF-receptor related gene associated with the melanoma oncogene locus ofXiphophorus maculatus.Nucl. Acids. Res. 167212.
Avise, J. C., Helfman, G. S., Saunders, N. C., and Hales, L. S. (1986). Mitochondrial DNA differentiation in North Atlantic eels: Population genetic consequences of an unusual life history pattern.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 834350.
Barbacid, M. (1986). Oncogenes and human cancer: Cause or consequences.Carcinogenesis 71037.
Ben-Neriah, Y., Bernards, A., Paskind, M., Daley, G. Q., and Baltimore, D. (1986). Alternative 5′ exons in c-abl mRNA.Cell 44577.
Bermingham, E., and Avise, J. C. (1986). Molecular zoogeography of freshwater fishes in the southeastern United States.Genetics 113939.
Bigelow, H., and Schroeder, W. (1953). Fishes of the Gulf of Maine.U.S. Fish Wildl. Serv. Fish. Bull. 741.
Borowsky, R. (1981). Tailspots ofXiphophorus and the evolution of conspicuous polymorphism.Evolution 35345.
Brown, W. M., George, M., Jr., and Wilson, A. C. (1979). Rapid evolution of animal mitochondrial DNA.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 761967.
Clark, S. S., McLauglin, J., Crist, W. M., Champlin, R., and Witte, O. N. (1987). Unique forms of theabl tyrosine kinase distinguish Ph1-positive CML from Ph1-positive ALL.Science 23585.
Cormier, S. M. (1986). Fine structure of hepatocytes and hepatocellular carcinoma of the Atlantic Tomcod,Microgadus tomcod (Walbaum).J. Fish Dis. 9179.
Cormier, S. M., and Racine, R. N. (1990). Histopathology of Atlantic tomcod: A possible monitor of xenobiotics in northeast tidal rivers and estuaries. In McCarthy, J. F., and Shugart, L. R. (eds.),Biological Markers of Environmental Contamination Lewis, Chelsea, Mich. (in press).
Cormier, S. M., Racine, R. N., Smith, C. E., Dey, W. P., and Peck, T. H. (1989). Hepatocellular carcinoma and fatty infiltration in the Atlantic tomcod,Microgadus tomcod (Walbaum).J. Fish Dis. 12105.
Dey, W., Peck, T., Smith, C., Cormier, S., and Kreamer, G.-L. (1985). A study of the occurrence of liver cancer in Atlantic tomcod (Microgadus tomcod) from the Hudson River estuary. Report from Ecological Analysts to the Hudson River Foundation, New York.
Downs, T. R., and Wilfinger, W. W. (1983). Fluorometic quantification of DNA in cells and tissues.Anal. Biochem. 131538.
Goff, S. P., Gilboa, E., Witte, O. N., and Baltimore, D. (1980). Structure of the Abelson murine leukemia virus genome and the homologous cellular gene: studies with cloned viral DNA.Cell 22777.
Heighway, J., Thatcher, N., Cerny, T., and Hasleton, P. S. (1986). Genetic predisposition to human lung cancer.Br. J. Cancer 53453.
Kellogg, T. B. (1980). Paleoclimatology and paleao-oceanography of the Norwegian and Greeland seas: Glacial-interglacial contrasts.Boreas 9115.
Klauda, R. J., Moos, R. E., and Schmidt, R. E. (1988). Life history of Atlantic tomcod (Microgadus tomcod) in the Hudson River estuary with emphasis on spatio-temporal distributions and movements. In Smith, C. L. (ed.),Fisheries Research in the Hudson River State University of New York Press, Albany, pp. 219–251.
Knudson, A. G., Jr. (1986). Genetic oncodemes and antioncogenes. In Harris, C. (ed.),Biochemical and Molecular Epidemiology of Cancer Alan R. Liss, New York, pp. 127–134.
Koepp, S. J., Santoro, E. D., and DiNardo, G. (1988). Heavy metals in finfish and selected macroinverterates of the lower Hudson River estuary. In Smith, C. L. (ed.),Fisheries Research in the Hudson River State University of New York Press, Albany, pp. 273–286.
Krontiris, T. G., DiMartino, N. A., Colb, M., Mitcheson, H. D., and Parkinson, D. R. (1986). Human restriction fragment length polymorphisms and cancer risk assessment. In Harris, C. (ed.),Biochemical and Molecular Epidemiology of Cancer Alan R. Liss, New York, pp. 99–109.
Maniatis, T., Fritsch, E. F., and Sambrook, J. (1982).Molecular Cloning Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
Maueler, W., Raulf, F., and Schartl, M. (1988). Expression of proto-oncogenes in embryonic, adult, and transformed tissue ofXiphophorus (Teleostei: Poeciliidae).Oncogene 2421.
