Abstract
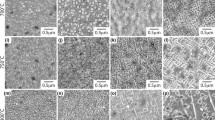
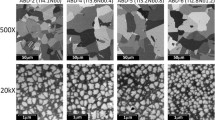
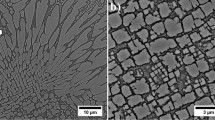
The structures of rapidly solidified APK1, In 100 and low-carbon In 792 are described and compared with that of Nimonic 80A. Under identical processing conditions, cellular, dendritic and homogeneous equiaxed structures can be obtained. This is not due to either the influence of cooling conditions or to any single alloying addition, but depends on the combined effects of the Ti, Cr and C contents. The spinodal-type formation of γ′, proposed for Nimonic 80A, cannot be suppressed in these alloys by pendant drop melt extraction or melt spinning techniques. However, detailed atom-probe field-ion microscopy suggests that the γ′ formation in APK1 does develop by a similar mechanism. Although not directly attributable to a modulated microstructure or to the presence of disordered particles, the extremely high strength levels observed in this alloy after heat treatment are due to the subsequent development of small, ordered, γ′ precipitates in a fine-grained matrix, together with the absence of deleterious grain boundary carbide precipitation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Williams, Powder Metallurgy 2 (1977) 84.
D. J. Looft and E. C. Van Reuth, Proceedings of the Conference on Rapid Solidification Processing, Reston Va., 1977 (Claitor Publishing, Baton Rouge, 1978) p. 1.
G. Thomas and R. M. Willens, Acta Met. 14 (1966) 1385.
S. C. Agarwa and H. Herman, Proceedings of the Conference on Phase Transitions (Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1973) p. 207.
J. V. Wood, J. K. Bingham and J. V. Bee, Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Rapidly Solidified Alloys, (Metals Society 1978), p. 94.
P. N. Ross and B. H. Kear, Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Rapidly Solidified Alloys, Brighton (Metals Society, 1979) p. 102.
J. V. Wood, P. F. Mills, J. K. Bingham and J. V. Bee, Met. Trans. 10A (1979) 575.
J. V. Wood and J. V. Bee, Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on the strength of metals and alloys, Aachen, 1979 (Pergamon, Oxford, 1979) p. 711.
R. B. Pond, R. E. Maringer and C. E. Mobley, “New Trends in Materials Processing” (ASTM, 1974) p. 128.
M. J. Southon, E. D. Boyes, P. J. Turner and A. R. Waugh, Surface Sci. 53 (1975) 554.
A. R. Waugh and M. J. Southon, ibid. 89 (1979) 718.
J. V. Wood and R. W. K. Honeycombe, Phil. Mag. 37A (1978) 501.
J. V. Wood and K. Akhurst, J. Mater. Sci. 11 (1976) 2142.
S. R. Robertson, T. J. Gorusch and R. P. I. Adler, Proceedings of the Conference on Rapid Solidification Processing, Reston Va., 1977 (Claitor Publishing, Baton Rouge, 1978) p. 188.
J. V. Wood, “Solidification and Casting of Metals” (Metals Society, Sheffield, 1979) p. 179.
W. Betteridge and J. Heslop, Eds., “The Nimonic Alloys” (Edward Arnold, London, 1974) Ch. 4.
F. A. Shunk, “Constitution of Binary Phase Diagrams” (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1969) p. 247.
R. C. Ruhl, Mater. Sci. Eng. 1 (1967) 313.
D. H. Warrington, University of Sheffield, private communication (1980).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wood, J.V., Mills, P.F., Waugh, A.R. et al. Rapidly solidified nickel-base superalloys. J Mater Sci 15, 2709–2719 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00550537
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00550537