Summary
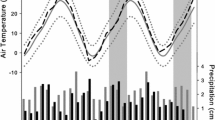
Based on the physiological characteristics and responses of C3, C4, and CAM plants to environmental factors, it is generally predicted that C4 and CAM plants will become more abundant with increasing temperature and decreasing precipitation. To test this prediction, the relative contribution of each photosynthetic type to total plant community biomass was examined at seven study areas along an altitudinal transect in southeastern Wyoming grassland. In going from high (2,652 m) to low (1,405 m) elevation along this transect, mean annual temperature increased and annual precipitation decreased.
The percentage of C4 biomass composing each study area decreased with increasing elevation, while the percentage of C3 biomass increased. All elevations had a significantly higher percentage of C4 biomass in August than in June, reflecting the warm season growth characteristic of C4 plants. Regressions of relative abundance of photosynthetic types on climatic variables showed that both mean annual temperature and annual precipitation were equally reliable as predictors of C3−C4 biomass, although we feel that temperature is of primary importance in explaining our observations. CAM species were present at all elevations, but showed no trends in biomass distribution with respect to elevation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Björkman, O.: Environmental and biological control of photosynthesis: inaugural address. In: Environmental and biological control of photosynthesis (R. Marcelle, ed.), pp. 1–16. The Hague: W. Junk 1975
Brown, W.: The Kranz syndrome and its subtypes in grass systematics. Memoirs Torr. Bot. Club 23(3), 1–97 (1977)
Burris, R., Black, C. (eds.): CO2 metabolism and plant productivity. Baltimore: Univ. Park Press 1976
Carmody, L.: Comparative physiological ecology of the montane grasses Muhlenbergia filiculmis and Leucopoa (Hesperochloa) kingii. M.S. thesis, Univ. of Wyoming 1975
Chazdon, R.: Ecological aspects of the distribution of C4 grasses in selected habitats of Costa Rica. Biotropica 10, 265–269 (1978)
Coleman, D., Andrews, R., Ellis, J., Singh, J.: Energy flow and partitioning in selected man-managed and natural ecosystems. Agro-Ecosystems 3, 45–54 (1976)
Cronquist, A., Holmgren, A., Holmgren, N., Reveal, J., Holmgren, P.: Intermountain flora, Vol. 6, Monocotyledons. New York; Columbia Univ. Press 1977
Dodd, J.: Grassland associations in North America. In: Grass systematics (F. Gould), pp. 324–338. New York: McGraw-Hill 1968
Downton, W.: The occurrence of C4 photosynthesis among plants. Photosynthetica 9, 96–105 (1975)
Doliner, L., Jolliffe, P.: Ecological evidence concerning the adaptive significance of the C4 dicarboxylic acid pathway of photosynthesis. Oecologia (Berl.) 38, 23–34 (1979)
Ehleringer, J.: Implications of quantum yield differences on the distribution of C3 and C4 grasses. Oecologia (Berl.) 31, 255–267 (1978)
Ehleringer, J., Mooney, H.: Leaf hairs: effects on physiological activity and adaptive value to a desert shrub. Oecologia (Berl.) 37, 183–200 (1978)
Eickmeier, W.: Photosynthetic pathway distributions along an aridity gradient in Big Bend National Park, and implications for enhanced resource partitioning. Photosynthetica 12, 290–297 (1978)
Harper, K.: The influence of soil temperature on the composition of seedling populations. J. Utah Acad. Sci., Arts, Letters 52(2), 96 (1977)
Harrington, H.: Manual of the plants of Colorado. Denver: Sage 1954
Harrison, A.: The C4 grass flora of North America: biogeographic implications. Bull. Ecol. Soc. Amer. 58(2), 14 (1977)
Hartley, W.: Studies on the origin, evolution, and distribution of the Gramineae. I. The tribe Andropogoneae Aust. J. Bot. 6, 116–128 (1958a)
Hartley, W.: Studies on the origin, evolution and distribution of the Gramineae. II. The tribe Paniceae. Aust. J. Bot. 6, 343–357 (1958b)
Hartley, W., Slater, C.: Studies on the origin, evolution, and distribution of the Gramineae. III. The tribes of the subfamily Eragrostoideae. Aust. J. Bot. 8, 256–276 (1960)
Hatch, M., Kagawa, T., Craig, S.: Subdivision of the C4-pathway species based on differing C4 acid decarboxylating systems and ultrastructural features. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 2, 111–128 (1975)
Hofstra, J., Aksornkoae, S., Atmowidjojo, S., Banaag, J., Santosa, Sastrohoetomo, R., Thu, L.: A study on the occurrence of plants with a low CO2 compensation point in different habitats in the tropics. Ann. Bogor. 5, 143–157 (1972)
Hurd, R.: Grassland vegetation in the Big Horn Mountains, Wyoming. Ecology 42, 459–467 (1961)
Johnson, H.: Gas-exchange strategies in desert plants. In: Perspectives of biophysical ecology (D. Gates, R. Schmerl, eds.), pp. 105–120. New York: Springer-Verlag 1975
Kawanabe S.: Temperature responses and systematics of the Gramineae. Proc. Jap. Soc. Plant Taxon. 2, 17–20 (1968)