McLaren, J. B., Peck, T. H., Dey, W. P., and Gardinier, M. (1988). Biology of the Atlantic tomcod in the Hudson River estuary. In Barnthouse, L. W., Klauda, R. J., Vaughn, D. S., and Kendall, R. L. (eds.),Science, Law, and Hudson River Power Plants, American Fisheries Society Monograph 4, pp. 102–112.
McMahon, G., Huber, L. J., Stegeman, J. J., and Wogan, G. N. (1988). Identification of a c-Ki-ras oncogene in a neoplasm isolated from winter flounder.Mar Environ. Res. 24345.
Nemoto, N., Kodama, K., Tazawa, A., Mashahito, Prince, and Ishikawa, T. (1986). Extensive sequence homology of the goldfishras gene to mammalianras genes.Differentiation 3217.
O'Connor, J. M., and Huggett, R. J. (1988). Aquatic pollution problems, North Atlantic coast, including Chesapeake Bay.Aquat. Toxicol. 11163.
Rigby, P. W. J., Dieckmann, M., Rhodes, C., and Berg, P. (1977). Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I.J. Mol. Biol. 113237.
Schartl, M. (1988). A sex chromosomal restriction-fragment-length marker linked to melanoma-determiningTu loci inXiphophorus.Genetics 119679.
Schwab, M. (1982). Genome organization inXiphophorus (Poeciliidae: Teleostei).Mol. Gen. Genet. 188410.
Shilo, B. (1984). Evolution of cellular oncogenes. In Klein, G. (ed.),Advances in Viral Oncology Raven Press, New York, Vol. 4, pp. 29–44.
Shilo, B., and Weinberg, R. A. (1981). DNA sequences homologous to vertebrate oncogenes are conserved inDrosophila melanogaster.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 786789.
Sloan, R. J., and Armstrong, R. W. (1988). PCB patterns in Hudson River fish. II. Migrant and marine species. In Smith, C. L. (ed.),Fisheries Research in the Hudson River State University of New York Press, Albany, pp. 325–350.
Smith, C., Peck, T., Klauda, R., and McLaren, J. (1979). Hepatomas in Atlantic tomcodMicrogadus tomcod (Walbaum) collected in the Hudson River estuary in New York.J. Fish Dis. 2313.
Southern, E. M. (1975). Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis.J. Mol. Biol. 98503.
Van Beneden, R. J., Watson, D. K., Chen, T. T., Lautenberger, J. A., and Papas, T. S. (1986). Cellularmyc (c-myc) in fish (rainbow trout): Its relationship to other vertebratemyc genes and to the transforming genes of the MC29 family of viruses.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 833698.
Vogelstein, D., Fearon, E. R., Hamilton, S. R., Kern, S. E., Presisinger, A. C., Leppert, M., Nakamura, Y., White, R., Smits, M. M., and Bos, J. L. (1988). Genetic alteration during colorectal-tumor development.N. Engl. J. Med. 319525.
Wahl, G. M., Stern, M., and Stark, G. R. (1979). Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 763683.
Wang, J. Y. J., Ledley, F., Goff, S., Lee, R., Groner, Y., and Baltimore, D. (1984). The mouse c-abl locus: Molecular cloning and characterization.Cell 36349.
Wirgin, I. I. (1987).Molecular Evolution in the Fish Genus Morone, Doctoral dissertation. City University of New York, New York.
Wirgin, I., Currie, D., and Garte, S. J. (1989a). Activation of the K-ras oncogene in liver tumors of Hudson River tomcod.Carcinogenesis 102311.
Wirgin, I. I., Silverstein, P., and Grossfield, J. (1989b). Restriction endonuclease analysis of striped bass mitochondrial DNA: The Atlantic coastal migratory stock.Am. Fish. Soc. Symp. 7475.
Wirgin, I. I., Proenca, R., and Grossfield, J. (1989c). Mitochondrial DNA diversity among populations of striped bass in the southeastern United States.Can. J. Zool. 67891.
Wittbrodt, J., Adam, D., Malitschek, B., Maueler, W., Raulf, F., Telling, A., Robertson, S. M., and Schartl, M. (1989). Novel putative receptor tyrosine kinase encoded by the melanoma-inducingTu locus inXiphophorus.Nature 341415.
Zarbl, H., Sukumar, S., Martin-Zanca, D., Santos, E., and Barbacid, M. (1985). Direct mutagenesis of Ha-ras-1 oncogenes by N-nitroso-N-methylurea during initiation of mammary carcinogenesis in rats. In Barrett, J. C., and Tennant, R. W. (eds.),Carcinogenesis Raven Press, New York, Vol. 9, pp. 1–16.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by NIH Grant BSRG S07 RR5399-27, Division of Research Resources, NIEHS Center Grant 00260, and NIH Grant ES 05003.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wirgin, I.I., D'Amore, M., Grunwald, C. et al. Genetic diversity at an oncogene locus and in mitochondrial DNA between populations of cancer-prone atlantic tomcod. Biochem Genet 28, 459–475 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00554374
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00554374