Kluge, M., Ting, I.: Crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM): analysis of an ecological adaptation. New York: Springer-Verlag 1978
Laetsch, W.: The C4 syndrome: a structural analysis. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 25, 27–52 (1974)
Limbach, W.: Comparative physiological ecology of Elymus canadensis L., a C3 grass, and Andropogon hallii Hack., a C4 grass, in Wyoming. M.S. thesis, Univ. of Wyoming, 1974
Livingstone, D., Clayton, W.: An altitudinal cline in tropical African grass floras and its paleoecological significance. Quaternary Res. (In press)
Mulroy, T., Rundel, P.: Annual plants: adaptations to desert environments. BioScience 27, 109–114 (1977)
Ode, D., Tieszen, L.: C3 and C4 grasses and the seasonal contribution to primary production in a mixed prairie. Ecology (In press)
Osmond, C.B.: Crassulacean acid metabolism: a curiosity in context. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 29, 379–414 (1978)
Raghavendra, A., Das, V.: The occurrence of C4-photosynthesis: a supplementary list of C4 plants reported during late 1974-mid 1977. Photosynthetica 12, 200–208 (1978)
Ramaley, F.: Dry grasslands of a high mountain park in northern Colorado. Plant World 19, 249–270 (1916)
Ramaley, F.: Xerophytic grasslands at different altitudes in Colorado. Bull. Torr. Bot. Club 46, 37–52 (1919)
Redmann, R.: Production ecology of grassland plant communities in western North Dakota. Ecol. Monogr. 45, 83–106 (1975)
Sankhla, N., Ziegler, H., Vyas, O., Stichler, W., Trimborn, P.: Ecophysiological studies on Indian arid zone plants. V. A screening of some species for the C4-pathway of photosynthetic CO2 fixation. Oecologia (Berl.) 21, 123–129 (1975)
Sims, P., Singh, J.: The structure and function of ten western North American grasslands. II. Intra-seasonal dynamics in primary producer compartments. J. Ecol. 66, 547–572 (1978)
Sims, P., Singh, J., Lauenroth, W.: The structure and function of ten western North American grasslands. I. Abiotic and vegetational characteristics. J. Ecol. 66, 251–285 (1978)
Sokal, R., Rohlf, F.: Biometry. San Francisco: Freeman 1969
Stowe, L., Teeri, J.: The geographic distribution of C4 species of the Dicotyledonae in relation to climate. Amer. Nat. 112, 609–623 (1978)
Szarek, S., Ting, I.: The occurrence of crassulacean acid metabolism among plants. Photosynthetica 11, 330–342 (1977)
Teeri, J., Stowe, L.: Climatic patterns and the distribution of C4 grasses in North America. Oecologia (Berl.) 23, 1–12 (1976)
Teeri, J., Stowe, L., Murawski, D.: The climatology of two succulent plant families: Cactaceae and Crassulaceae. Can. J. Bot. 56, 1750–1758 (1978)
Tieszen, L.: Photosynthetic properties of some grasses in eastern South Dakota. Proc. S. Dakota Acad. Sci. 49, 78–89 (1970)
Tieszen, L., Senyimba, M., Imbamba, S., Troughton, J.: The distribution of C3 and C4 grasses and carbon isotope discrimination along an altitudinal and moisture gradient in Kenya. Oecologia (Berl.) 37, 337–350 (1979)
U.S. Dept. of Commerce: Climatography of the United States. Wyoming. Washington: U.S. Govt. Printing Office
Vogel, J., Fuls, A., Ellis, R.: The geographic distribution of Kranz grasses in South Africa. S. Afr. J. Sci. 74, 209–215 (1978)
Walter, H.: Vegetation of the earth in relation to climate and the eco-physiological conditions. New York: Springer-Verlag 1973
Weaver, J., Albertson, F.: Grasslands of the Great Plains. Their nature and use. Lincoln, Nebr.: Johnsen Publishing Co. 1956
Webb, W., Szarek, S., Lauenroth, W., Kinerson, R., Smith, M.: Primary productivity and water use in native forest, grassland, and desert ecosystems. Ecology 59, 1239–1247 (1978)
Whittaker, R., Niering, W.: Vegetation of the Santa Catalina Mountains, Arizona. V. Biomass, production, and diversity along the elevation gradient. Ecology 56, 771–790 (1975)
Williams, G., Markley, J.: The photosynthetic pathway type of North American shortgrass prairie species and some ecological implications. Photosynthetica 7, 262–270 (1973)
Wilson, J., Ford, C.: Temperature influences on the growth, digestibility, and carbohydrate composition of two tropical grasses, Panicum maximum var. trichoglume and Setaria sphacelata, and two cultivars of the temperate grass Lolium perenne. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 22, 563–571 (1971)
Winter, K., Troughton, J.: Photosynthetic pathways in plants of coastal and inland habitats of Israel and the Sinai. Flora 167, 1–34 (1978)
Winter, K., Troughton, J., Card, K.: δ 13C values of grass species collected in the northern Sahara Desert. Oecologia (Berl.) 25, 115–123 (1976)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boutton, T.W., Harrison, A.T. & Smith, B.N. Distribution of biomass of species differing in photosynthetic pathway along an altitudinal transect in southeastern wyoming grassland. Oecologia 45, 287–298 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00540195
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00540195